IL-1 Family
Creative BioMart IL-1 Family Product List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for CX3C Chemokines & Receptors Research
Creative BioMart offers researchers a wide variety of products concerning CC chemokines and receptors, ranging from recombinant proteins and magnetic protein beads to cells, tissues, chromatography reagents, and others.
Our vast array of resources delves into various facets of CC chemokines and receptors, providing detailed perspectives on involved pathways, protein functions, related literature, specialized research domains, and vital subjects. These extensive resources empower researchers to explore the profound importance of these crucial biomolecules, facilitating a comprehensive comprehension of their pivotal functions.
Our Featured Products
| Class | Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CX3C Chemokines | CX3CL1-86H | Recombinant Human CX3CL1 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CX3CL1-11712H | Recombinant Human CX3CL1, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST | |
| CX3CL1-4319B | Recombinant Bovine CX3CL1 Protein | Bovine | Yeast | N/A |
About CX3C Chemokines & Receptors
CX3C chemokines and their receptors form a unique subgroup within the chemokine family. The CX3C motif refers to the presence of two cysteine residues separated by three amino acids (X3C) near the amino terminus of the chemokine. The sole member of this subgroup is CX3CL1, also known as fractalkine, while its receptor is called CX3CR1.
CX3CL1 is a transmembrane protein that can exist in two forms: a membrane-bound form and a soluble form. It is expressed by various cell types, including endothelial cells, neurons, epithelial cells, and immune cells such as monocytes and macrophages. CX3CR1, on the other hand, is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) predominantly expressed on immune cells, particularly monocytes, macrophages, and natural killer (NK) cells.
The CX3CL1-CX3CR1 axis is unique among chemokine systems due to several distinctive features. Firstly, CX3CL1 acts as both a chemoattractant and an adhesion molecule. It can mediate the firm adhesion of immune cells to endothelial cells, as well as induce chemotaxis and migration of CX3CR1-expressing immune cells. This dual function allows CX3CL1 to play a role in selective immune cell recruitment and trafficking.
Secondly, CX3CL1 is notable for its transmembrane structure, with the chemokine domain located on the extracellular portion. The soluble form of CX3CL1 can be generated through proteolytic cleavage at the cell surface. This soluble form can act as a chemotactic factor and modulate immune responses independently of cell adhesion.
The CX3CL1-CX3CR1 axis is involved in various physiological and pathological processes. It contributes to immune cell trafficking and adhesion, regulating immune responses and inflammation. Additionally, CX3CL1 has been implicated in neuronal development, synaptic communication, and neuroinflammatory disorders. Dysregulation of CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 has been associated with conditions such as atherosclerosis, neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and autoimmune disorders.
Research on CX3C chemokines and their receptors has provided valuable insights into their roles in immune responses, inflammation, and disease pathogenesis. The unique properties of CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 have led to investigations into their potential as therapeutic targets for modulating immune cell functions, reducing inflammation, and treating various diseases.
In summary, CX3C chemokines, represented by CX3CL1, and their receptor CX3CR1 form a distinct chemokine system characterized by unique functions and features. The CX3CL1-CX3CR1 axis plays important roles in immune cell trafficking, adhesion, and modulation of immune responses. Understanding the biology of CX3C chemokines and receptors has implications for various physiological processes and disease conditions.
