Principle and Protocol of Native-PAGE
Polyacrylamide gel is mainly used for protein electrophoresis. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is a process in which polyacrylamide gel is used as a support medium to separate the action of charged particles in an electric field. Many important biomolecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, have ionizable groups. They can be positively or negatively charged at a specific pH. Under the action of electric field, these charged molecules will move towards the electrode opposite to the polarity of the charge they carry. Their migration speed is related to the charged properties of molecules and the size and shape of molecules themselves. Main factors affecting electrophoresis separation:
(1) Properties of biomacromolecules to be separated, such as charge, diameter and shape;
(2) The properties of buffer solution, such as pH, ionic strength and viscosity of buffer solution;
(3) Electric field strength and electrophoresis temperature;
(4) Electroosmosis, the relative movement of the liquid in the electric field to the solid supporting medium, is called electroosmosis;
(5) Sieve size of the supporting medium.
Non denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is the polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of active proteins without adding denaturants such as SDS and mercaptoethanol, which is commonly used for the identification and purification of isoenzymes.
Polyacrylamide gel is a three-dimensional polymer formed by acrylamide (Acr for short) monomer and a small amount of crosslinking agent methylene bisacrylamide (Bis for short) through chemical catalyst (ammonium persulfate), tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) as accelerator or photocatalytic polymerization. The pore size of gel can be controlled by changing the concentration of acrylamide and methylene bisacrylamide, and the content of acrylamide can be 3%~30%. Low concentration gel has a large pore size, for example, 3% polyacrylamide gel has no obvious blocking effect on protein, and can be used as a concentrated gel for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; High concentration gel has a small pore size and acts as a molecular sieve for proteins, which can be used in electrophoresis to separate proteins according to their relative molecular weight. The polymerized polyacrylamide gel forms a network structure with concentration effect, charge effect and molecular sieve effect. Non denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis can make biological macromolecules maintain their natural shape and charge in the process of electrophoresis. Their separation can obtain high resolution according to their different electrophoretic mobility and the role of molecular sieve of gel, and can still maintain the biological activity of biological macromolecules such as proteins and enzymes after electrophoresis separation.
For non-denaturing gel electrophoresis of proteins, it is necessary to distinguish whether the proteins are alkaline or acidic. Low pH gel system shall be used to separate alkaline proteins, and high pH gel system shall be used to separate acidic proteins. Acidic proteins usually use the pH 8.8 buffer system in non-denaturing gel electrophoresis, and the proteins will be negatively charged and move to the anode; The electrophoresis of basic proteins is usually carried out in a slightly acidic environment, with positive and neutral charges. The cathode and anode must be inverted during electrophoresis separation.
The strength, elasticity, transparency, viscosity and pore size of the polymerized polyacrylamide gel depend on 2 important parameters, T (total concentration of acrylamide and methylene bisacrylamide) and C (mass fraction of crosslinking agent).
T% = (Grams of acrylamide + grams of crosslinking agent) / Total volume (mL) × 100
C% = Grams of crosslinking agent / (Grams of acrylamide dozens of grams of crosslinking agent) × 100
1. Main Instruments and Equipment
Micropipette, gel filling bracket, glass plate, comb, power supply, heater, electrophoresis tank, scanner, balance.
2. Experimental Materials
Protein sample to be tested.
3. Main reagents
40% Acr-Bis (Acr: Bis=19:1) *1.
4 × Separating gel buffer (1.5 mol/L Tris HCl, pH 8.8): 18.2g Tris base is dissolved in 80 mL of water, adjusted to pH 8.8 with concentrated HCl, added water to a constant volume of 100 mL, and stored at 4°C.
4 × Stacking gel buffer solution (0.5mol/L Tris HCl, pH6.8): 6g Tris base is dissolved in 80mL water, adjusted to pH6.8 with concentrated HCl, added water to a constant volume of 100mL, and stored at 4°C.
10 × Electrophoretic buffer (pH 8.8 Tris Gly): 30.3g Tris base, 144g glycine, add water to a constant volume of 1L, and store at 4°C.
2 × Bromophenol blue loading buffer solution: 1.25mL 0.5mol/L Tris HCl, pH 6.8, 3.0mL glycerol, 0.2mL 0.5% bromophenol blue, 5.5mL double distilled water, and stored at - 20°C.
10% APS: weigh 100mg ammonium persulfate and dissolve it in 1mL sterile water.
0.25% Coomassie brilliant blue dye solution: Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 2.5g, methanol 400mL, HAc100mL. Double distilled water 500mL.
Coomassie brilliant blue bleaching solution: 400mL methanol, 100mL glacial acetic acid, 500mL double distilled water.
1. Preparation of Gel
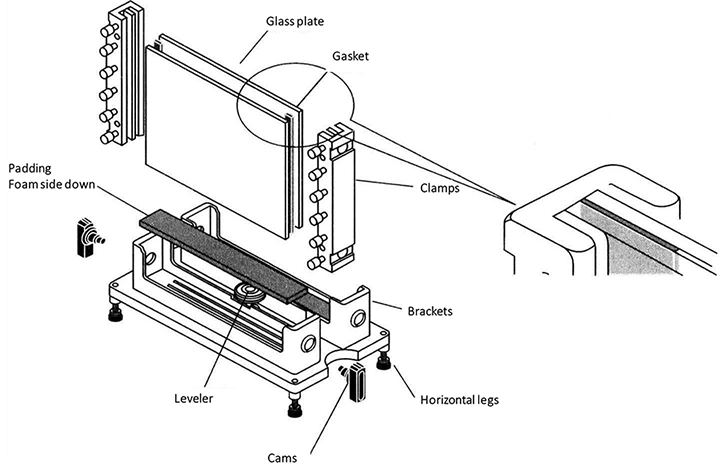
Basic non-denatured gel (discontinuous gel) for separating acidic protein was prepared.
