What is CD209A Protein?
CD209A, or Cluster of Differentiation 209A, is a protein encoded by the CD209A gene in Homo sapiens. Since its discovery and identification, it has gradually come to be recognized as an integral player in the human immune system's function, predominantly due to its involvement in several signal pathways and its association with certain diseases.
The CD209A protein was initially identified in a comprehensive survey of the human genome and its protein sequences. The search for new and important proteins and their encoding genes has been a pivotal part of genomics research for decades. In the early phase of the human genome project, the presence of the CD209A gene was confirmed in chromosome 19p13.3. The gene locus for CD209A has a considerable significance as other genes in this region are also connected to crucial human physiological processes.
The CD209A protein structure, as studied with the help of x-ray crystallography and other means, reveals that this is a transmembrane protein with carbohydrate recognition domains (CRDs), enabling it to recognize and interact with many different pathogens. These CRDs allow CD209A to serve as a pathogen receptor and introduce the pathogen to the immune system for effective action.
Function of CD209A protein
The primary function of the CD209A protein involves the initiation of the body's immune response. It does so by binding to specific carbohydrate structures found on the surface of many pathogenic organisms. Once identified, the CD209A protein acts as a bridge, facilitating the interaction between the pathogen and the immune cells, essentially informing the immune system about the foreign invader.
The CD209A protein is highly involved in dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing non-integrin (DC-SIGN) signaling pathways. These pathways are critical for mediating interactions between dendritic cells (DCs) and T cells in the immune response process. Therefore, the CD209A protein plays an instrumental role in the body's defense strategy by linking innate and adaptive immunity.
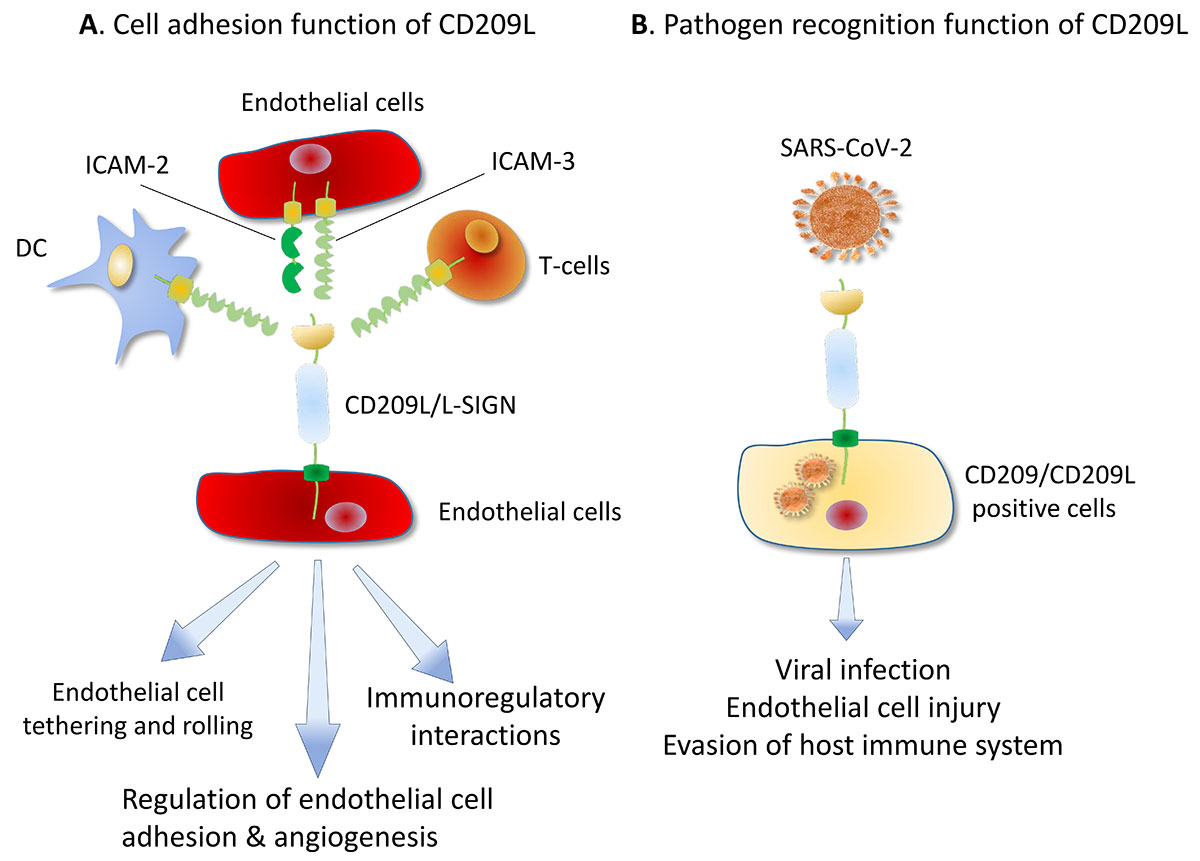
CD209A protein related diseases
The relevance of the CD209A protein extends beyond general physiology into the domain of pathological conditions. When dysregulated, this protein has been linked to diseases such as infectious diseases like HIV and tuberculosis, autoimmune disorders like systemic lupus erythematosus, and metabolic diseases like diabetes. This connection is primarily due to the CD209A protein's role in immunity and its ability to facilitate the introduction of pathogens into the immune system.
CD209A protein's applications in biomedical
On the biomedical front, the importance of the CD209A protein goes beyond basic research. Its implications in disease progression opened avenues for therapeutic intervention strategies for a range of diseases. For instance, interfering with the interaction between DC-SIGN and its viral ligands could potentially prevent viral infection. Further, CD209A could be a critical indicator in predicting disease progression in HIV and TB, providing vital information to clinicians about the course of the disease in the patient.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd209a-166M-B | Recombinant Mouse Cd209a Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | Mouse | HEK293 | |
| Cd209a-166M | Recombinant Mouse Cd209a Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Rahimi, N. (2020). C-type Lectin CD209L/L-SIGN and CD209/DC-SIGN: Cell Adhesion Molecules Turned to Pathogen Recognition Receptors. Biology, 10(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010001

