Principle and Protocol of Yeast One-hybrid Analysis
Yeast one-hybrid method is a method to analyze the interaction between DNA and intracellular proteins in vitro. It can identify DNA binding sites and find potential binding protein genes by analyzing the expression of reporter genes in yeast cells, or analyze the binding sites. Using this technology, we can screen the protein binding with DNA, and directly obtain the nucleotide sequence encoding the protein from the gene library without complicated protein separation and purification operation, so it has certain advantages in protein research. Moreover, yeast is an eukaryotic cell. The results obtained by yeast system can better reflect the regulation of gene expression in eukaryotic cells than those obtained by other in vitro technologies.
Understand the basic principle and application of yeast single hybridization, master the main steps and precautions of yeast one-hybrid, learn the production and transformation of yeast receptive state, and the construction and screening of gene library.
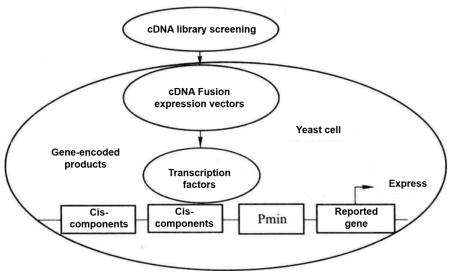 Figure 5-5-1 Schematic Diagram of Yeast One-hybrid
Figure 5-5-1 Schematic Diagram of Yeast One-hybrid
Yeast one-hybrid method is to clone the gene (cDNA) encoding the target transcription factor according to the principle that DNA-binding protein (i.e. transcription factor) and DNA cis-acting element combine to regulate the expression of reporter gene. This method is also an effective method to analyze and identify the binding of transcription factors and cis-acting elements in vivo. As shown in Figure 5-5-1, the known specific cis-acting elements are constructed to the upstream of the minimal promoter (Pmin), and the downstream of the Pmin promoter is connected with the reporter gene. When screening the cDNA fusion expression library, after the cDNA fusion expression vector encoding the target transcription factor is transformed into yeast cells, its coding product (transcription factor) combines with the cis-acting element to activate the Pmin promoter and promote the expression of the reporter gene. According to the expression of the reporter gene, the transcription factors that bind to known cis elements were screened.
"Matchmaker Gold Yeast One-Hybrid Library Screening System" provides a simple and efficient method for constructing cDNA library and performing yeast single-hybrid screening. It uses aureobasidin A resistance gene as the reporter gene, with high screening efficiency and low background. Single hybrid screening is developed from yeast two-hybrid screening. Single hybrid screening can be used to screen the cDNA library and directly obtain the protein combined with the target cis-acting element (Figure 5-5-2).
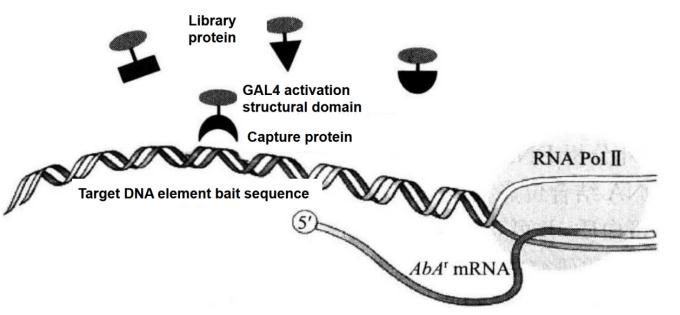 Figure 5-5-2 Principle of Screening Proton-DNA Interaction with Matchmaker Gold One-hybrid System
Figure 5-5-2 Principle of Screening Proton-DNA Interaction with Matchmaker Gold One-hybrid System
The Matchmaker Gold One-hybrid Library Screening process mainly includes the following steps:
1. Clone the target sequence (bait) into pAbAi vector.
2. pBait-AbAi plasmid was transformed into Y1HGold yeast strain, which was recombined with yeast genome to generate Bait/reporter yeast strain.
