ROCK1
-
Official Full Name
Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 -
Overview
ROCK-1, a 160 kDa small-GTP-effector protein, is a serine/threonine kinase involved in the induction of focal adhesions and stress fibers, and can play a major role in vascular smooth muscle contraction, malignant cell transformation, tumor invasion and m -
Synonyms
ROCK1;Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1;rho-associated protein kinase 1;p160ROCK;p160-ROCK;Rho kinase;p160 ROCK-1;renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-35;rho-associated, coiled-coil-containing protein kinase 1;rho-associated, coil
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Insect Cells
- HEK293
- His
- GST
- Flag
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
Background
 in cardiac remodeling.jpg)
Fig1. Role of Rho-associated coiled-coil containing kinases (ROCKs) in cardiac remodeling. (Toru Shimizu, 2016)
What is ROCK1 protein?
ROCK1 (Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 18 at locus 18q11. This gene encodes a protein serine/threonine kinase that is activated when bound to the GTP-bound form of Rho. The small GTPase Rho regulates formation of focal adhesions and stress fibers of fibroblasts, as well as adhesion and aggregation of platelets and lymphocytes by shuttling between the inactive GDP-bound form and the active GTP-bound form. Rho is also essential in cytokinesis and plays a role in transcriptional activation by serum response factor. This protein, a downstream effector of Rho, phosphorylates and activates LIM kinase, which in turn, phosphorylates cofilin, inhibiting its actin-depolymerizing activity. The ROCK1 protein is consisted of 1354 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 158.2 kDa.
What is the function of ROCK1 protein?
ROCK1 is involved in regulating the dynamic recombination of the cytoskeleton by phosphorylating a variety of substrates, such as actin-binding proteins, affecting cell morphology and movement. ROCK1 plays a key role in regulating cell migration and invasion, which is critical for physiological and pathological processes such as embryonic development, wound healing, and tumor metastasis. ROCK1 is involved in the regulation of angiogenesis and affects the proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells. ROCK1 plays a role in the nervous system and is involved in learning and memory processes; ROCK1 is also involved in the regulation of metabolic processes such as glycogen synthesis and lipolysis.
ROCK1 Related Signaling Pathway
Rho/ROCK signaling pathway: ROCK1 directly binds to Rho family GTP enzymes such as RhoA, which can phosphorylate a variety of substrates after activation, affecting cytoskeletal recombination and cell motility.
MAPK/ERK signaling pathway: ROCK1 is involved in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation by interacting with the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family.
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway: ROCK1 interacts with phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K) and protein kinase B (AKT) to influence cell survival and apoptosis.
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway: ROCK1 is involved in the regulation of Wnt signaling pathway, influencing cell fate determination and tissue development.
ROCK1 Related Diseases
ROCK1 plays a role in the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and the formation of atherosclerosis, and is associated with cerebrovascular disease, coronary artery disease and hypertension. ROCK1 is involved in the regulation of cytoskeleton changes, affects insulin signaling, and is associated with metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Elevated levels of ROCK1 have been observed in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), suggesting that it may play a role in the neurodegenerative disease. It is also closely related to fibrosis, autoimmune diseases and tumors.
Bioapplications of ROCK1
ROCK1 is a potential therapeutic target for a variety of diseases, and a variety of small molecule inhibitors are being developed for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, metabolic diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer, among others. ROCK1 inhibitors such as fasudil have been used to treat certain conditions such as cerebral vasospasm, glaucoma, and chronic graft-versus-host disease.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Changpeng Hu, 2019
ROCK1 has been found to be overexpressed in several types of cancers. However, the role of ROCK1 in non‑small‑cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is poorly understood. In the present study, ROCK1 was found to be overexpressed in NSCLC cells and tissues, and it was associated with poor survival of NSCLC patients. Subsequently, ROCK1 knockdown NSCLC cell lines were established using shRNA. ROCK1 knockdown significantly reduced the migration and invasion ability in the cell monolayer scratching and Transwell assays. ROCK1 knockdown was also found to markedly inhibit cell adhesion ability. Moreover, the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) was inhibited by ROCK1 knockdown, reducing NSCLC cell migration and invasion ability. This mechanistic study revealed that ROCK1 significantly enhanced cell migration and invasion by inhibiting the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)/phosphoinositide 3‑kinase (PI3K)/FAK pathway. More importantly, the interruption of the PTEN/PI3K/FAK pathway markedly rescued the inhibition of cell migration and invasion mediated by ROCK1 knockdown.