Clean the glass plate until there is no water drop hanging on the wall, then rinse it with clean water for 3 times, and with distilled water for one time, and stand on the glass plate frame to dry in the shade. Assemble the long and short glass according to the requirements of the electrophoresis mold used.
Prepare the separating gel components as shown in Table 2-2-1, and add ammonium persulfate *2 and TEMED *3 before gel filling.
Table 2-2-1 Basic Non-denatured Gel
| Reagent | Separating gel (17%) 10 mL | Stacking gel (4%) 5 mL |
| 40% Acr-Bis (40% T, 5% C) | 4.25 mL | 0.5 mL |
| 4 × Separating gel buffer (1.5 mol/L Tris HCl, pH 8.8) | 2.5 mL | - |
| 4 × Stacking gel buffer solution (0.5mol/L Tris HCl, pH6.8) | - | 1.25 mL |
| Deionized water | 3.2 mL | 3.2 mL |
| 10% APS | 35 μL | 35 μL |
| TEMED | 15 μL | 15 μL |
When the separating gel is poured to 3/4 of the height of the short glass plate, stop pouring gel, and add 1mL isopropanol or water for sealing. After about 30min, an obvious boundary appears between the gel and the sealing layer, indicating that the gel is fully polymerized. Pour out the sealing layer liquid, wash it with distilled water and absorb excess water with filter paper.
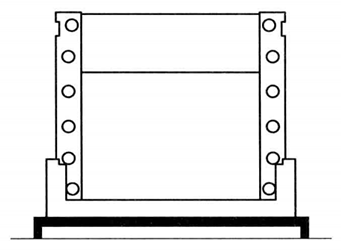
Prepare the stacking gel components as shown in Table 2-2-1. Pour the rubber 0.5cm away from the upper edge of the short glass plate in the same way, and insert the sample comb. After gel polymerization for about 30min, carefully pull out the sample comb.
2. Sample Electrophoresis
Dilute 10 × electrophoresis buffer (pH8.8 Tris-Gly) 100mL to 1L and pour it into the upper and lower reservoirs of the electrophoresis tank, the lower reservoir should not exceed 2/3 of the glass plate, and the upper reservoir should not exceed 0.5cm of the short plate, ready for sample loading.
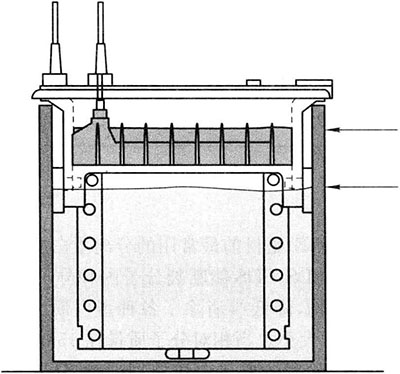
Take 10 μ L Protein sample added 5 μL 3 × Sample loading buffer, mix well and then sample loading. Electrophoresis*4 When the indicator moves to about 1cm from the bottom of the rubber plate, stop electrophoresis. The whole process takes about 80min.
1. The 40% acrylamide aqueous solution can be stored for 1 month at 4°C. During storage, acrylamide will be hydrolyzed to acrylic acid, which will increase the electroosmosis phenomenon and slow down the mobility of electrophoresis.
2. Acrylamide and methylene bisacrylamide are toxic reagents to the central nervous system. Avoid direct contact with the skin during operation, but they are non-toxic after polymerization.
3. In the process of non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, the mobility of protein is not only related to the isoelectric point of the protein, but also related to the relative molecular weight and molecular shape of the protein. The isoelectric point of the protein is the most important influencing factor, and the corresponding electrophoresis buffer system should be selected according to the isoelectric point of the protein.
4. In the process of non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, attention should be paid to the heating caused by high voltage, which leads to protein denaturation. Therefore, it is better to place ice cubes outside the electrophoresis tank to reduce the temperature.
5. If the relative molecular weight of the protein is large, the electrophoresis time can be appropriately extended so that the target protein has sufficient mobility to separate from other proteins.
*1 Dissolve 380 g acrylamide and 20 g N, N '- methylene bisacrylamide in 600 mL distilled water. Heat to 37 °C for dissolution and make up with distilled water until the final volume is 1 L. Use filter (0.45 μm pore diameter), put it in a brown bottle and store it at 4 °C away from light.
*2 Provide free radicals.
*3 It is the catalyst, which catalyzes the polymerization reaction caused by free radicals.
*4 MiniVE electrophoresis tank conditions: 100 V constant pressure for about 20 min, the indicator enters the separation gel, and the 160 V constant pressure is changed.
*5 Electrophoresis of two identical samples can be carried out on the gel. After electrophoresis, the gel is cut into two halves. One half is used for active dyeing to identify a specific biomacromolecule, and the other half is used for dyeing all samples to analyze the types and contents of various biomacromolecules in the sample.