3. Detect the background expression level of AbAr gene of Y1HGold bait strain.
4. The cDNA was synthesized and co-transformed into yeast by cDNA and pGADT7-Rec vector for intracellular homologous recombination and screening of cDNA library.
5. Verification and analysis of screening results.
1. Main Instruments and Equipment
Micropipette (2.5 μL, 20 μL, 50 μL, 100 μL, 200 μL, 1000μL),PCR instrument, cryogenic centrifuge, desktop centrifuge, CHROMA SPINTM+TE-400 purification column, agarose gel electrophoresis system, gel imaging system, thermostatic shaking table, thermostatic incubator, fume hood, ice maker, oscillator, thermostatic metal bath, alcohol bath, sterile inoculation ring, 10cm petri dish, 15cm petri dish, etc.
2. Material
Y1HGold yeast strain, TOP10 E. coli strain, RNA extracted by various methods, pGADT7-Rec plasmid, pBait-AbAi plasmid, etc.
3. Main Reagents
(1) Advantage 2 PCR kit, Easy Yeast Plasmid Isolation kit, Match-maker Insert Check PCR Mix 1, Matchmaker Insert Check PCR Mix 2.
(2) Various basic media and nutrient deficiency media: minimal SD base, minimal SD agar base, YPD medium, YPD agar medium, -Leu DO supplement, -Ura DO supplement, adenine, PEG8000, vector DNA, aureobasidin A, LB medium, ampicillin.
(3) NaCl solution (0.9%), sodium acetate (3 mol/L), 50% PEG, 10 × LiAc (1 mol/L), 10 × TE buffer, DTT (100 mmol/L), RNaseH, restriction endonuclease.
Construction of pBait-AbAi Vector
(1) Two reverse parallel oligonucleotide sequences containing the target sequence were designed and synthesized, and the two ends were added with sticky ends consistent with the digestion products of pAbAi vector (it is recommended to synthesize a mutant sequence of the target sequence as a control to eliminate possible false positives).
(2) Dissolve oligonucleotides with TE buffer to the final concentration of 100 μmol/L.
(3) Mix the sense and antisense sequences in a ratio of 1:1 (the maximum concentration of double-stranded oligonucleotides after annealing is 50 μmol/L).
(4) Heat preservation at 95°C for 30s, remove secondary structure.
(5) 72°C for 2 min, 37°C for 2 min, 25°C for 2 min*2.
(6) Place on ice. The products after annealing can be stored in a refrigerator at - 20°C for standby.
(7) Enzyme digestion 1 μL pAbAi vector*3, the digestion product is purified by gel recovery and purification or column purification.
(8) Dilute the annealed oligonucleotides 100 times to the final concentration of 0.5 μmol/L.
(9) Add the following components into the connecting reaction tube:
| pAbAi vector (50 ng/μL) | 1μL |
| Annealed oligonucleotide (0.5 μmol/L) (target and mutant) | 1μL |
| 10×T4 DNA ligase buffer | 1.5μL |
| BSA (10 mg/mL) | 0.5μL |
| Nuclease-free H2O | 10.5μL |
| T4 DNA ligase (400 U/μL) | 0.5μL |
| Total volume | 15μL |
Note: If necessary, 1 μL of nuclease-free H2O can be used as a negative control instead of oligonucleotide.
(10) Leave the reaction system at room temperature for 3h for ligation, transform E. coli, and detect positive clones using conventional methods*4.
2. Plasmid Transforms into Yeast Cells to Generate Bait-Reporter Yeast Strain (Figure 5-5-3)
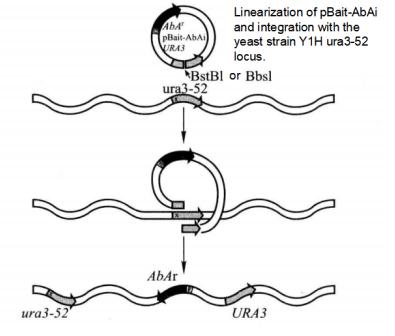 Figure 5-5-3 Principle of Screening Proton-DNA Interaction with Matchmaker Gold One-hybrid System
Figure 5-5-3 Principle of Screening Proton-DNA Interaction with Matchmaker Gold One-hybrid System
(1) 2 μL of pBait-AbAi, pMutant-AbAi and p53-AbAi plasmids were digested with BstB I or Bbs I to disconnect them at the URA3 gene and purify the digested products.