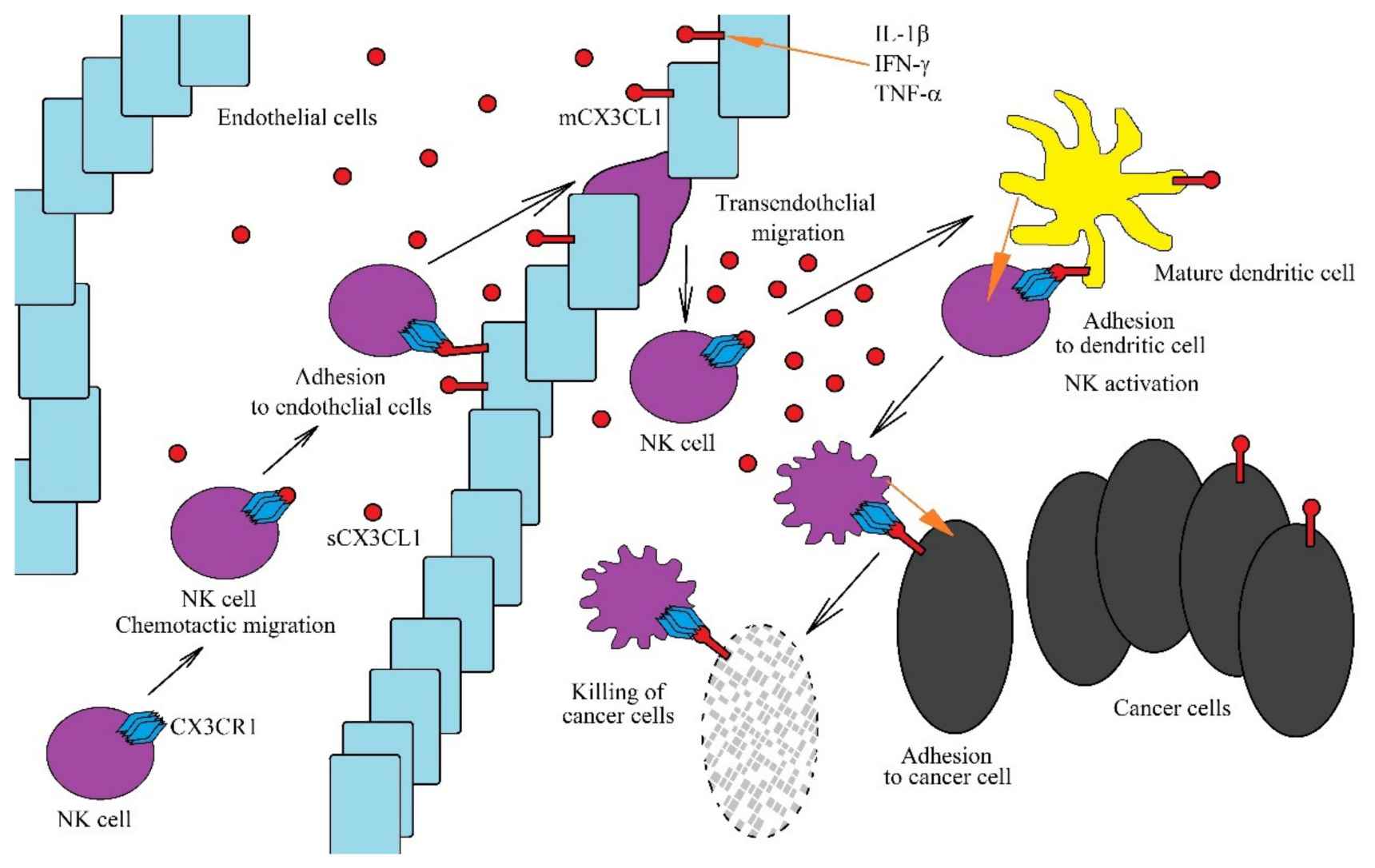 Fig.1 Role of the CX3CL1-CX3CR1 axis in anti-cancer NK cells functions. (Korbecki J, et al., 2020)
Fig.1 Role of the CX3CL1-CX3CR1 axis in anti-cancer NK cells functions. (Korbecki J, et al., 2020)
Signaling of CX3C Chemokines & Receptors
The signaling of CX3C chemokines, particularly CX3CL1 (fractalkine), and their receptor CX3CR1 involves a series of intracellular events upon ligand-receptor interaction. Here is an overview of the signaling pathway activated by CX3CL1-CX3CR1 interaction:
- Ligand Binding: CX3CL1, either in its soluble form or membrane-bound form, interacts with CX3CR1 on the target cell surface. This binding triggers the initiation of downstream signaling events.
