CD200R1
-
Official Full Name
CD200 receptor 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a receptor for the OX-2 membrane glycoprotein. Both the receptor and substrate are cell surface glycoproteins containing two immunoglobulin-like domains. This receptor is restricted to the surfaces of myeloid lineage cells and the receptor-substrate interaction may function as a myeloid downregulatory signal. Mouse studies of a related gene suggest that this interaction may control myeloid function in a tissue-specific manner. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. This gene encodes a receptor for the OX-2 membrane glycoprotein. Both the receptor and substrate are cell surface glycoproteins containing two immunoglobulin-like domains. This receptor is restricted to the surfaces of myeloid lineage cells and the receptor-substrate interaction may function as a myeloid downregulatory signal. Mouse studies of a related gene suggest that this interaction may contr -
Synonyms
CD200R1;CD200 receptor 1;OX2R;MOX2R;CD200R;HCRTR2;Orexin receptor 2;OTTMUSP00000015932;OTTMUSP00000030764;antigen identified by monoclonal antibody MRC OX-2 receptor
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- Chicken
- Bovine
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- CHO
- Human Cells
- Insect Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- E.coli
- GST
- His
- Fc
- Avi
- Non
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is CD200R1 protein?
CD200R1 (CD200 receptor 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3q13. This gene encodes a receptor for the OX-2 membrane glycoprotein. Both the receptor and substrate are cell surface glycoproteins containing two immunoglobulin-like domains. This receptor is restricted to the surfaces of myeloid lineage cells and the receptor-substrate interaction may function as a myeloid downregulatory signal. Mouse studies of a related gene suggest that this interaction may control myeloid function in a tissue-specific manner. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. The CD200R1 protein is consisted of 348 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 39 kDa.
What is the function of CD200R1 protein?
CD200R1 is an inhibitory receptor for the CD200/OX2 cell surface glycoprotein which limits inflammation by inhibiting the expression of pro-inflammatory molecules including TNF-alpha, interferons, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in response to selected stimuli. Also it binds to HHV-8 K14 viral CD200 homolog with identical affinity and kinetics as the host CD200.
CD200R1 Related Signaling Pathway
CD200 is an immunosuppressive molecule that regulates the function of immune cells by binding to CD200R1. CD200R1 can activate PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and MAPK/ERK signaling pathway, thereby affecting cell survival, proliferation, metabolism and other processes. CD200R1 can regulate the stability and nuclear localization of β-catenin, the core component of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, and affect the tumorigenesis and development. CD200R1 regulates the phosphorylation and stability of YAP/TAZ, a core component of the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway.
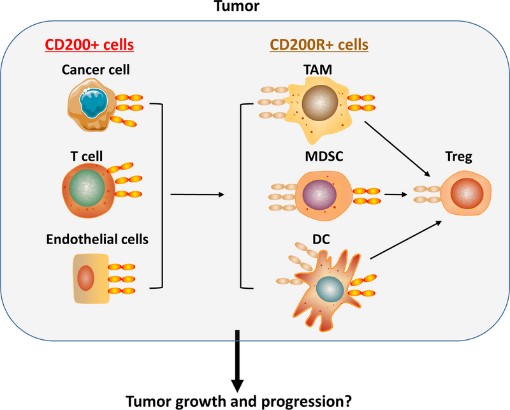
Fig1. CD200-CD200R interaction in tumor microenvironment. (Jin-Qing Liu, 2020)
CD200R1 Related Diseases
CD200R1 protein plays an important role in immune regulation, and the abnormal function of CD200R1 may lead to the overactivation of immune cells and the dysregulation of immune response, resulting in autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Abnormal expression of CD200R1 protein may affect the body's immune response to pathogens, leading to uncontrolled inflammatory response and even increasing the risk of infection. It is also associated with the occurrence and development of some tumors and neurological diseases.