(2) Transform Y1HGold yeast with 1 μL of the digested plasmid according to the Yeastmaker Yeast Transformation System 2.
(3) Dilute each transformation system to 1/10, 1/100, 1/1000, and take each dilution evenly onto SD/-Ura agar plates, respectively. 3 d later, pick 5 monoclones and use Matchmaker Insert Check PCR Mix1*5 for PCR to detect positive clones (Figure 5-5-4), and use monoclones of YlHGoldas negative control.
(4) Add 25 μL of PCR-grade H2O to the PCR tube.
(5) Gently touch the yeast monoclonal*6 with a clean gun tip to obtain a very small amount of yeast cells. Stretch the tip of the gun into PCR-grade H2O and stir to disperse the yeast cells.
(6) Add 25 μL Matchmaker Insert Check PCR Mix to each tube, mix well, and centrifuge. Each PCR tube now contains the following reagents.
| Matchmaker Insert Check PCR Mix | 25μL |
| H2O/yeast | 25μL |
| Total volume | 50μL |
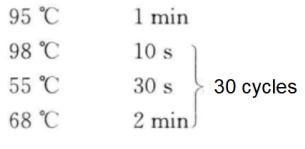
(7) PCR reactions were performed according to the following procedure.
(8) 5 μL of PCR products were taken and analyzed by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis*7.
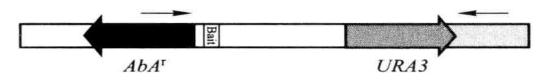 Figure 5-5-4 PCR detection of insertion of pBait-AbAi
Figure 5-5-4 PCR detection of insertion of pBait-AbAi
The correct PCR test result should be
Positive control: 1.4kb
Negative control: no band
Decoy strain: 1.35kb + insert size
(9) The bait clones and p53 AbAi control clones that were positive for PCR detection were selected and cultured on SD/Ura plate. After incubation at 30°C for 3 days, the plate was stored at 4°C, namely the newly constructed Y1HGold [Bait/AbAi] strain and [p53/AbAi] control strain.
(10) After long-term storage, select the monoclone and culture it overnight in YPDA liquid medium, collect the cell by centrifugation, resuspend the cell with 1mL of precooled medium (100mL of sterilized YPDA mixed with 50mL of sterilized 75% glycerol), and store it at - 70°C after rapid freezing.
3. Detection of AbAr Gene Expression in Bait Strains*8
In the absence of a trap, the background expression level of the reporter gene of the bait strain is different due to the different bait sequences cloned into the pAbAi vector. For example, the lowest inhibitory concentration of aureobasidin A in p53-AbAi control is 100 ng/mL.
(1) Select the bait clone and the control strain clone respectively, resuspend cells with 0.9% NaCl, and regulate A600 to 0.002 (about 2000 cells/100 μL).
(2) Apply 100 on the following media respectively μL resuspended bacterial solution, cultured at 30°C for 2-3d.
SD/-Ura
SD/-Ura with AbA (100 ng/mL)
SD/-Ura with AbA (150 ng/mL)
SD/-Ura with AbA (200 ng/mL) *9
The expected results are shown in Table 5-5-1.
Table 5-5-1 Expression Results of AbAr gene
| [AbA]/(ng/mL) | Clone number of Y1HGold [p53-AbAi] | Clone number of Y1HGold [pBait-AbAi] |
| 0 | ~2000 | ~2000 |
| 100 | 0 | Bait dependent |
| 150 | 0 | Bait dependent |
| 200 | 0 | Bait dependent |
(3) When performing library screening, use AbA at the lowest inhibitory concentration or use a slightly higher AbA concentration than the lowest inhibitory concentration (~50-100 ng/mL higher) to completely inhibit the growth of the decoy strain.
