What is RPA1 Protein
In the intricate tapestry of molecular biology, the Replication Protein A1 (RPA1) takes center stage, orchestrating critical functions in DNA metabolism.
What is RPA1 Protein?
The Replication Protein A1 (RPA1) is a linchpin in cellular processes, belonging to the Replication Protein A (RPA) family. This family is renowned for its indispensable roles in DNA replication, repair, and recombination. RPA1, specifically, is a single-stranded DNA (ssDNA)-binding protein, exhibiting a unique affinity for DNA strands in single-stranded conformation.
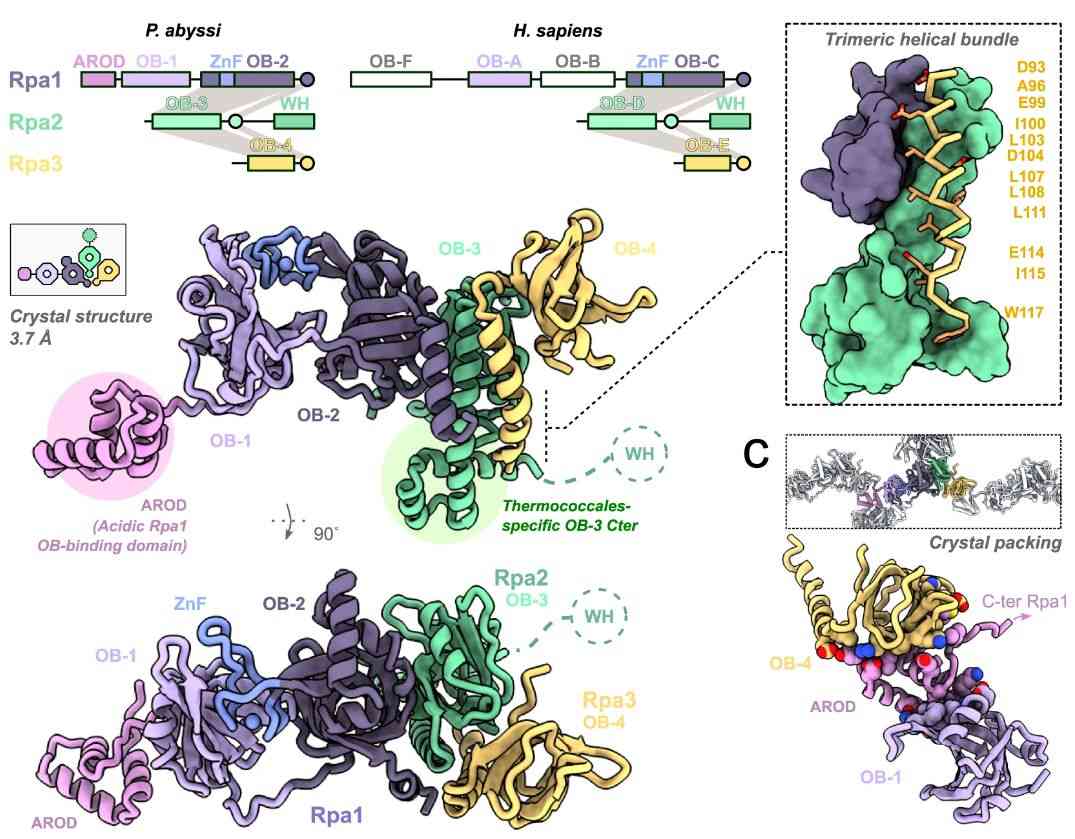
Figure 1. Structure of the archaeal RPA. (Madru, C., et al. 2023)
The Function of RPA1 Protein
- DNA Replication
RPA1 plays a pivotal role in DNA replication by stabilizing exposed single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) regions. As the DNA double helix unwinds during replication, RPA1 promptly binds to prevent the formation of secondary structures, ensuring a smooth progression of the replication process.
