What is RLN1 Protein
RLN1, or Relaxin 1, is a crucial protein with multifaceted roles in various physiological processes. Also known as H2 relaxin, RLN1 belongs to the relaxin family peptide hormones. The official full name of this protein is Relaxin-1, and it has synonyms such as RLX and INSL7. Structurally, RLN1 is characterized by its unique two-chain structure, consisting of an A and B chain connected by disulfide bonds. This protein is classified as a member of the insulin superfamily and is primarily synthesized in the corpus luteum of the ovary during pregnancy.
RLN1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
RLN1 plays a pivotal role in several biological functions and molecular mechanisms. One of its primary functions is to facilitate the relaxation of uterine muscles during pregnancy, ensuring optimal conditions for embryo implantation. Moreover, RLN1 exhibits vasodilatory properties, contributing to increased blood flow in various tissues. Beyond its reproductive functions, RLN1 has been implicated in the regulation of collagen metabolism, suggesting its involvement in tissue remodeling.
The molecular mechanisms underlying RLN1's actions involve binding to its receptor, RXFP1, triggering a cascade of intracellular events. Activation of RXFP1 leads to the production of secondary messengers, ultimately influencing cellular processes such as smooth muscle relaxation, angiogenesis, and collagen degradation.
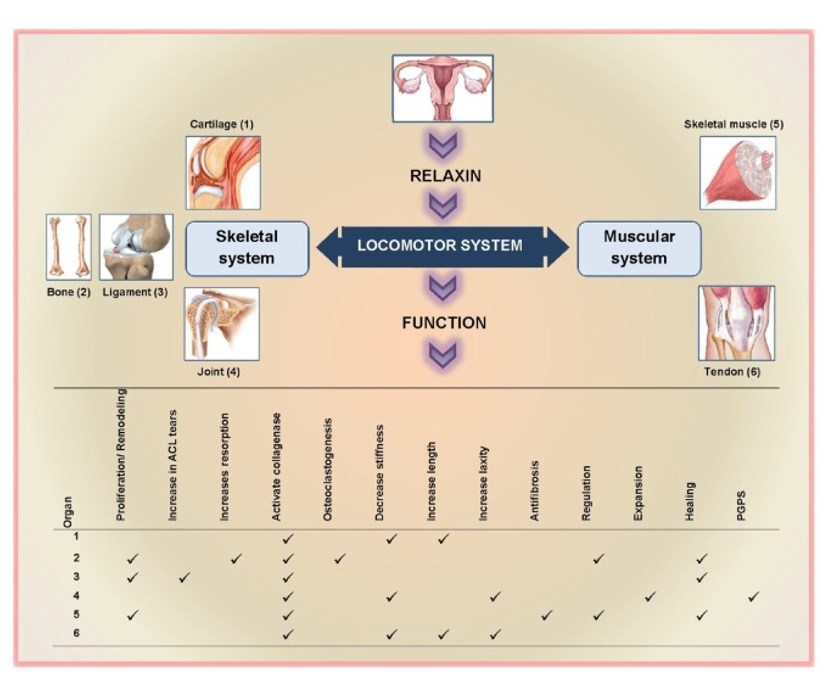
Figure 1. A summary of relaxin role in the locomotor system. (Dehghan F, et al., 2014)
RLN1 Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathway of RLN1 involves its binding to the RXFP1 receptor, initiating a series of events within the cell. Upon RLN1 binding, RXFP1 activates the adenylate cyclase pathway, leading to an increase in cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels. Elevated cAMP levels, in turn, activate protein kinase A (PKA) and other downstream effectors, influencing cellular responses.
This signal pathway is intricately involved in the modulation of smooth muscle tone, angiogenesis, and collagen metabolism. Understanding the specifics of the RLN1-related signal pathway is crucial for unraveling the intricate network of interactions that govern its physiological effects.
RLN1 Related Diseases
While RLN1 is essential for normal physiological functions, dysregulation of its expression or signaling pathways can contribute to various diseases. Abnormalities in RLN1 levels have been associated with conditions such as preeclampsia, a hypertensive disorder during pregnancy. Additionally, altered RLN1 expression has been observed in certain cancers, suggesting a potential role in tumorigenesis and tumor progression.
Understanding the link between RLN1 and diseases provides valuable insights into the development of targeted therapeutic interventions and diagnostic strategies.
RLN1's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique properties and functions of RLN1 make it a promising candidate for various biomedical applications. Researchers are exploring its potential in diagnostics, vaccine development, and therapeutics.
In diagnostics, RLN1 may serve as a biomarker for conditions associated with pregnancy complications or abnormal collagen metabolism. Its presence or absence can be indicative of certain pathophysiological states, aiding in early detection and intervention.
In vaccine development, RLN1's ability to modulate immune responses and tissue remodeling makes it an intriguing target. By harnessing its properties, researchers aim to develop vaccines that can elicit specific immune responses for therapeutic purposes.
Therapeutically, RLN1 has shown promise in the treatment of conditions characterized by smooth muscle dysfunction, such as asthma and certain cardiovascular diseases. The vasodilatory effects of RLN1 also make it a potential candidate for conditions where improved blood flow is beneficial.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RLN1-193H | Recombinant Human Relaxin 1 | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| RLN1-245H | Recombinant Human RLN1 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| RLN1-219H | Recombinant Human RLN1 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| Rln1-656M | Active Recombinant Mouse Rln1 | Mouse | E.coli | Met |
| Rln1-5821M | Recombinant Mouse Rln1 protein, His-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His |
| RLN1-5055R | Recombinant Rat RLN1 Protein | Rat | Mammalian Cell | His |
| Rln1-5822R | Recombinant Rat Rln1 protein, His-tagged | Rat | E.coli | His |
| RLN1-4714R | Recombinant Rat RLN1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| RLN1-8321Z | Recombinant Zebrafish RLN1 | Zebrafish | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Dehghan F, et al. The effect of relaxin on the musculoskeletal system. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports. 2014, 24(4): e220-e229.