4. Synthesis of Library cDNA
Extract total RNA from the test material and synthesize cDNA by reverse transcription*10.
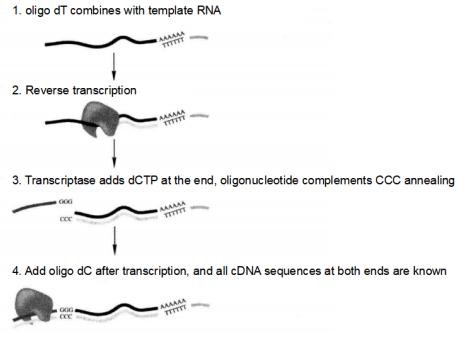 Figure 5-5-5 Principle of SMARTTM Technology to Synthesize cDNA
Figure 5-5-5 Principle of SMARTTM Technology to Synthesize cDNA
(1) Synthesis of the first strand of cDNA
① Prepare high quality poly A and/or total RNA*11 with human placenta poly A + RNA as a positive control.
② Add the following reagents to the microcentrifuge tube.
| RNA template (0.025-1.0 μg poly A and/or 0.10-2.0 μg total RNA) | 1~2μL |
| Primer of CDS III (oligo-dT) or CDS III/6 (random) | 1μL |
| Deionized H2O (bringing the total volume to 4.0 μL) | 1~2μL |
| Total volume | 4μL |
③ Incubate at 72°C for 2min.
④ Place on ice for 2min, mix gently and immediately add the reagents from step (5).
⑤ Add the following reagents*12 for each reaction, and gently mix and centrifuge.
| 5×first-strand buffer | 2μL |
| DTT (100 mmol/L) | 1μL |
| dNTP mix (10 mmol/L) | 1μL |
| SMART MMLV RT | 1μL |
| Total volume | 5μL |
⑥ If CDS III/6 random primers are used, hold for 10 min at 25-30°C. If CDS Ⅲ primers are used, omit this step and proceed to step (7).
⑦ Hold at 42°C for 10min.
⑧ Add 1μLSMART III oligo, mix thoroughly, and hold at 42°C for 1h.
⑨ Terminate the synthesis of the first chain by holding at 75°C for 10min.
⑩ Decrease to room temperature, add 1μL RnaseH (2units).
⑪ Thermally hold at 37°C for 20min.
⑫ cDNA first strand synthesis product should be stored at -20°C and available for 3 months.
(2) Long-distance PCR (LD-PCR) synthesis of cDNA second strand.
Based on the amount of RNA used in the synthesis of the first strand of cDNA, Table 5-5-2 gives the optimal number of thermal cycles to perform LD-PCR. The lower the number of thermal cycles used, the less non-specific PCR products.
Table 5-5-2 RNA Volume and Optimal Number of Thermal Cycles*13
| Total RNA/μg | Poly A RNA/μg | Cycle |
| 1.0-2.0 | 0.5-1.0 | 15-20 |
| 0.5-1.0 | 0.25-0.5 | 20-22 |
| 0.25-0.5 | 0.125-0.25 | 22-24 |
| 0.05-0.25 | 0.025-0.125 | 24-26 |
① The following substances were added to the LD-PCR reaction mixture (make two 100 μL systems for each sample and one 100 μL system for the control).
| First-strand cDNA (from protocol A) | 2μL |
| Deionized H2O | 70μL |
| 10×advantage® 2PCR buffer | 10μL |
| 50×dNTP mix | 2μL |
| 5' PCR primer | 2μL |
| 3'PCR primer | 2μL |
| Melting solution | 10μL |
| 50×advantage 2 polymerase mix | 2μL |
| Total volume | 100μL |
② PCR reactions should be performed according to the following procedure.
