PDE6B
-
Official Full Name
phosphodiesterase 6B, cGMP-specific, rod, beta -
Overview
Photon absorption triggers a signaling cascade in rod photoreceptors that activates cGMP phosphodiesterase (PDE),;resulting in the rapid hydrolysis of cGMP, closure of cGMP-gated cation channels, and hyperpolarization of the cell.;PDE is a peripheral membrane heterotrimeric enzyme made up of alpha, beta, and gamma subunits. This gene encodes the;beta subunit. Mutations in this gene result in retinitis pigmentosa and autosomal dominant congenital stationary night;blindness. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
PDE6B;phosphodiesterase 6B, cGMP-specific, rod, beta;PDEB;rod cGMP-specific 3,5-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit beta;congenital stationary night blindness 3;autosomal dominant;CSNB3;rd1;RP40;GMP-PDE beta;rod cGMP-phosphodiesterase beta-subunit
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Sf9 Cells
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDE6B-1530H |
Active Recombinant Human PDE6B, GST-tagged
|
Sf9 Cells | Human | GST | Full length | |
| PDE6B-150H | Recombinant Human PDE6B protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 1-88 aa | |
| PDE6B-3295H | Recombinant Human PDE6B protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 198 - 428 aa | |
| PDE6B-12559M | Recombinant Mouse PDE6B Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| PDE6B-3346HCL | Recombinant Human PDE6B 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| PDE6B-151H | Recombinant Human PDE6B protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His |
|
|
| PDE6B-3296H | Recombinant Human PDE6B protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST |
|
|
| PDE6B-6588M | Recombinant Mouse PDE6B Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| PDE6B-6588M-B | Recombinant Mouse PDE6B Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is pde6b protein?
The PDE6B protein, part of the phosphodiesterase family of proteins, plays a crucial role in the phototransduction pathway in cells, contributing significantly to vision science on a cellular level. This protein is primarily created by the PDE6B gene, providing indispensable insight into multiple facets of cellular reproduction and function.
The PDE6B protein was discovered while professionals were looking into genetic causes of certain types of blindness. The connection between PDE6B and retinal degeneration sparked interest in understanding more about the protein and its function, opening new avenues for research. With increased attention to the protein and the gene that encodes it, scientists have successfully managed to gain a comprehensive background of the protein's structure and mechanism of action.
The PDE6B gene, which encodes the PDE6B protein, is located on the human chromosome 4, locus 4p16.3. The protein structure of PDE6B, as predicted from its genetic composition, appears to be relatively complex. It features multiple domains including a phosphorylation domain, a GAF domain, and a catalytic domain. The GAF domain stands out as it has a cyclic GMP (cGMP) binding site, indicating the protein's ability to bind cGMP, an essential messenger molecule in the phototransduction pathway.
What are the functions of PDE6B protein?
The principal function of the PDE6B protein is to act as a catalyst in the breakdown of cGMP in the eye's photoreceptor cells. Photoreceptor cells, particularly rods, contain a significant concentration of the PDE6B protein, critical in the vision process. The PDE6B protein acts by catalyzing the hydrolysis of cGMP to 5' GMP, ultimately lowering the intracellular concentration of cGMP and causing the closure of cGMP-gated ion channels. This results in hyperpolarization and subsequent signal generation that allows the vision process to proceed.
PDE6B Protein Related Signal Pathway
From a signaling perspective, PDE6B plays a vital role in the phototransduction pathway - the process by which light is converted into electrical signals within the rod cells of the retina. Upon absorbing light, the photoreceptor pigment, rhodopsin, gets activated. Activated rhodopsin, in turn, activates the enzyme transducin. It then stimulates PDE6B, which hydrolyzes intracellular cGMP, closing cGMP-gated channels. This change in membrane potential generates an electrical signal transmitted through the optic nerve to the brain, facilitating the perception of vision.
PDE6B Protein Related Diseases
Mutations in the PDE6B gene and, subsequently, the protein can lead to several ocular diseases, most notably retinitis pigmentosa (RP). RP is a type of inherited retinal degeneration that leads to progressive vision loss due to the rod photoreceptor cells' destruction. Additionally, PDE6B-related mutations have also been implicated in congenital stationary night blindness and certain types of Leber's congenital amaurosis.
PDE6B Protein's Applications
Understanding the function and structure of the PDE6B protein has several significant applications. Firstly, it has helped shape our understanding of the phototransduction cascade, leading to advancements in vision science. Identification of mutations in the PDE6B gene linked to ocular diseases has enabled genetic testing for at-risk individuals and families, leading to early intervention and potential treatments.
In terms of therapeutic interventions, the PDE6B protein has been a target of interest. Gene therapy aiming to restore normal PDE6B function in affected individuals is one area of active research. For instance, viral vectors are engineered to deliver a normal copy of the PDE6B gene to photoreceptor cells, allowing the production of functional protein and potentially slowing or halting disease progression.
Case Study
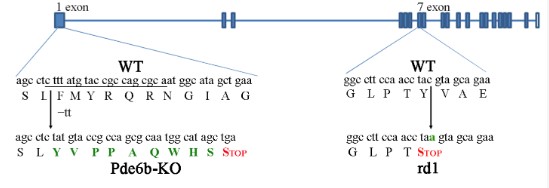
(Angelina V. Chirinskaite, 2023)
Fig2. the positions of mutations in rd1 and Pde6b-KO mice; the sequence of sgRNA spacer is underlined, and amino acid substitution and nucleotide substitutions are shown in green.
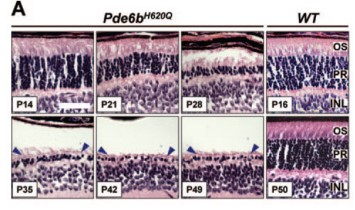
(Richard J. Davis, 2008)
Fig3.H&E-stained paraffin-embedded sections of Pde6bH620Q mutant (P14 –P49) and wildtype control (P16 and P50) mice. Shown are the outer segments (OS) photorecep-tors (PR) and inner nuclear layer (INL). Blue arrowheads: mutant photoreceptor layer after P35.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
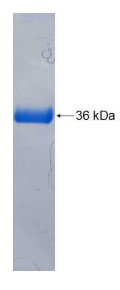
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (Cat. No.: PDE6B-150H)
Involved Pathway
PDE6B involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PDE6B participated on our site, such as Purine metabolism,Phototransduction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PDE6B were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Phototransduction | GUCY2E,CALM3,CALML3,GNB1,GRK7,CALM3B,PDE6A,GRK1A,CALM4,RLN1 |
| Purine metabolism | ADKB,URAD,AK1,PAPSS1,NME2B.2,PNP5A,AK3,POLR2I,POLR3D,NT5C1A |
Protein Function
PDE6B has several biochemical functions, for example, 3,5-cyclic-GMP phosphodiesterase activity,metal ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PDE6B itself. We selected most functions PDE6B had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PDE6B. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| metal ion binding | GNAI2,TGM1,NRXN3A,SRSF7A,ZNF41,SPNA1,TRIM35,CSH2,Car9,DRL |
| 3,5-cyclic-GMP phosphodiesterase activity | PDE10A,PDE11A,PDE6G,PDE6H,PDE6A,PDE9A,PDE6C,PDE5A |
Interacting Protein
PDE6B has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PDE6B here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PDE6B.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