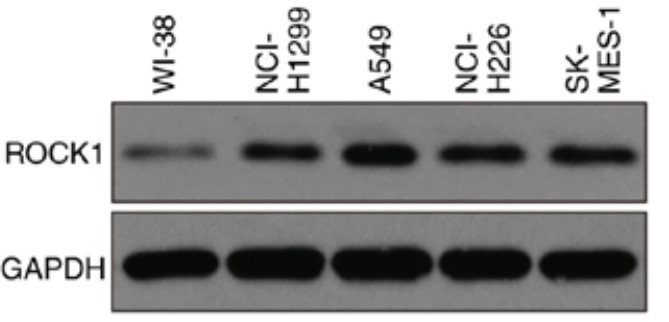
Fig1. The expression level of ROCK1 was detected by western blotting in NSCLC cell lines.
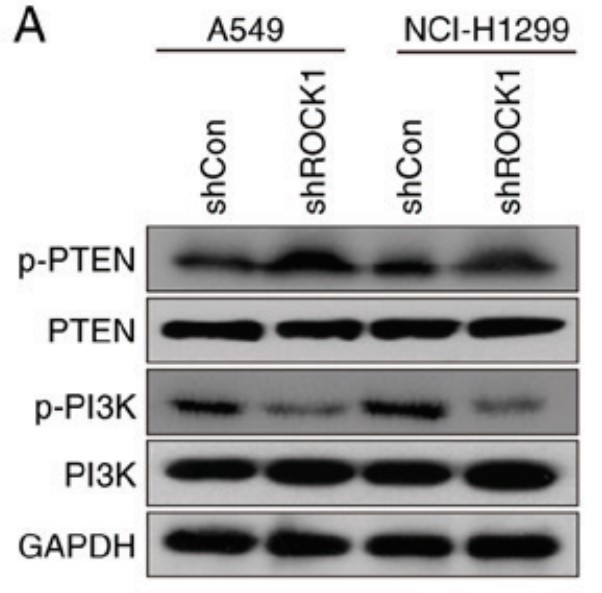
Fig2. Following transfection with ROCK1 shRNA, the expression levels of p-PTEN/PTEN and p-PI3K/PI3K were analyzed by western blotting in A549 and NCI-H1299 cells.
Case Study 2: Yong-Bo Hu, 2019
Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase 1 (ROCK1) is proposed to be implicated in Aβ suppression; however, the role for ROCK1 in amyloidogenic metabolism of amyloid precursor protein (APP) to produce Aβ was unknown. In the present study, the researchers showed that ROCK1 kinase activity and its APP binding were enhanced in AD brain, resulting in increased β-secretase cleavage of APP. Furthermore, they firstly confirmed that APP served as a substrate for ROCK1 and its major phosphorylation site was located at Ser655. The increased level of APP Ser655 phosphorylation was observed in the brain of APP/PS1 mice and AD patients compared to controls. Moreover, blockade of APP Ser655 phosphorylation, or inhibition of ROCK1 activity with either shRNA knockdown or Y-27632, ameliorated amyloid pathology and improved learning and memory in APP/PS1 mice.
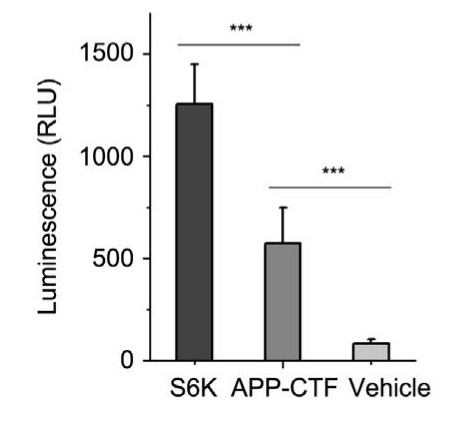
Fig3. ROCK1 activity assay when recombinant ROCK1 protein was incubated with S6K, APP-CTF, and vehicle.