 Figure 5-5-6 CHROMA SPINTM + TE-400 column
Figure 5-5-6 CHROMA SPINTM + TE-400 column
③ Take 7 μL of PCR products and detecte it on a 1.2% agarose gel using a 1kb DNA ladder.
(3) Purification of ds cDNA using CHROMA SPINTM + TE-400 column.
- Prepare one CHROMA SPINTM + TE-400 column for each cDNA sample to be purified (Figure 5-5-6).
- Flip the purification column over several times to fully suspend the gel matrix.
- Remove the top and bottom caps of the column and place the column in a 2 mL collection tube.
- Place the column into a centrifuge and centrifuge at 700g for 5min to remove the equilibration buffer and discard the liquid in the collection tube.
- Place the column into a new collection tube and add the cDNA to the center of the gel matrix*14, do not allow the sample to flow down the inner wall of the column.
- Centrifuge at 700g for 5min and purified cDNA is collected into the tube.
- Combine the two purified cDNA samples into one tube and measure the volume.
- Add 1/10 volume of 3 mol/L sodium acetate (pH 5.3) and mix well.
- Add 2.5 times the volume of anhydrous ethanol.
- Chill at -20°C for 1h.
- Centrifuge at room temperature, 14000r/min for 20min.
- Carefully discard the supernatant, do not touch the precipitate.
- Centrifuge instantaneously at 14000r/min to remove residual supernatant.
- Dry the precipitate in air for 10min*15.
- Dissolve the precipitate with 20μL of sterilized deionized water. This cDNA can be used for homologous recombination to construct libraries. The purified cDNA was detected by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis (Figure 5-5-7).
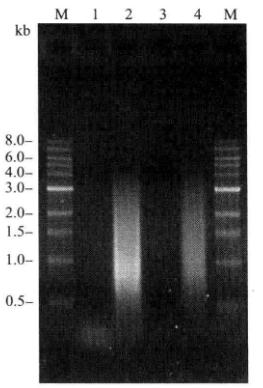 Figure 5-5-7 Detection of the Purified cDNA
Figure 5-5-7 Detection of the Purified cDNA
5. Construction and Screening of Yeast Single Hybrid Library (construction and screening of cDNA fusion expression library) (Figure 5-5-8)
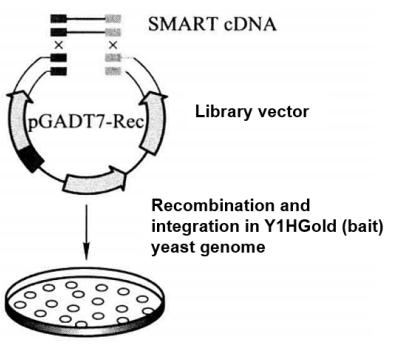 Figure 5-5-8 Construction and Screening of cDNA Fusion Expression Library
Figure 5-5-8 Construction and Screening of cDNA Fusion Expression Library
(1) Construct and assay Y1HGold [Bait/AbAi] strain on SD/-Leu/AbA*16 medium.
(2) Synthesize ds cDNA at a concentration of 2-5 μg/20 μL according to SMART technology steps.
(3) Yeast was transformed by the Yeastmaker Transformation System 2 method, and the following substances were added to the transformation system.
① cDNA library transformation of Y1HGold [Bait/AbAi] strain.
20 μL SMART-amplified ds cDNA (2-5 μg)
6 μL pGADT7-Rec, (Smal-linearized) (3μg)
② Transformation of Y1HGold [53/AbAi]
5 μL p53 fragment (125 ng)
2 μL pGADT7-Rec, (Smal-linearized) (1μg)
Dilute the conversion system to 1/10, 1/100, 1/1000 and 1/10 000 respectively, and take 100 μL coated with 100mm flat plate.
The library was transformed into SD/- Leu and SD/- Leu/AbA* plates.
P53 control conversion was coated with SD/- Leu and SD/- Leu/Ab A200 plates.
