What is PLA2 Protein
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2), a protein wielding a name that echoes its intricate function, stands as a key player in various biological processes. Officially known as Phosphatidylcholine 2-acylhydrolase, PLA2 also goes by synonyms such as Group I PLA2, sPLA2, and, intriguingly, bee venom PLA2. Belonging to the phospholipase enzyme family, PLA2 is a diverse group with members scattered across organisms, contributing to an array of physiological and pathological phenomena.
Structural Characteristics and Classification
PLA2 possesses a catalytic domain that allows it to cleave the sn-2 position of phospholipids. This cleavage liberates fatty acids, notably arachidonic acid, setting the stage for the production of various bioactive lipid mediators. Structurally, PLA2 exhibits diversity, with distinct isoforms found in different tissues and organisms. It is broadly classified into several groups, including secretory PLA2, cytosolic PLA2, and calcium-independent PLA2. The structural nuances of PLA2 confer upon it the ability to interact with cell membranes, influencing cellular responses and signaling cascades.
In the realm of scientific exploration, recent advances in PLA2 research have unveiled its multifaceted roles. Studies delve into the intricate mechanisms that govern PLA2's involvement in cellular signaling, inflammation, and immune responses. Notably, researchers are unraveling the implications of PLA2 in diseases ranging from neurodegenerative disorders to inflammatory conditions. This expanding knowledge base not only deepens our understanding of PLA2 but also presents promising avenues for therapeutic interventions.
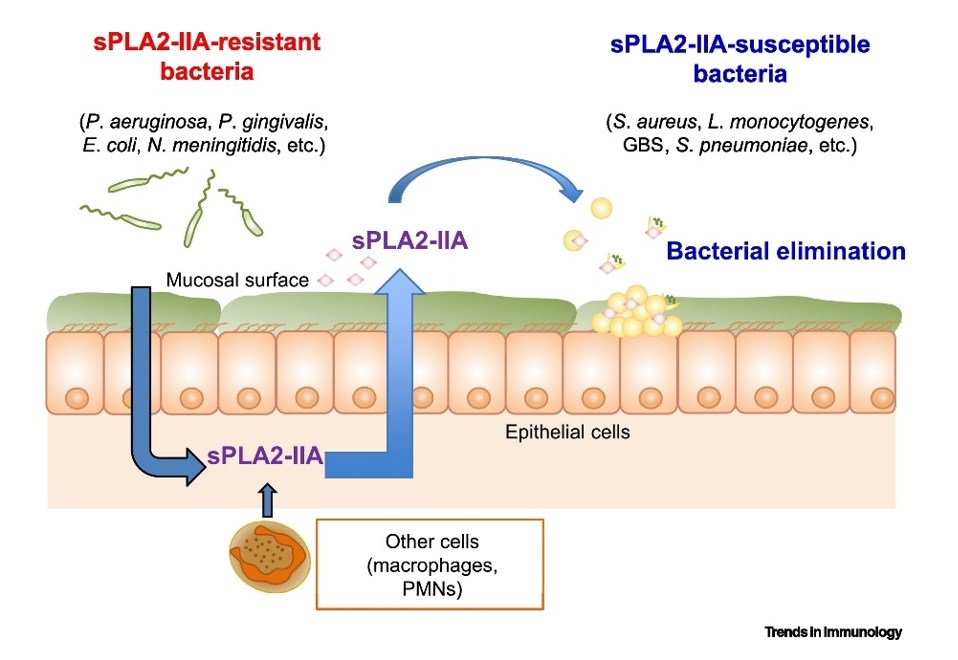
Figure 1. Type IIA secreted phospholipase A2 (sPLA2-IIA) is induced by bacteria to eradicate competitor bacteria in the same niche. (van Hensbergen V P, et al., 2020)
PLA2 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
Primarily recognized for its role in lipid metabolism, PLA2 catalyzes the hydrolysis of phospholipids, releasing arachidonic acid. This liberated acid becomes a precursor for the synthesis of eicosanoids, potent signaling molecules involved in inflammation and immune responses.
Furthermore, PLA2 participates in membrane remodeling and cellular homeostasis. By modulating the composition of cell membranes, PLA2 influences membrane fluidity and permeability, crucial for cellular integrity. Its presence in various cellular compartments, including the cytosol and extracellular spaces, underscores its versatility in regulating diverse physiological processes.
PLA2 Related Signaling Pathway
PLA2's involvement in cellular signaling pathways is akin to a navigator steering the course of cellular responses. It integrates with diverse signaling cascades, including the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) pathway. These interactions intricately modulate cellular activities, influencing inflammation, proliferation, and apoptosis. The dysregulation of PLA2-related signaling pathways contributes to the aberrant cellular responses observed in pathological conditions.
PLA2 Related Diseases
The intricate web of PLA2's functions also entwines it with various diseases. Dysregulation of PLA2 activity has been implicated in conditions such as atherosclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and neuroinflammatory disorders. The excessive release of arachidonic acid and subsequent eicosanoid production contributes to the inflammatory milieu associated with these diseases. Understanding the role of PLA2 in disease pathogenesis provides a potential avenue for targeted therapeutic interventions.
PLA2's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique properties of PLA2 have not gone unnoticed in the biomedical realm, where researchers are harnessing its potential for diagnostic, therapeutic, and vaccine development.
In diagnostics, PLA2 serves as a biomarker for certain inflammatory conditions. Elevated levels of PLA2 in biological fluids, such as serum or synovial fluid, can be indicative of ongoing inflammation, aiding in disease diagnosis and monitoring.
Vaccine development has also embraced PLA2, particularly in the context of bee venom allergies. The protein's immunogenic properties make it a potential candidate for desensitization therapies, paving the way for effective bee venom allergy vaccines.
Therapeutically, PLA2 inhibitors are being explored as a strategy to mitigate inflammatory diseases. By targeting PLA2 activity, researchers aim to intervene in the inflammatory cascade, offering novel avenues for drug development.Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pla2-343B | Recombinant Bee Phospholipase A2 | Bee | E.coli | N/A |
| PLA2-006B | Recombinant Bee PLA2 Protein | Bee | E.coli |
Reference
- van Hensbergen V P, et al. Type IIA secreted phospholipase A2 in host defense against bacterial infections. Trends in Immunology. 2020, 41(4): 313-326.

