What is GZMB Protein
The GZMB protein, officially known as Granzyme B, is a crucial component in the field of immunology and cellular biology. Granzyme B is often referred to by its acronym, GZMB, and is alternatively known as Granzyme-2 or C11orf33. Belonging to the family of serine proteases, GZMB plays a pivotal role in various cellular processes, particularly those related to the immune system.
GZMB Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Structurally, GZMB is characterized by its compact, globular shape, typical of serine proteases. It is encoded by the GZMB gene, located on chromosome 14 in humans. This protein is classified as a member of the granzyme family, which consists of several serine proteases involved in immune response modulation.
Recent Research Advances about GZMB Protein
Recent advancements in the study of GZMB have illuminated its multifaceted roles in immune regulation and host defense. Research has highlighted the diverse mechanisms through which GZMB influences cellular processes, making it a subject of significant interest in both basic and clinical research.
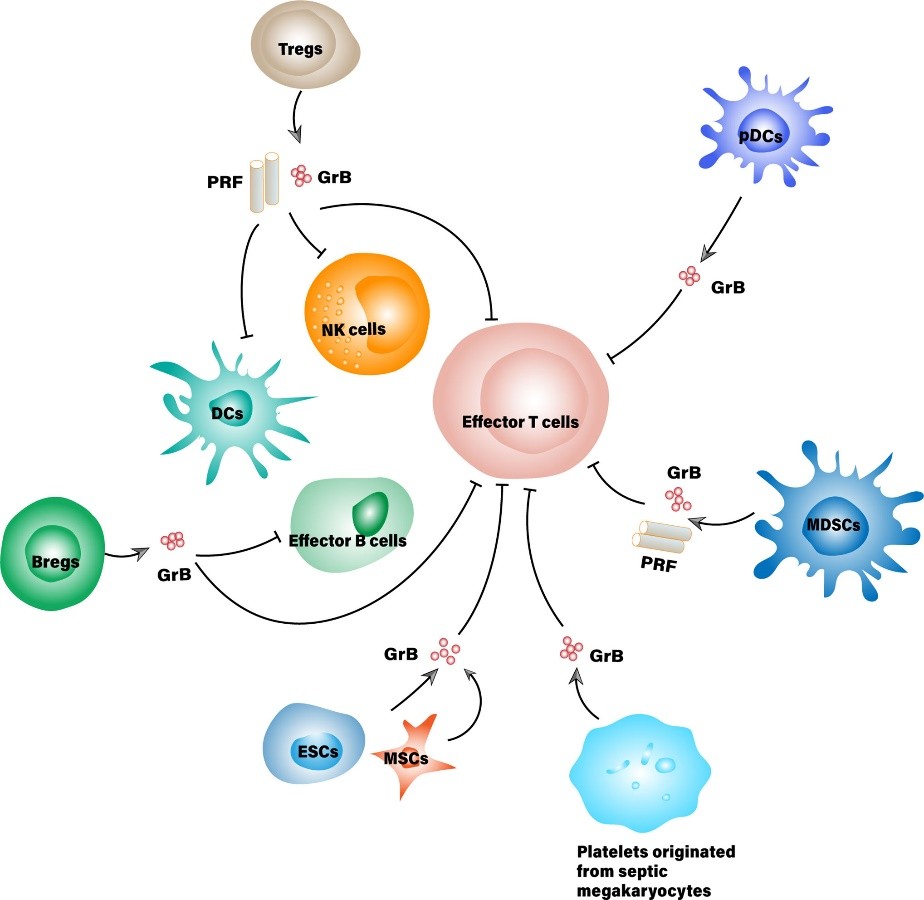
Figure 1. Suppressor cells that secrete granzyme B for immunosuppressive purposes. (Wang W, et al., 2021)
GZMB Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The primary biological function of GZMB is its involvement in immune response and cytotoxicity. GZMB is a key component of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and natural killer (NK) cells, where it acts as an executor of apoptosis in target cells. Its ability to induce programmed cell death is crucial for the elimination of virus-infected cells, tumor cells, and other aberrant cells.
GZMB exerts its cytotoxic effects by entering target cells and activating apoptosis through cleaving specific substrates. Once inside the target cell, GZMB activates a cascade of events leading to programmed cell death. Notably, it cleaves proteins such as caspase-3 and PARP (Poly ADP-ribose polymerase), triggering the apoptotic pathway.
GZMB Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathways involving GZMB are intricate and interconnected. GZMB is often activated downstream of immune cell receptors, such as the T cell receptor (TCR) and NK cell receptors. These receptors transmit signals that lead to the release of GZMB-containing granules, facilitating targeted cytotoxicity.
GZMB Related Diseases
GZMB's involvement in immune regulation positions it as a key player in various diseases. Imbalances in GZMB expression and activity are associated with autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells. Additionally, GZMB is implicated in cancer, as its dysregulation can affect the surveillance and elimination of tumor cells by the immune system.
GZMB's Applications in Biomedicine
- Diagnostic Development: GZMB's presence in immune cells makes it a potential diagnostic marker for certain diseases. Elevated levels of GZMB in the blood or tissues may indicate increased cytotoxic activity, providing valuable insights into immune responses and potential pathological conditions.
- Vaccine Development: Understanding GZMB's role in immune response opens avenues for vaccine development. Targeting GZMB in vaccine formulations may enhance the immune system's ability to eliminate infected or cancerous cells, potentially improving vaccine efficacy.
- Therapeutics: GZMB's cytotoxic properties make it an attractive target for therapeutic interventions. In cancer treatment, strategies to enhance GZMB activity or deliver GZMB directly to tumor cells are being explored to harness its apoptotic effects selectively.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GZMB-33H | Active Recombinant Human GZMB protein | Human | Insect Cell | N/A |
| GZMB-296H | Active Recombinant Human GZMB, His tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| GZMB-5421H | Recombinant Human GZMB protein, His-tagged | Human | Yeast | His |
| GZMB -158H | Recombinant Human GZMB Protein, GST/His-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST/His |
| GZMB-680HF | Recombinant Full Length Human GZMB Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| GZMB-2634H | Recombinant Human GZMB protein, His & T7-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/T7 |
| GZMB-3248H | Recombinant Human GZMB Protein (Ile21-Arg246), N-His tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
| GZMB-01H | Active Recombinant Human GZMB protein, His-tagged | Human | NS0 | His |
| GZMB-3249H | Recombinant Human GZMB Protein (Ala18-Tyr247), C-His tagged | Human | E.coli | C-His |
| GZMB-757H | Recombinant Human GZMB | Human | E.coli | N/A |
Reference
- Wang W, et al. Interaction networks converging on immunosuppressive roles of granzyme B: special niches within the tumor microenvironment. Frontiers in Immunology. 2021, 12: 670324.