(4) Apply all remaining library transformation mixture (~15mL) on 150mm SD/-Leu/AbA* plates at 150μL per plate.
(5) Incubate upside down for 3-5 d.
(6) After 3-5 d, count the number of clones screened by counting the number of clones on SD/-Leu 100 mm plates*17.
The number of clones screened=[cfu/ml on SD/-Leu] × [dilution factor] × [resuspension volume(15mL)]
For example:
Resuspension volume=15mL
Plating volume=100μL
250 colonies grew on the 1/100 dilution on SD/-Leu plates
The number of clones screened=250 cfu/ 0.1 mL × 100 × 15 mL
=3.75 million
(7) Expected results
Positive control test: the number of gram drops on SD/-Leu and SD/-Leu/AbA200 media is similar.
Library screening test: the number of clones screened is calculated from the number of clones on SD/-Leu plates, the result should be greater than 1 million and the number of clones on SD/-Leu/AbA*18 plates is much less than 1 million, the number of positive clones depends on the decoy sequence.
6. Identification of Positive Clones and Isolation of cDNA Plasmids
(1) Positive clones were re-linearized and cultured for phenotype confirmation.
① Positive clones were re-screened on SD/-Leu/AbA* medium to generate new monoclonal clones.
② After 2-4 d, clones that can grow normally are selected for subsequent analysis.
(2) Yeast clone PCR to eliminate duplicate clones.
① PCR was performed with Matchmaker Insert Check PCR Mix 2 (Cat. No. 630497) to amplify the cDNA fragment inserted into the pGADT7 vector. the following reagents were added to the PCR tubes.
| Matchmaker Insert Check PCR Mix | 25μL |
| H2O/yeast | 25μL |
| Total volume | 50μL |
② PCR reactions should be performed according to the following procedure.

③ PCR products were analyzed by electrophoresis on 1% agarose gel*19. It is normal that the product is not a single band, which indicates that there is more than one capture carrier in the same yeast cell.
④ If a large number of clones contain the same insertion fragment, another 50 clones will be taken for PCR analysis.
⑤ In order to quickly verify the clone, the PCR product can be purified and sequenced with T7 primer.
(3) Isolation and acquisition of positive cDNA plasmids.
① Separation of library plasmids in yeast.
Unlike transformed E. coli, transformed yeast cells can contain multiple related plasmids, which means that positive clones contain not only plasmids that activate the AbAr reporter gene, but may also contain one or more cDNA plasmids that do not express interacting proteins. If the plasmids are obtained directly by transforming E. coli without previously separating out the non-interacting plasmids, there is a high probability that non-interacting plasmids will be obtained. To increase the chances of obtaining a positive capture plasmid, the positive clone can be repeatedly coated 2-3 times on SD/-Leu/AbA* medium, each time picking a single clone for the next coating.
② Positive cDNA plasmids were obtained from yeast.
To identify positive reciprocal related genes, positive plasmids were obtained from yeast using Easy Yeast Plasmid Isolation Kit (Cat. No. 630467).
③ Transform E. coli and isolate the positive cDNA plasmid*20.
Cloning of the positive cDNA plasmids was performed with commonly used cloning strains, and selection was performed with LB plus 100 g/mL ampicillin.
(4) Identification of positive and false positive interactions.
Yeast monohybrid screens may detect false positives, and the following criteria can be used to distinguish between positives and false positives (Figure 5-5-9):
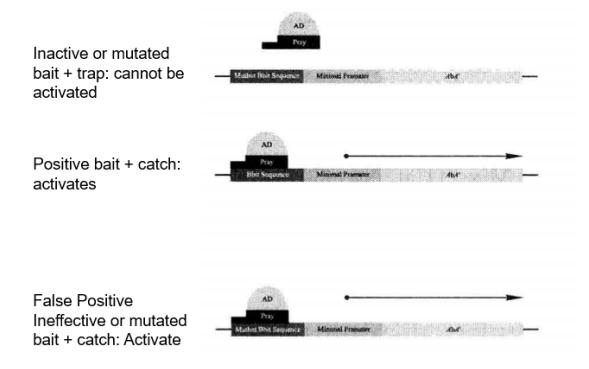 Figure 5-5-9 Expression of Reporter Genes within Positive and False Positive Clones
Figure 5-5-9 Expression of Reporter Genes within Positive and False Positive Clones
Positive: The correct bait sequence and trap are necessary to activate the AbAr reporter gene.