- G Protein Activation: CX3CR1 is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), and upon ligand binding, it undergoes a conformational change that allows it to activate G proteins. Specifically, CX3CR1 couples with Gαi-type G proteins.
- G Protein-Mediated Signaling: Activated Gαi dissociates from the receptor and interacts with downstream effectors. The Gαi subunit inhibits adenylyl cyclase, leading to decreased levels of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). This reduction in cAMP levels affects various intracellular signaling pathways.
- β-Arrestin Recruitment: In addition to G protein activation, CX3CR1 can recruit β-arrestin molecules upon ligand binding. β-arrestins play a role in receptor internalization, desensitization, and can also initiate distinct signaling pathways.
- Downstream Signaling: The activation of CX3CR1 and recruitment of β-arrestins trigger intracellular signaling cascades, which can involve multiple pathways such as mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway, and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway. These pathways regulate gene expression, cell survival, migration, and other cellular responses.
- Cellular Responses: The signaling events initiated by CX3CL1-CX3CR1 interaction lead to various cellular responses depending on the cell type and context. These responses include chemotaxis, cell adhesion, modulation of immune cell functions, cytokine production, and regulation of inflammatory processes.
It is important to note that the exact signaling mechanisms and downstream effects of CX3CL1-CX3CR1 signaling can vary depending on the cell type, cellular context, and the presence of other signaling molecules or receptors. The signaling pathways activated by CX3CL1-CX3CR1 interaction are still an active area of research, and further studies are needed to fully elucidate the intricacies of this signaling axis.
In summary, CX3CL1 binding to CX3CR1 triggers G protein-mediated signaling, recruitment of β-arrestins, and activation of downstream signaling pathways such as MAPK, PI3K/Akt, and NF-κB. These signaling events regulate various cellular responses and play a role in immune cell functions, inflammation, and other physiological processes.
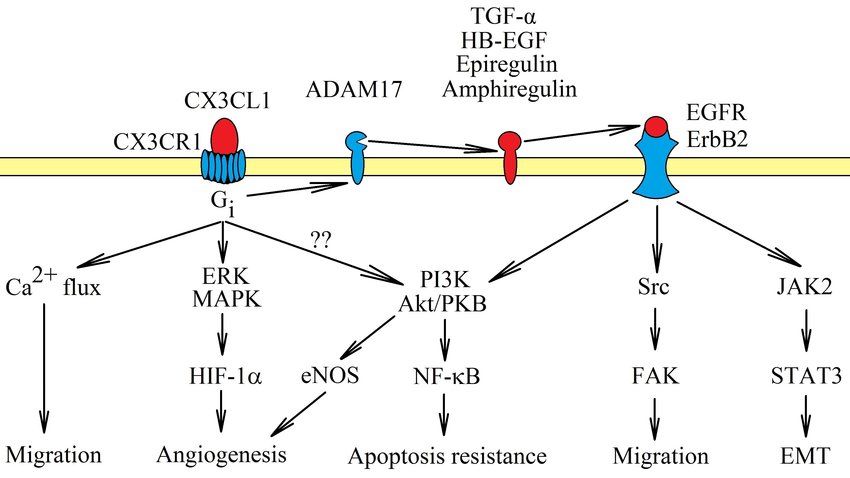 Fig.2 Signal transduction from CX3C chemokine receptor 1 (CX3CR1). (Korbecki J, et al., 2020)
Fig.2 Signal transduction from CX3C chemokine receptor 1 (CX3CR1). (Korbecki J, et al., 2020)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Korbecki J, Simińska D, Kojder K, et al. Fractalkine/CX3CL1 in Neoplastic Processes. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3723.
- Ferretti E, Pistoia V, Corcione A. Role of fractalkine/CX3CL1 and its receptor in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and malignant diseases with emphasis on B cell malignancies. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:480941.
- Gao XW, Hu HL, Xie MH, Tang CX, Ou J, Lu ZH. CX3CL1/CX3CR1 axis alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in human nucleus pulpous cells via M2 macrophage polarization. Exp Ther Med. 2023;26(1):359.