- DNA Repair
In the realm of DNA repair, RPA1 emerges as a key facilitator. Upon DNA damage, RPA1 swiftly associates with exposed ssDNA, acting as a beacon for other repair proteins. This interaction accelerates the recruitment of repair machinery, expediting the resolution of DNA lesions.
- Homologous Recombination
RPA1 is integral to homologous recombination, a process vital for accurate DNA repair. By binding to ssDNA regions, RPA1 promotes the exchange of genetic material between homologous DNA strands, ensuring fidelity in the repair process.
RPA1-Related Diseases
- Cancer
Dysregulation of RPA1 is implicated in cancer development. Studies indicate that overexpression of RPA1 is associated with heightened genomic instability, a hallmark of cancer progression. Conversely, reduced RPA1 levels compromise DNA repair mechanisms, contributing to mutagenesis and cancer evolution.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases
A potential connection between RPA1 dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases surfaces. In conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, where DNA damage and impaired repair mechanisms prevail, RPA1's role in maintaining genomic stability becomes pivotal.
RPA1 Related Signaling Pathways
- ATR-Chk1 Pathway
RPA1 activates the ATR (Ataxia Telangiectasia and Rad3-related) kinase and its downstream effector Chk1 (Checkpoint kinase 1). This activation occurs when RPA1 binds to ssDNA, initiating a signaling cascade that leads to cell cycle arrest. This pause provides a window for DNA repair before cell division proceeds.
- p53 Pathway
RPA1 regulates the tumor suppressor protein p53. Upon DNA damage, RPA1 aids in the activation of p53, which subsequently induces cell cycle arrest or apoptosis. This orchestrated response prevents the propagation of damaged DNA and maintains genomic integrity.
Applications of RPA1 in Biomedical Research
- Cancer Therapeutics
Understanding RPA1's role in cancer development opens avenues for targeted therapies. Researchers explore modulating RPA1 expression or activity to selectively induce cell death in cancer cells, offering a promising approach to cancer treatment.
- DNA Repair Enhancement
Manipulating RPA1 presents an opportunity to enhance DNA repair efficiency. This concept holds potential in developing therapies for diseases characterized by defective DNA repair, such as certain cancers and neurodegenerative disorders.
- Biomarker Development
RPA1 levels and activity serve as valuable biomarkers for disease diagnosis and prognosis. Monitoring RPA1 expression in tissues or biological fluids provides insights into DNA integrity, offering a potential tool for assessing the risk of diseases associated with DNA damage.
- Gene Editing Technologies
RPA1's role in DNA repair mechanisms is crucial for advancing gene editing technologies. Understanding its interactions with technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 could lead to improvements in precision and efficiency, heralding a new era in genetic manipulation.
The RPA1 protein emerges as a linchpin in the intricate machinery of cellular processes, wielding influence over DNA replication, repair, and recombination. Its dysregulation underlies diseases, making it a focal point for biomedical research. From targeted cancer therapies to advancements in gene editing technologies, RPA1's diverse applications underscore its potential in shaping the future landscape of medicine.
Recommended Products for RPA1 Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPA1-2366H | Human | Recombinant Human RPA1, GST-tagged | E.coli | GST |
| RPA1-31145TH | Human | Recombinant Human RPA1, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| RPA1-31147H | Human | Recombinant Human RPA1 protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | GST |
| RPA1-31146H | Human | Recombinant Human RPA1, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| RPA1-2030H | Human | Recombinant Human RPA1 Protein, His&GST-tagged | E.coli | N-His&GST |
| RPA1-685HFL | Human | Recombinant Full Length Human RPA1 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| RPA1-1909H | Human | Recombinant Human RPA1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| Rpa1-5578M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Rpa1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| Rpa1-2029R | Rat | Recombinant Rat Rpa1 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | N-His |
| RPA1-1369C | Chicken | Recombinant Chicken RPA1 | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Madru, C., et al. DNA-binding mechanism and evolution of replication protein A. Nat Commun. 2023, 14: 2326.