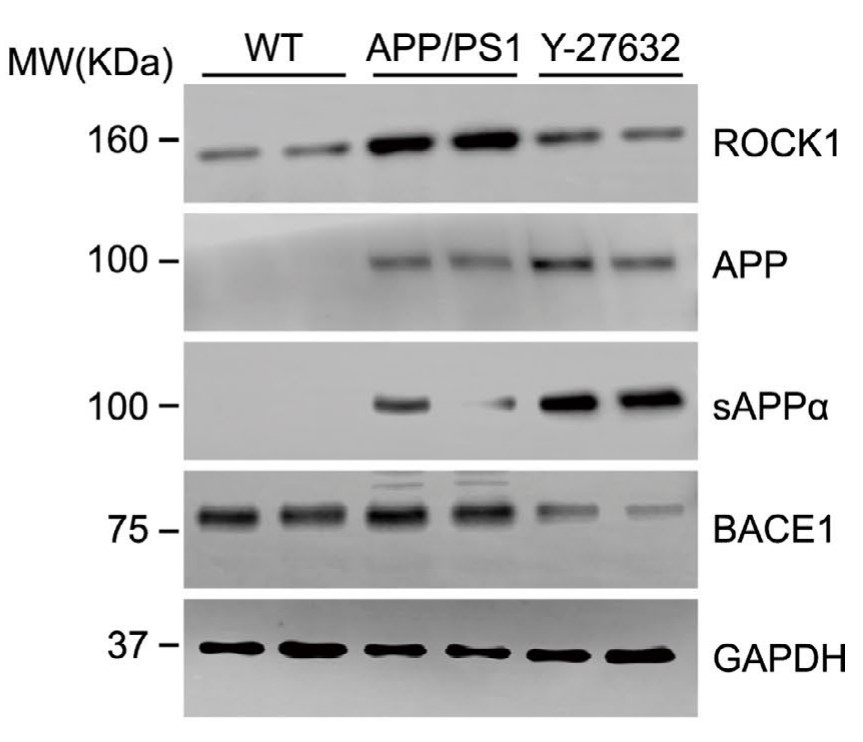
Fig4. ROCK1, APP, sAPPα, and BACE1 in mouse brain homogenates were analyzed by Western blot.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
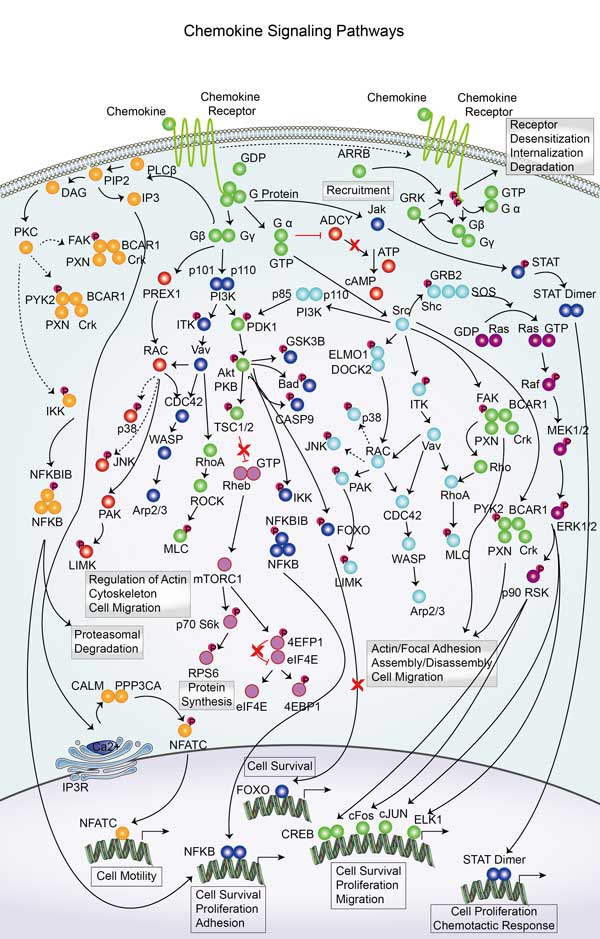
ROCK1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ROCK1 participated on our site, such as cGMP-PKG signaling pathway,cAMP signaling pathway,Chemokine signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ROCK1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | VAV2,PRKCA,CXCL12,ACTN3,PTK2,ACTB,ITGB2,CLDN23,PIK3CB,TXK |
| Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection | NCL,RHOA,FYN,TUBB2B,NCK1,CTTN,TUBA4A,ACTG1,WAS,CDH1 |
| Shigellosis | U2AF1,ABL1,MAPK11,ITGB1,MAD2L2,CDC42,MAPK13,PFN4,IKBKB,RHOG |
| Platelet activation | GNAQ,GP6,MAPK12,GNAS,ITGB1,MAPK3,MYL12B,TBXAS1,F2R,PLA2G4A |
| Focal adhesion | PTENB,ACTN3,SHC1,COL6A3,PPP1CA,VEGFA,BAD,IGF1,ITGA8,MYL2B |
| Oxytocin signaling pathway | RHOA,CAMK2D,CAMK4,PRKAG3,PTGS2,EEF2K,MYL6B,PLCB3,NFATC1,ELK1 |
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | GNA11B,RHOAB,ADORA2AB,AGTR1A,PRKCBA,CALM1,PPP1R14AA,KCNMA1A,GNA13A,CALM3B |
| Pathways in cancer | WNT7B,AHA-1,IKBKB,PIK3R1,RASGRP3,VEGFB,BDKRB2,GNAI2,STK36,TGFBR1 |
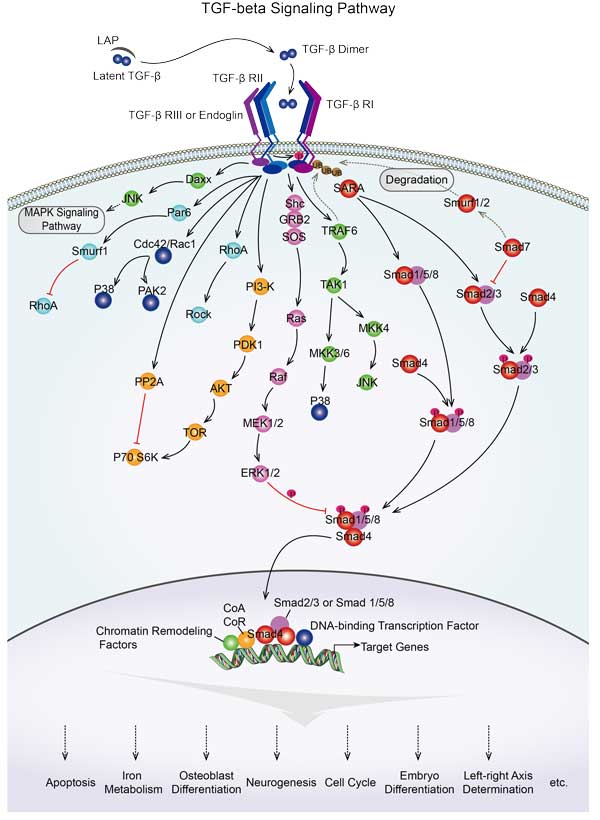
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | SMAD3A,NBL1,BMPR1AB,ID4,PPP2R1A,TGFB2,BMP5,ACVR2A,GDF6A,PITX2 |
Protein Function
