What is CILP Protein
In the intricate tapestry of cellular biology, proteins play a pivotal role in orchestrating various physiological processes. Among the multitude of proteins, the Cartilage Intermediate Layer Protein, or CILP protein, stands out as a fascinating molecule with diverse functions and implications.
What is CILP Protein?
CILP emerges as a pivotal player in cellular biology, encoded by the CILP gene. Characterized by a sophisticated structure, including the von Willebrand factor type A (vWFA) domain, a thrombospondin type 1 (TSP1) repeat, and a C-terminal globular domain, CILP predominantly expresses in cartilage tissues.
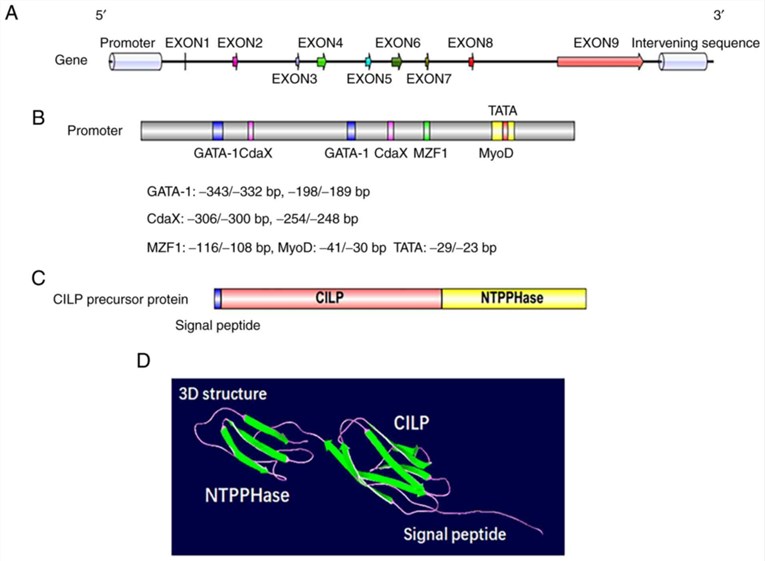
Figure 1. Genetic and protein structure of CILP in humans. (Liu, L., et al. 2021)
The Function of CILP Protein
- Structural Support in Cartilage
CILP's fundamental role lies in providing structural support to cartilage, a connective tissue vital for resisting mechanical stress. This structural integrity is crucial for maintaining the overall functionality of joints and ensuring their smooth movement. Through intricate interactions within the extracellular matrix (ECM), CILP influences the synthesis and assembly of collagen and proteoglycans, contributing to the resilience of cartilage.
- Regulation of Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Components
Beyond structural support, CILP plays a pivotal role in regulating ECM components. Its interactions with molecules like collagen and proteoglycans influence the dynamic balance within the extracellular matrix, a critical determinant of tissue homeostasis. CILP's involvement in ECM regulation extends its impact beyond cartilage, potentially affecting various tissues throughout the body.
- Cell Signaling Modulation
CILP's versatility extends to cell signaling modulation, where it interacts with both cell surface receptors and intracellular signaling molecules. This suggests a broader role in influencing cellular responses, although the specific mechanisms and downstream effects are areas of ongoing research.
CILP-Related Diseases
- Osteoarthritis
The intricate relationship between CILP and osteoarthritis has garnered significant attention. Altered CILP expression has been linked to the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease characterized by cartilage breakdown. Investigating these alterations provides insights into potential diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for mitigating the progression of osteoarthritis.
- Connective Tissue Disorders
Mutations in the CILP gene have been implicated in various connective tissue disorders. These disorders extend beyond joint tissues, affecting ligaments and tendons. The systemic impact of CILP dysfunction underscores its significance in maintaining the integrity of diverse connective tissues.
- Cardiovascular Diseases
Emerging evidence suggests a potential link between CILP and cardiovascular diseases. Understanding the implications of this association is crucial, as it could unveil novel pathways connecting cartilage biology with cardiovascular health. However, further research is needed to elucidate the precise mechanisms and therapeutic implications.
CILP Related Signaling Pathways
- TGF-β Signaling Pathway
The interaction between CILP and the Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway unveils a potential regulatory role in cellular processes. This includes the modulation of cell growth, differentiation, and extracellular matrix synthesis. Investigating the specifics of this interaction provides a nuanced understanding of CILP's contributions to cellular dynamics.
- Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
CILP's connection to the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway adds another layer to its signaling capabilities. This pathway, known for its involvement in development and tissue homeostasis, suggests that CILP could influence cellular responses and contribute to the regulation of extracellular matrix components.
- MAPK Signaling
The intricate Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways, essential for cellular responses to external stimuli, have been implicated in CILP's modulatory role. The interactions with MAPK pathways suggest potential implications for cell proliferation, differentiation, and other crucial cellular processes.
Applications of CILP in Biomedical Research
- Diagnostic Biomarker
The potential of CILP as a diagnostic biomarker is grounded in observations of its altered expression in various diseases, particularly those affecting cartilage and connective tissues. Monitoring CILP levels could offer valuable insights into the progression of conditions like osteoarthritis, providing clinicians with a tool for early detection and intervention.
- Therapeutic Target in Osteoarthritis
Considering its involvement in osteoarthritis pathogenesis, CILP emerges as a promising therapeutic target. Strategies aimed at modulating CILP expression or activity could hold the key to developing interventions that mitigate the degenerative processes associated with this prevalent joint disease.
- Drug Development
The intricate signaling pathways influenced by CILP present a rich landscape for drug development. Targeting specific interactions or pathways involving CILP opens avenues for the development of novel therapeutic agents, potentially offering innovative solutions for conditions associated with cartilage and connective tissue dysfunction.
- Regenerative Medicine
Insights into CILP's role in regulating extracellular matrix components position it as a potential player in regenerative medicine. Exploring ways to manipulate CILP expression or activity could be a strategy to enhance tissue regeneration, particularly in the context of cartilage repair and other regenerative processes.
The CILP protein, with its intricate structure and multifaceted functions, continues to unravel as a key player in cellular dynamics. From providing structural support to influencing signaling pathways and contributing to disease processes, CILP's significance spans various facets of biomedical research. As we delve deeper into its complexities, the promise of diagnostic, therapeutic, and regenerative applications emerges, marking CILP as a focal point in advancing our understanding of cellular biology and its clinical implications.
Recommended Products for CILP Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CILP-538H | Human | Active Recombinant Human CILP Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian cells | His |
| CILP-69H | Human | Recombinant Human CILP protein, T7/His-tagged | E.coli | T7/His |
| CILP-1367H | Human | Recombinant Human CILP Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | GST |
| CILP-2755H | Human | Recombinant Human CILP Protein (725-1184 aa), His-MBP-tagged | Insect Cell | His/Myc |
| CILP-610H | Human | Recombinant Human CILP Protein, His/GST-tagged | E.coli | His/GST |
| CILP-2678H | Human | Recombinant Human CILP Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| CILP-2243H | Human | Recombinant Human CILP Protein (Ile603-Ala846), N-GST tagged | E.coli | N-GST |
| CILP-3475M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse CILP Protein | Mammalian Cell | His |
| CILP-1693M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse CILP Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| CILP-7851Z | Zebrafish | Recombinant Zebrafish CILP | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Liu, L., et al. Cartilage intermediate layer protein affects the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating the extracellular microenvironment (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2021, 47(2): 475-484.

