What is TSH Protein
In the intricate tapestry of human physiology, the thyroid gland plays a pivotal role in regulating various bodily functions. At the center of this thyroid orchestration is the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) protein, a critical molecular player that orchestrates thyroid function.
TSH stands as a pivotal glycoprotein hormone, originating from the anterior pituitary gland. Its structural composition involves two subunits—alpha and beta. The alpha subunit is shared with other glycoprotein hormones, while the beta subunit imparts specificity to TSH. This unique structure enables TSH to bind selectively to receptors on the thyroid cell surface.
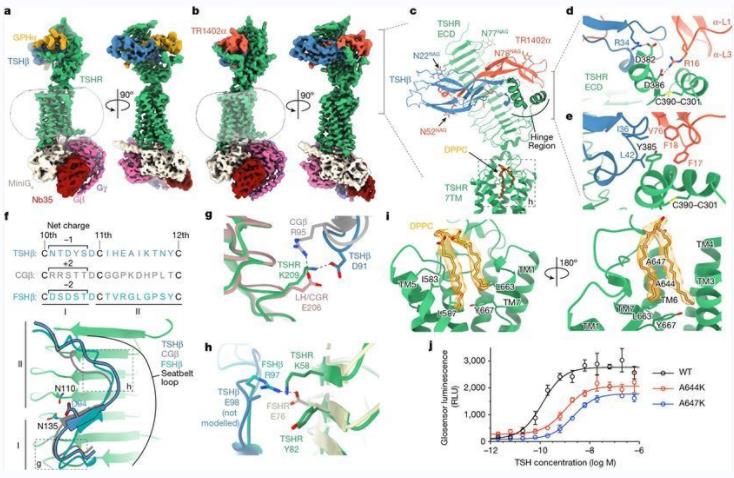 Figure 1. Cryo-EM structures of native human TSH and TR1402 bound to active TSHR complexed with heterotrimeric Gs. (Faust, B., et al. 2022)
Figure 1. Cryo-EM structures of native human TSH and TR1402 bound to active TSHR complexed with heterotrimeric Gs. (Faust, B., et al. 2022)The Function of TSH Protein
TSH's primary function revolves around orchestrating thyroid gland activity, influencing the synthesis and release of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Upon TSH binding, a cascade of events ensues, involving adenylate cyclase, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), and protein kinase A (PKA). This culminates in the synthesis and secretion of T4 and T3, regulating metabolic processes throughout the body.
TSH-Related Diseases
The delicate balance of TSH is essential, and deviations can lead to debilitating disorders. Hypothyroidism, a consequence of insufficient TSH stimulation, manifests in symptoms like fatigue and weight gain. Conversely, hyperthyroidism, often associated with excessive TSH production, results in symptoms such as weight loss and increased heart rate. Grave's disease exemplifies an autoimmune disorder where antibodies mimic TSH, causing uncontrolled thyroid hormone release.
Thyroid function tests, measuring TSH, T4, and T3 levels, serve as invaluable diagnostic tools, guiding interventions for thyroid disorders.
TSH Related Signaling Pathways
The TSH signal pathway intricately unfolds within thyroid cells. TSH binding triggers adenylate cyclase activation, converting ATP to cAMP. Elevated cAMP levels activate PKA, initiating phosphorylation of key proteins involved in thyroid hormone synthesis. This cascade ensures the orchestrated release of T4 and T3 into the bloodstream, where their effects permeate target tissues.
Applications of TSH in Biomedical Research
- Diagnostic Applications
TSH emerges as a diagnostic linchpin for thyroid disorders. Monitoring TSH levels aids in assessing thyroid functionality and refining thyroid replacement therapy. Precision in dosage, guided by TSH levels, is paramount in maintaining optimal thyroid hormone levels.
- Targeted Therapies
Beyond diagnostics, TSH receptors found not only in the thyroid but also in certain thyroid cancers have paved the way for targeted therapies. Radioiodine therapy exploits TSH receptors, delivering radioactive iodine directly to cancerous thyroid cells. This innovative approach shows promise in treating thyroid cancer with minimal collateral damage.
- Research into Metabolic Disorders
TSH's central role in metabolism has sparked interest in its implications for metabolic disorders. Exploring connections between TSH and conditions like obesity and insulin resistance may unveil novel therapeutic targets. The potential intersection of TSH with metabolic pathways presents a frontier for groundbreaking interventions in prevalent health issues.
- Neuroprotective Effects
Recent studies hint at TSH's neuroprotective effects, suggesting its influence on neuronal survival and function. This opens avenues for research into its role in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. TSH's multifaceted involvement expands its relevance beyond endocrinology, demonstrating its potential impact on diverse facets of human health.
TSH, once perceived as a hormone confined to thyroid regulation, has evolved into a multifaceted player with far-reaching implications in biomedical research. Its intricate structure, vital functions, and involvement in diverse signal pathways underscore its significance in maintaining physiological equilibrium. From diagnostics to innovative therapies, TSH's role continues to expand, promising novel insights into human health and potential therapeutic avenues for a spectrum of disorders. As research unfolds, TSH stands as a beacon in our journey to decode the intricacies of human physiology and pathology.
Recommended Products for TSH Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSH-42H | Human | Recombinant Human Thyroid Stimulating Hormone | Yeast | N/A |
| TSH-01H | Human | Recombinant Human Thyroid Stimulating Hormone(TSH) Protein, His-tagged | CHO | His |
Reference
- Faust, B., et al. Autoantibody mimicry of hormone action at the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022, 609(7928): 846-853.