ROCK1 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,GTP-Rho binding,metal ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ROCK1 itself. We selected most functions ROCK1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ROCK1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein kinase activity | DCLK1,NPR1,ACVR1L,MAP2K2A,EPHB4A,PDK3,CHEK1,FGFR1B,PDK1,PRPF4BB |
| GTP-Rho binding | CDC42EP2,RTKN2B,STXBP6L,CDC42EP1B,ROCK2A,EXOC1,TNFAIP1,PKN1,CDC42EP1,CDC42EP5 |
| ATP binding | KITB,PTK6B,PRKAA2,RBKS,KHK,HSPH1,CAMK2A,ATP1A1A.5,PIP4K2A,UCKL1 |
| protein binding | LSM10,FLOT2,VPS52,MRPS27,DNAJB1,TCF7L1A,PLSCR3,KPNA3,C5orf13,CASR |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | ULK1,ADCK1,AKT2L,RPS6KA2,LRRK1,MAP3K4,PAK2,DSTYK,TAOK2,PLK4 |
| metal ion binding | NOS2A,ZNF562,SNAI1,PDE8B,ATP2A1L,PDE1B,KLF2A,MICALL2A,AARS,CMTM2A |
Interacting Protein
ROCK1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ROCK1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ROCK1.
RHOA;MAGEB4;LMO2;FAM124A;C6orf165;POLR3C;MYBPH
ROCK1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Ashley, N; Jones, M; et al. Rapidly derived colorectal cancer cultures recapitulate parental cancer characteristics and enable personalized therapeutic assays. JOURNAL OF PATHOLOGY 234:34-45(2014).
- Rentala, S; Chintala, R; et al. Atorvastatin inhibited Rho-associated kinase 1 (ROCK1) and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) mediated adhesion and differentiation of CD133(+)CD44(+) prostate cancer stem cells. BIOCHEMICAL AND BIOPHYSICAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 441:586-592(2013).


.jpg)
.jpg)