What is MUC1 Protein
Mucin 1 (MUC1) protein is a transmembrane glycoprotein encoded by the MUC1 gene and is a molecular key in coordinating key cellular processes.
MUC1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein closely related to cell physiology. The protein's modular structure includes tandem repeats and a cytoplasmic tail. The heavily glycosylated extracellular domain forms a mucus-like coat that protects the cell from external threats, while the cytoplasmic tail serves as a nexus for intracellular signaling.
The Structure of MUC1
The structure of the MUC1 protein is the interaction of tandem repeats and a cytoplasmic tail, epitomizing its modular nature. The extracellular domain has extensive O-linked glycosylation, which not only strengthens the cell membrane but also participates in cell adhesion. In contrast, the cytoplasmic tail interacts with intracellular signaling molecules to coordinate cellular responses.
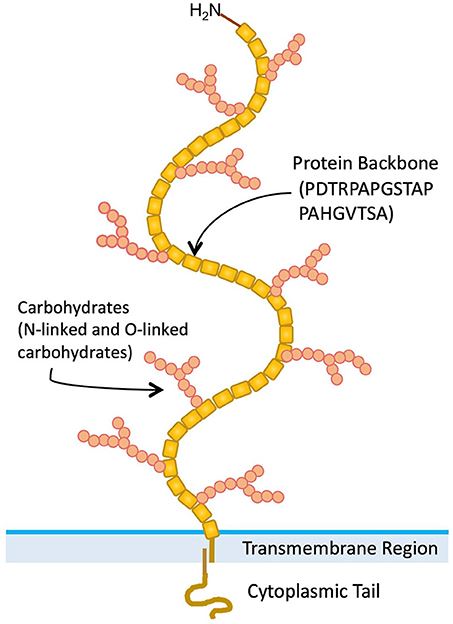 Figure 1. Structure of MUC1 mucin (Agrawal, B., et al. 2018)
Figure 1. Structure of MUC1 mucin (Agrawal, B., et al. 2018)The Function of MUC1 Protein
- Cell Adhesion and Signaling
The involvement of MUC1 in cell adhesion is critical for maintaining tissue integrity. Its role goes beyond adhesion; the cytoplasmic tail serves as a docking site for signaling molecules that influence key cellular processes such as growth and survival. This duality emphasizes its importance in cellular homeostasis.
- Immune Response Modulation
The MUC1 protein is an important regulator of immune responses. Its presence in healthy tissue prevents unwarranted immune activation, whereas in diseases such as cancer, altered expression of MUC1 promotes immune evasion. Unraveling these dynamics holds promise for developing strategies to harness the immune system for disease management.
MUC1-Related Diseases
- Cancer
The role of MUC1 in cancer is profound, and overexpression of MUC1 has been observed in various malignancies. Its abnormal glycosylation pattern contributes to immune evasion, allowing cancer cells to evade detection. Studies have linked MUC1 to breast, pancreatic, ovarian, and lung cancers, positioning it as a potential target for therapeutic intervention.
- Inflammatory Disorders
The MUC1 protein's complex association with chronic inflammatory states highlights its role in inflammatory disorders, including inflammatory bowel disease and rheumatoid arthritis, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target to modulate inflammation.
MUC1 Related Signaling Pathways
- Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
The interaction of MUC1 with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway reveals its effects on cell proliferation and differentiation. The influence of the cytoplasmic tail on β-catenin activity adds a layer of complexity to our understanding of Wnt signaling, implicating MUC1 in diseases in which this pathway is compromised.
- EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) Signaling
The fusion of MUC1 and EGFR signaling introduces a dynamic interaction that influences cell behavior. Targeting this axis offers potential avenues for therapeutic intervention, particularly in cancers where EGFR signaling plays a critical role..
Applications of MUC1 in Biomedical Research
- Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
The overexpression of MUC1 in cancer makes it a valuable biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis. Monitoring MUC1 levels in patient samples could provide insights into the presence, stage and aggressiveness of the cancer, paving the way for personalized treatment strategies.
- Immunotherapy Targets
The unique glycosylation pattern on MUC1 provides a promising target for immunotherapy. Vaccines that stimulate immune responses against MUC1 and monoclonal antibodies against this glycoprotein emerge as innovative strategies to enhance the body's ability to fight cancer.
- Drug Development
Understanding the role of MUC1 in disease-relevant signaling pathways lays the foundation for drug development. Small molecules or biologics targeting MUC1 or its related pathways hold promise as new treatments for cancer and inflammatory diseases.
Taken together, the MUC1 protein transcends its role as a mere cellular component to become a key player in health and disease. From influencing cell adhesion to regulating immune responses to causing diseases such as cancer, the importance of MUC1 is undeniable. Continued exploration of MUC1-related signaling pathways and their applications in biomedicine is expected to reveal new therapeutic prospects and bring hope for improved diagnosis and treatment of various diseases.
Recommended Products for MUC1 Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MUC1-342HAF555 | Human | Recombinant Human MUC1 Protein, Fc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated | HEK293 | Fc |
| MUC1-448HAF555 | Human | Recombinant Human MUC1 Protein, Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated | HEK293 | LEVLFQ |
| MUC1-3952HAF647 | Human | Recombinant Human MUC1 Protein, Fc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 647 conjugated | HEK293 | Fc |
| MUC1-3952HF | Human | Recombinant Human MUC1 Protein, Fc-tagged, FITC conjugated | HEK293 | Fc |
| MUC1-342HAF488 | Human | Recombinant Human MUC1 Protein, Fc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated | HEK293 | Fc |
| MUC1-3952HAF488 | Human | Recombinant Human MUC1 Protein, Fc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated | HEK293 | Fc |
| MUC1-448HAF488 | Human | Recombinant Human MUC1 Protein, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated | HEK293 | LEVLFQ |
| MUC1-342HF | Human | Recombinant Human MUC1 Protein, Fc-tagged, FITC conjugated | HEK293 | Fc |
| MUC1-448HF | Human | Recombinant Human MUC1 Protein, FITC conjugated | HEK293 | LEVLFQ |
| Muc1-106M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Muc1 protein, His/GST-tagged | E.coli | His/GST |
Reference
- Agrawal, B., Gupta, N., Konowalchuk, J.D. MUC1 Mucin: A Putative Regulatory (Checkpoint) Molecule of T Cells. Front Immunol. 2018, 9: 2391.

