WAS
-
Official Full Name
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome -
Overview
The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS) family of proteins share similar domain structure, and are involved in transduction of signals from receptors on the cell surface to the actin cytoskeleton. The presence of a number of different motifs suggests that they are regulated by a number of different stimuli, and interact with multiple proteins. Recent studies have demonstrated that these proteins, directly or indirectly, associate with the small GTPase, Cdc42, known to regulate formation of actin filaments, and the cytoskeletal organizing complex, Arp2/3. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is a rare, inherited, X-linked, recessive disease characterized by immune dysregulation and microthrombocytopenia, and is caused by mutations in the WAS gene. The WAS gene product is a cytoplasmic protein, expressed exclusively in hematopoietic cells, which show signalling and cytoskeletal abnormalities in WAS patients. A transcript variant arising as a result of alternative promoter usage, and containing a different 5 UTR sequence, has been described, however, its full-length nature is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
WAS;Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome;THC;IMD2;SCNX;THC1;WASP;wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein;eczema-thrombocytopenia;thrombocytopenia 1 (X-linked)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Bacteria
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- His
- GST
- T7
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
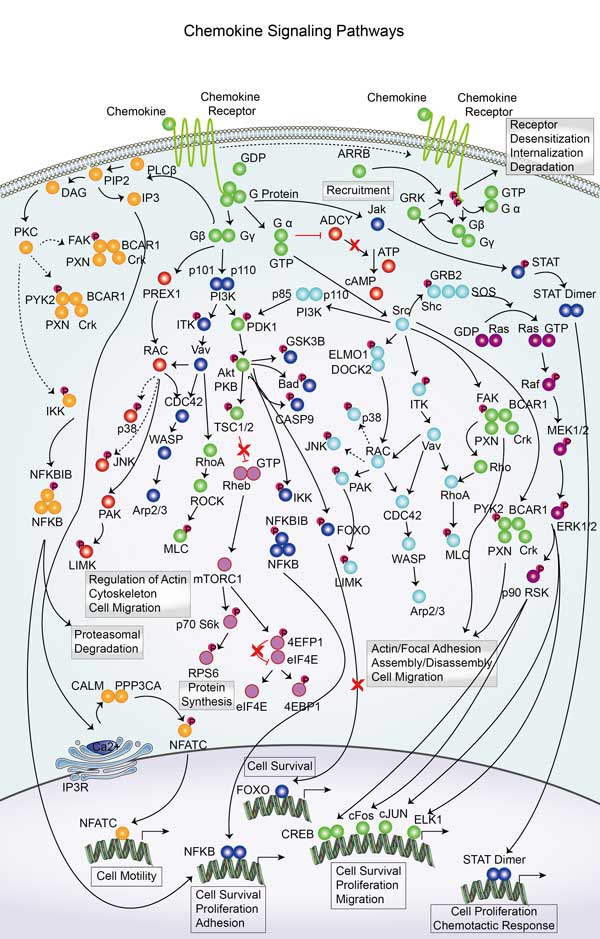
Involved Pathway
WAS involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways WAS participated on our site, such as Chemokine signaling pathway,Endocytosis,Adherens junction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with WAS were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Chemokine signaling pathway | HRAS,GRK7,RELA,STAT2,CCR6,PRKACG,GM2506,NCF1,CXCL6,CCL24 |
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | PPAP2A,RPS6KB2,PIP5K1B,WASF2,PLA2G4F,FCGR3A,PRKCE,VAV2,PLA2G4D,GSN |
| Endocytosis | PARD6A,CAPZA1A,WASB,RUFY1,CSF1R,VTA1,TGFB2,HLA-E,RHOAA,WASL |
| Regulation of Actin Cytoskeleton | CD14,DIAP3,GNG12,ROCK1,MYLK,NCKAP1L,PXN,RRAS,PIP4K2C,CHRM5B |
| Salmonella infection | MYH10,PFN1,PLEKHM2,PKN1,MAPK13,MYH9,RAB7B,PKN2,CDC42,TLR5B |
| Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection | EZR,TUBB2B,ITGB1,TUBAL3,CLDN1,KRT18,CTTN,ABL1,ROCK1,ARPC5L |
| Adherens junction | TGFBR2,ACTB1,ERBB2,TCF7,FYN,PTPRJA,MLLT4,RHOAC,RAC3,WASF3B |
| Choline metabolism in cancer | KRAS,PDGFB,RALGDS,SOS1,NRAS,HIF1A,PIP5K1A,Pdgfa&Pdgfb,SLC22A1,SLC22A3 |
| Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells | VCL,CDC42,ELMO2,GAB1,PTK2,PIK3CA,SEPT11,DNM1,CTNNA1,CLTC |
Protein Function
WAS has several biochemical functions, for example, GTPase regulator activity,SH3 domain binding,actin binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by WAS itself. We selected most functions WAS had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with WAS. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | CD22,HAPLN2,TNFAIP8L1,JAK2,ZNHIT6,TSPAN12,SRSF5,NUPL1,EPHA3,AGXT |
| GTPase regulator activity | DNAJA3,PCP2,GPSM1B,WASL,GPSM2L,RHPN1,TSC1A,GPSM2,GPSM3,RUNDC3A |
| protein kinase binding | PRKAG1,AP2A1,CD36,CAV2,GPRC5B,GSK3B,TBL2,CCNYL1,CALM3,KCNQ3 |
| identical protein binding | TLE1,RAF1,CLDN3,ZNHIT6,GDF5,MAP1S,PCM1,CLDN14,ACY3,PRPF3 |
| SH3 domain binding | GJA1,EVL,ARHGAP31,ITGB1BP2,PTPN22,GRIK5,PDE4D,MICAL1,PTTG1,MYPN |
| phospholipase binding | CALM3,PTPN11,SERPINB1A,PRKCZ,LMNB1,PDPK1,CALM1,APOC2,Pla2r1,NEFL |
| actin binding | WASH1,SLC4A1,TNNI1,SNTG1,MYO1C,FHOD1,TPM4,EPB41L3,ITGB1,MICAL1 |
Interacting Protein
WAS has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with WAS here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of WAS.
CDC42;WIPF1
WAS Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Jahandar, H; Vaziri, B; et al. Effect of Cysteamine on Cell Growth and IgG(4) Production in Recombinant Sp2.0 Cells. IRANIAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH 14:177-187(2015).
- Al-Bahrani, R; Tuertcher, D; et al. Differential SIRT1 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinomas and Cholangiocarcinoma of the Liver. ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIENCE 45:3-9(2015).