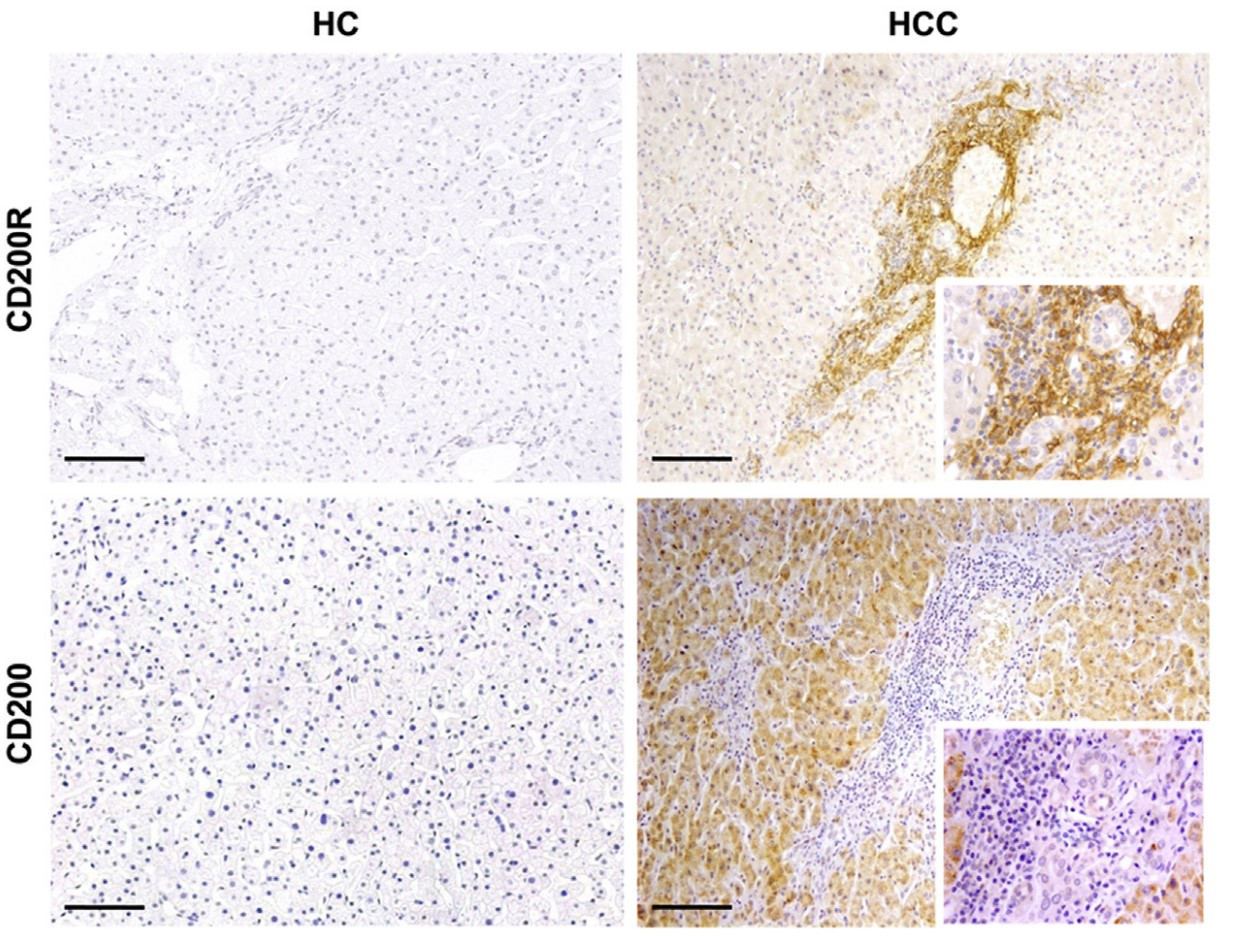
Fig2. CD200R and CD200 were positively correlated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients.
Bioapplications of CD200R1
The CD200R1 protein is also used in diagnosis. For example, in the diagnosis of breast cancer, the expression level of CD200R1 protein can be used as an important indicator to judge the malignancy and prognosis of the tumor. This diagnostic method has been widely used in clinical practice. The development of drugs to target it is also under way.
Case Study
Case study 1:Xiao-Guang Luo, 2010
Microglia are the representative myeloid cells in the brain, and their over-activation plays an important role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD). Microglia activation is believed to be regulated by the CD200-CD200R signaling. As the peripheral counterpart of microglia, monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs) share the same progenitor and antigen markers, and they have similar biological behaviors and mirror microglial function in the brain.
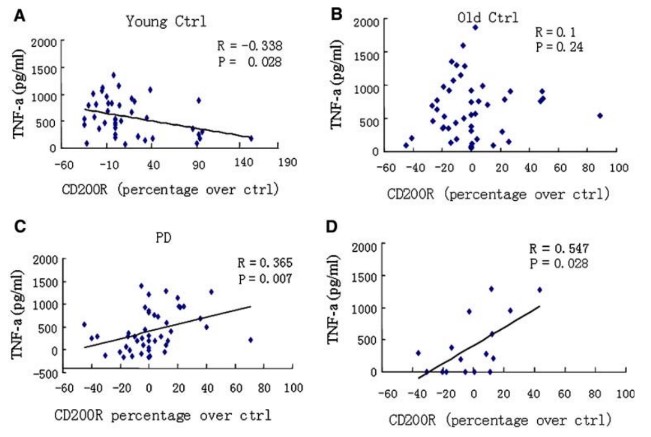
Here, the team studied CD200R expression and its regulation in MDMs from 32 PD cases, 27 age-matched old controls, and 28 young controls. We found that the basal CD200R expression is similar in MDMs from young control, old control and PD patients. The study indicates that inducible CD200R expression correlated inversely with the onset age of PD and to tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) released from MDMs. These results suggest an intrinsic abnormality in the CD200-CD200R signaling in MDMs during aging and, especially, in PD.