False positive: In the case of bait sequence mutation, the bait can still activate the AbAr reporter gene.
Use the following procedure to confirm the positive and false positive interactions on the selected medium (Table 5-5-10):
① Transform 100 ng of the obtained capture plasmids into Y1HGold [Bait/AbAi] and Y1HGold [Mutant/AbA] strains*21 using Yeastmaker Transformation System 2 reagents and the small-scale transformation procedure.
② Apply 100 μL of dilutions of 1/10 and 1/100 of the transformation mixture on SD/-Leu and SD/-Leu/AbA* media.
③ After incubation at a constant temperature of 30°C for 3 to 5 d, the expected results are shown in Table 5-5-10 and Figure 5-5-11.
Table 5-5-10 Positive and False Positive Interaction Validation Results
a.Positive
| Sample | Selective culture medium | 2mm clear clone |
| Yeast | SD/-Leu | Yes |
| Y1HGold [bait/AbAi] +target yeast | SD/-Leu/AbA | Yes |
| Yeast | SD/-Leu | Yes |
| Y1HGold [mutation/AbAi] +target yeast | SD/-Leu/AbA | None (or very small) |
b.Negative
| Sample | Selective culture medium | 2mm clear clone |
| Yeast | SD/-Leu | Yes |
| Y1HGold [bait/AbAi] +target yeast | SD/-Leu/AbA | Yes |
| Yeast | SD/-Leu | Yes |
| Y1HGold [mutation/AbAi] +target yeast | SD/-Leu/AbA | Yes |
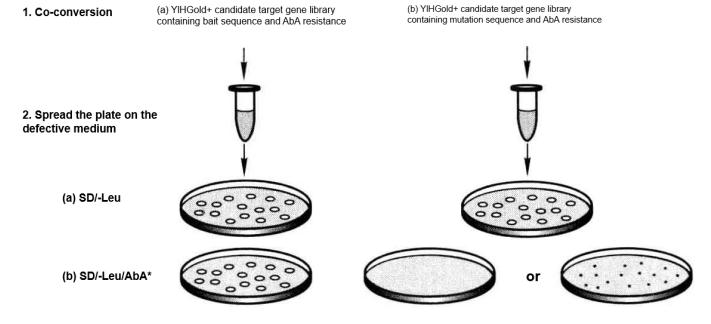 Figure 5-5-11 Verification of Positive and False Positive Interactions with Selection Media
Figure 5-5-11 Verification of Positive and False Positive Interactions with Selection Media
(5) Sequencing analysis of positive clones
Once the interaction is verified as positive, the insert cDNA fragment of the capture vector can be sequenced*22 to identify the open reading frame (ORF) sequence fused to the GAL4 AD sequence and compared to sequences in GenBank, EMBL or other databases.
1. After a round of yeast single hybridization screening, the positive clones obtained may be very few or very many. In this case, the following treatment is recommended.
(1) Too few positive clones:
Check whether the number of clones filtered is greater than 1 million;
Check whether the culture medium is normal through positive control and negative control;
Retest the lowest AbA inhibition concentration of bait;
Try to increase the number of copies of the target sequence. Generally, the test effect is best when the number of copies of the target sequence is 3.
(2) Too many positive clones:
Check whether the best AbA inhibition concentration is used;
If 100 ng/mL AbA is used, use 200 ng/mL AbA concentration to screen again;
Check whether the nutrient deficiency of culture medium is normal through positive control and negative control;
There may be a large number of cDNA in the library that can encode the binding protein with the bait sequence. The clones can be classified by yeast PCR, and the representatives in each class can be used for false positive interaction analysis.
