What is HA Protein
In the intricate field of molecular biology, hyaluronic acid (HA) emerges as a key player with multifaceted roles. This glycoprotein is abundant in various tissues, plays a crucial role in physiological processes, signaling pathways, and is of great significance in biomedical applications.
HA, a glycoprotein composed of glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine, stands out in the complex field of molecular biology. Despite its nomenclature, HA is not a traditional protein but a polysaccharide with unique properties. This long-chain molecule plays a key role in various tissues, contributing to their structural integrity and physiological function.
The Function of HA Protein
- Hydration and Lubrication
The hydrophilic nature of HA is critical to its role in maintaining tissue hydration and lubrication. This property is found in joint synovial fluid, which ensures optimal lubrication, reduces friction and promotes smooth joint movement. The molecular structure of HA enables it to attract and retain water molecules, providing essential moisture to tissues.
- Extracellular Matrix Support
HA is a component of the extracellular matrix (ECM), which provides important structural support to tissues such as skin and cartilage. In connective tissue, HA contributes to tissue integrity and elasticity. In the skin, it demonstrates its multifaceted functions by promoting cell migration and proliferation to aid tissue repair and wound healing.
- Cell Signaling and Migration
In addition to its structural role, HA also plays a key role in cell signaling and migration. Interactions between HA and cell surface receptors, particularly CD44 and RHAMM, regulate cell behavior. This involvement extends to processes such as embryonic development, tissue regeneration, and immune responses, emphasizing the diversity of HA's functions.
HA-Related Diseases
- Cancer Metastasis
Aberrant expression of HA is associated with cancer progression and metastasis. The interaction between HA and its receptor promotes cancer cell migration and invasion. Elevated HA levels in the tumor microenvironment are associated with increased malignancy, making HA a potential target for anticancer therapy.
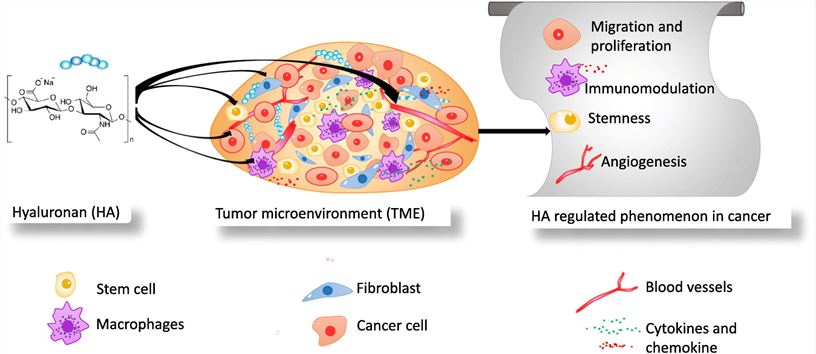 Figure 1. HA and Cancer (Bhattacharyya, M., et al. 2023)
Figure 1. HA and Cancer (Bhattacharyya, M., et al. 2023)- Osteoarthritis
In joint diseases such as osteoarthritis, alterations in HA concentration and distribution play a key role. Reduced levels of HA in synovial fluid impair joint lubrication, leading to increased friction, inflammation, and ultimately cartilage degradation. Understanding the involvement of HA can provide insight into potential therapeutic strategies.
- Inflammatory Disorders
HA regulates inflammatory responses, and its production is increased in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Excessive amounts of HA can cause tissue swelling and inflammation, highlighting the complex relationship between HA and inflammatory disorders.
HA Related Signaling Pathways
- CD44 Signaling
The CD44 signaling pathway is activated by the interaction between HA and CD44 receptors, affecting various cellular processes. CD44 signaling is integral to multiple physiological functions, from cell adhesion to migration and survival. Furthermore, the CD44-HA interaction plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses and inflammation.
- RHAMM-mediated Motility
The RHAMM-mediated motility pathway is activated by the binding of HA to RHAMM receptors and is involved in cell motility and migration. This signaling cascade contributes to processes such as embryonic development and tissue repair, emphasizing the role of HA in dynamic cellular events.
Applications of HA in Biomedical Research
- Dermal Fillers and Cosmetic Surgery
The unique properties of HA make it a cornerstone of cosmetic surgery. HA-based dermal fillers effectively address wrinkles, fine lines, and volume loss. The molecule has the ability to retain water and add volume, providing a natural and rejuvenated look.
- Ophthalmology
In ophthalmic procedures, HA helps improve lubrication and reduce friction within the eye. Its use as a viscoelastic agent in cataract surgery maintains the shape of the eye during surgery, demonstrating the versatility of HA in medical interventions.
- Drug Delivery Systems
The biocompatibility of HA makes it suitable for use in drug delivery systems. HA-based nanoparticles and hydrogels enable controlled and sustained release of therapeutic agents, providing a promising approach for targeted drug delivery.
- Tissue Engineering
The role of HA in the extracellular matrix makes it valuable in tissue engineering. HA-based scaffolds create three-dimensional structures that mimic the natural tissue environment, promoting regeneration of damaged tissue. This application has great potential in the field of regenerative medicine.
- Anti-cancer Therapies
Targeting the HA-CD44 interaction has emerged as a potential strategy for anti-cancer therapies. Inhibiting this interaction has the potential to prevent cancer cell migration and invasion, providing a new way to fight cancer.
In conclusion, despite its polysaccharide nature, HA protein has emerged as a versatile and indispensable player in the field of molecular biology. From structural support to cell signaling and biomedical applications, the diverse functions of HA are constantly being revealed, leading to innovative solutions in medicine and healthcare.
Recommended Products for HA Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA-412I | H9N2 | Recombinant H9N2 (A/Guinea fowl/Hong Kong/WF10/99) HA Protein, His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated | HEK293 | His/Avi |
| HA-001I | Influenza A Virus | Recombinant Influenza A virus HA protein | Insect Cell | N/A |
| HA-1533V | 2019-nCoV | Recombinant 2019-nCoV HA protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | His |
| HA-412H | H10N3 | Recombinant H10N3 HA, His-tagged | Human Cell | His |
| HA-458H | H7N9 | Active Recombinant H7N9 HA, His-tagged | Insect Cell | His |
| HA-713V | Influenza B | Active Recombinant Influenza B (B/Massachusetts/03/2010) HA Protein, His-tagged | Insect Cell | His |
| HA-423H | H2N2 | Active Recombinant H2N2 HA, His-tagged | Insect Cell | His |
| HA-002 | H1N1 | Recombinant A/Brisbane/02/2018(H1N1) HA1 Protein, His-tagged | E. coli | His |
| HA-001 | H1N1 | Recombinant A/Brisbane/02/2018(H1N1) HA1 Protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | His |
| HA-429H | H3N2 | Active Recombinant H3N2 HA, His-tagged | Insect Cell | His |
Reference
- Bhattacharyya, M., Jariyal, H., Srivastava, A. Hyaluronic acid: More than a carrier, having an overpowering extracellular and intracellular impact on cancer. Carbohydr Polym. 2023, 317: 121081.