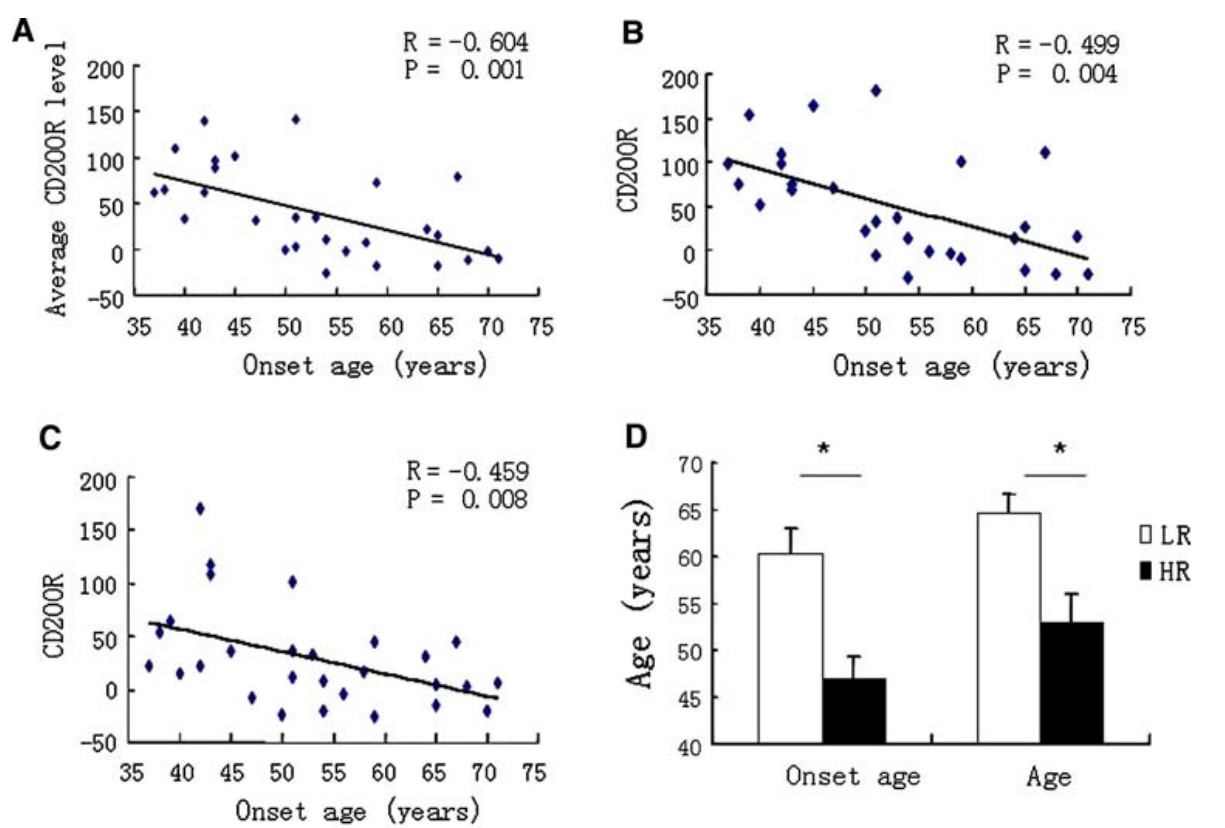
Fig1. Correlation between CD200R response and the onset ages of PD patients.
Case study 2: Seung-Phil Shin, 2021
CD200 is known as an immune checkpoint molecule that inhibits innate immune cell activation. Using a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) model, this team sought to determine whether localized delivery of adenovirus-expressing sCD200R1-Ig, the soluble extracellular domain of CD200R1, enhances antitumor immunity.
CD200 is known as an immune checkpoint molecule that inhibits innate immune cell activation. Using a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) model, we sought to determine whether localized delivery of adenovirus-expressing sCD200R1-Ig, the soluble extracellular domain of CD200R1, enhances antitumor immunity. Adenovirus-expressing sCD200R1-Ig (Ad5sCD200R1) was designed, and its effect was tested. CD200 induced M2-like polarization both in vitro and in vivo. These protumor effects of CD200 were driven through the β-catenin/NF-κB/M-CSF axis. Ad5sCD200R1 injection could be an effective targeted strategy to enhance antitumor immunoediting.