2. The following tests are required before sequencing the positive clones.
(1) The positive clones were re-lined and cultured with fresh selective medium for phenotypic confirmation;
(2) Yeast clone PCR to classify duplicate clones;
(3) Isolation of positive cDNA plasmid;
(4) Identification of positive and false positive interactions.
*1 The yeast reporter (pBait-AbAi) contains one or more copies of the target cis-acting element and is inserted into the upstream of the pAbAi vector AbAr reporter gene. A large number of studies have shown that the most effective construction should contain more than three copies of the end-to-end connection of the target DNA. There are many ways to produce the copy of the head and tail connection, but for the regulatory elements with the length less than 20 bp, the synthetic oligonucleotide is the most convenient and reliable way.
*2 Slow annealing is conducive to the formation of double-stranded oligonucleotides.
*3 Before recovery, agarose gel can be used to detect whether the digestion is complete.
*4 Enzyme digestion or sequencing can be used for detection.
*5The kit contains sequence primers at both ends of the insertion site, which can be used for positive clone detection.
*6 Do not select the whole yeast monoclone, because too many cells will prevent the PCR reaction. If the water becomes turbid after adding cells, it indicates that too many yeast cells are added.
*7 The primer was combined with the AbA gene and the YIHgold genome downstream of URA3, and the amplified fragment was about 1.4 kb.
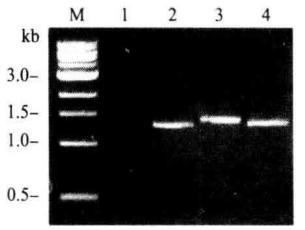
1.negative control; 2. positive control; 3. 4. different biat strains
*8 The premise of successful yeast single hybridization experiment is that no endogenous transcription factor can bind to the target sequence or the binding ability is very weak. Therefore, it is very important to detect the expression of AbAr gene of the constructed bait strain before screening the library. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out experiments to determine the concentration of AbA required to inhibit the background expression of the reporter gene of the bait strain during library screening.
*9 If 200 ng/mL AbA cannot inhibit the background expression, try to increase the concentration of AbA to 500-1000 ng/mL. However, if the concentration of AbA at 1000ng/mL still cannot inhibit the expression of AbAr gene in the absence of capture, it is likely that there are endogenous regulatory factors that can recognize and combine with the target sequence, so the target sequence cannot be used for yeast single hybridization screening.
*10 The end of the synthesized cDNA has the same restriction site as pGADT7-Rec.
*11 The quality of RNA determines the quality of the library. RNA should be the RNA of the specific period and specific tissue to be studied.
*12 The reagent in step (5) can be added to the ice before step (2). This step is the initial key step of cDNA synthesis. The time of placing denatured RNA/primer mix on ice should not exceed 2min.
*13 It is recommended to set the number of PCR cycles according to the parameters in the following table. Too many cycles can easily form a large number of redundant fragments.
*14 When added to the edge, it is easy to make the sample flow down the inner wall of the column and mix with small fragments of cDNA.
*15 Generally, it should be dried to the point where there is no alcohol smell, and should not be excessively dried, otherwise it is difficult to dissolve.
*16 The concentration of AbA is determined by the concentration when the bait vector is transferred into yeast to inhibit the background expression.
*17 The number of clones screened should reach at least 1 million, otherwise the possibility of screening the target product will be reduced.
*18 The concentration of AbA is determined by the background expression of the bait strain.
*19 In order to confirm whether the bands of similar size are the same insertion segment, the PCR products are digested with AluI or Haell or other commonly used restriction enzymes, and the products are electrophoretic analyzed with 2% agarose gel.
*20 Antibiotic screen positive clones for extraction of plasmid DNA.
*21 Positive control and negative control experiments should be performed together.
*22 Sequencing primers were used with T7 sequencing primer.