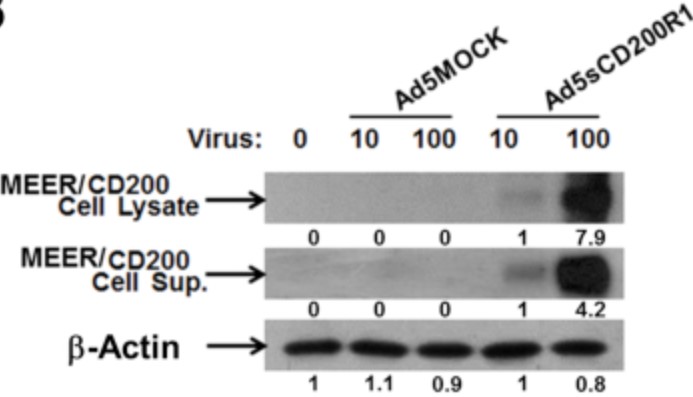
Fig3. MEER/CD200High cells were infected at MOIs of 10 and 100 for 2 h to confirm the secretion of soluble sCD200R1-Ig (sCD200R1-Ig) into the culture medium.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
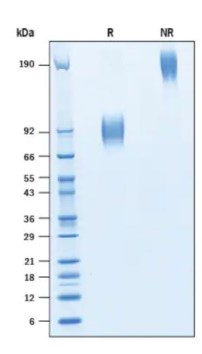
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD200R1-051H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
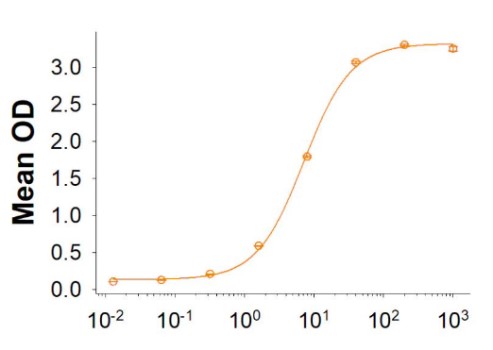
Fig2. Activity Data. (CD200R1-051H)
Involved Pathway
CD200R1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CD200R1 participated on our site, such as Adaptive Immune System,Immune System,Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CD200R1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Immune System | ASB4,BTR16,RNF138,TRIM17,AGER,RAET1E,CFHL2,ASB13,IFIT3,EGR1 |
| Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell | LILRB3,LAIR2,SIGLEC6,SIGLEC11,LILRA2,CLEC2G,CD300LG,SIGLEC5,KLRB1B,LILRA1 |
| Adaptive Immune System | OSBPL1A,CD200R2,LILRA3,LILRA1,LILRB1,LRR1,CRTAM,THEM4,UBR2,UBE2L6 |
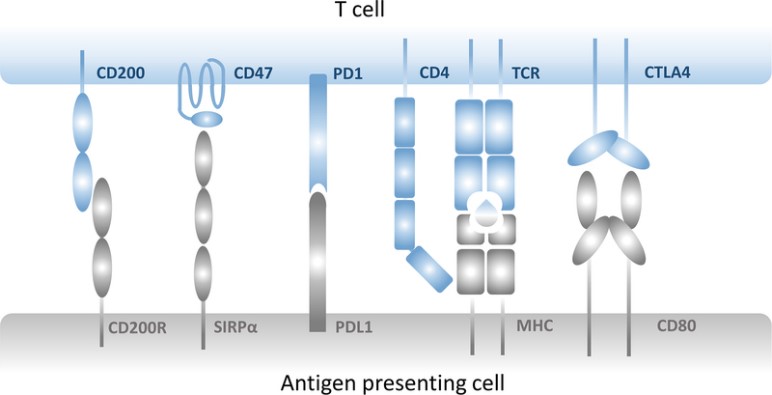
Fig2. CD200-CD200R axis is considered to be a pair of checkpoint molecules that regulate tumor-specific immune responses. (Jin-Qing Liu, 2020)
Protein Function
CD200R1 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CD200R1 itself. We selected most functions CD200R1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CD200R1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | S100A12,NUDT4,BASP1,CTDSP2,MT1F,LIMS1,KIAA0141,GFI1B,CALCA,PTPN4 |
Interacting Protein
CD200R1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CD200R1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CD200R1.
CD200
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Nicholls, SM; Copland, DA; et al. Local targeting of the CD200-CD200R axis does not promote corneal graft survival. EXPERIMENTAL EYE RESEARCH 130:1-8(2015).
- Gorczynski, R; Yu, K; et al. Anti-CD200R2, Anti-IL-9, Anti-IL-35, or Anti-TGF-A Abolishes Increased Graft Survival and Treg Induction Induced in Cromolyn- Treated CD200R1KO. CD200tg Mice. TRANSPLANTATION 97:39-46(2014).



