IL-1 Family Ligands
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for IL-1 Family Ligands Research
Creative BioMart is pleased to offer a diverse array of products related to the IL-1 family ligands. Our selection includes recombinant proteins, magnetic beads pre-coupled with proteins, and cell and tissue lysates, providing researchers with the essential tools for their investigations. Our customizable services are tailored to meet your specific needs, ensuring that you receive the most suitable product for your research.
In addition to our extensive product line, we provide a wealth of information on IL-1 family ligands. Our resources cover a range of topics such as pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, and research areas. These resources are invaluable references that enable researchers to deepen their understanding of IL-1 family ligands and their importance in physiological processes. By offering both products and knowledge, we are dedicated to supporting researchers and contributing to advancements in this area of study.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL18-1941H | Recombinant Human IL18, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| IL18BP-14162H | Recombinant Human IL18BP, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| IL1A-01H | Recombinant Human IL1A protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| IL1B-02H | Recombinant Human IL1B protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| IL1F10-14168H | Recombinant Human IL1F10, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| IL1RA-3697H | Recombinant Human IL1RA protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| Il1f6-382M | Recombinant Mouse Il1f6, None tagged | Mouse | E.coli | N/A |
| IL1F8-14172H | Recombinant Human IL1F8, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| IL1F9-14173H | Recombinant Human IL1F9, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| IL1F5-14169H | Recombinant Human IL1F5, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| IL1F7-14171H | Recombinant Human IL1F7, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
About IL-1 Family Ligands
The IL-1 (Interleukin-1) family of ligands encompasses a group of cytokines that play critical roles in regulating immune responses, inflammation, and various physiological processes. These ligands are produced by different cell types, including immune cells, and they exert their effects by binding to specific receptors on target cells. The IL-1 family ligands are characterized by their structural similarities and functional overlap, contributing to their diverse roles in immune regulation and disease pathogenesis.
The IL-1 family includes several members, with IL-1α, IL-1β, and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) being the most well-known ligands. Other members of the IL-1 family include IL-18, IL-33, IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ, IL-36 receptor antagonist (IL-36Ra), IL-37, and IL-38. Each ligand binds to specific receptors, initiating intracellular signaling cascades that modulate immune cell activation, tissue repair, and inflammatory processes.
- IL-1α and IL-1β are pro-inflammatory cytokines that are produced during infections, tissue injury, and inflammatory diseases. They bind to the IL-1 receptor type 1 (IL-1R1), activating signaling pathways that induce the production of other inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules. IL-1Ra, on the other hand, acts as a competitive antagonist by binding to IL-1R1 without activating downstream signaling, thus dampening the pro-inflammatory effects of IL-1α and IL-1β.
- IL-18 is another pro-inflammatory cytokine that plays a role in immune regulation. It binds to the IL-18 receptor, triggering signaling pathways that promote the production of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and other inflammatory molecules. IL-33 acts as an alarmin, released by damaged or stressed cells, and binds to the IL-33 receptor (IL-1RL1), activating immune cells such as mast cells, eosinophils, and T helper 2 (Th2) cells.
- The IL-36 family members (IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ) and IL-36Ra are involved in skin inflammation and immune responses. IL-36 ligands bind to the IL-36 receptor (IL-36R), initiating signaling pathways that promote the recruitment and activation of immune cells in the skin. IL-36Ra acts as an antagonist, preventing excessive IL-36 signaling and controlling inflammation.
- IL-37 and IL-38 are anti-inflammatory cytokines that suppress immune responses. They bind to IL-18 receptor accessory protein (IL-18RAP) and IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP), respectively, and modulate inflammatory signaling pathways, leading to the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine production and immune cell activation.
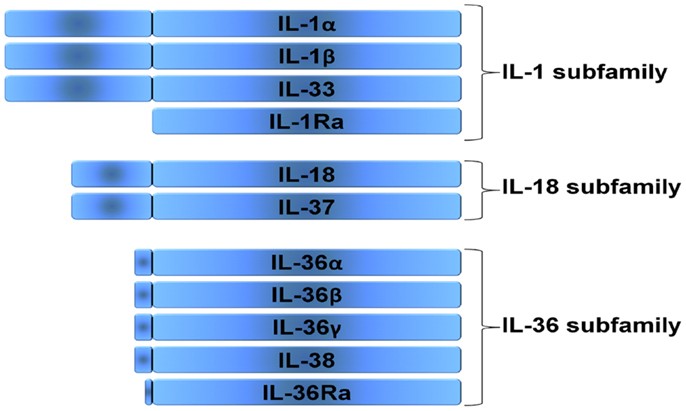 Fig.1 The IL-1 family is divided into three subfamilies based on the length of its predecessor. (van de Veerdonk FL, et al., 2013)
Fig.1 The IL-1 family is divided into three subfamilies based on the length of its predecessor. (van de Veerdonk FL, et al., 2013)
Three families can be distinguished in the IL-1 family, the IL-1 subfamily, the IL-18 subfamily, and the IL-36 subfamily. The IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) cannot be categorized in these subfamilies, since it has a signal peptide and is readily secreted.
Role of IL-1 Family Ligands in the Immune System
IL-1 family ligands play crucial roles in the immune system, functioning as key mediators of immune responses and inflammation. They regulate various aspects of immune cell activation, differentiation, and communication. Here are some important roles of IL-1 family ligands in the immune system:
- Pro-inflammatory Cytokines: IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-18, and IL-33 are potent pro-inflammatory cytokines that promote immune cell activation and the production of other inflammatory mediators. They play critical roles in initiating and amplifying immune responses to infections, tissue damage, and other inflammatory stimuli.
- Immune Cell Activation: IL-1 family ligands activate various immune cells, including macrophages, dendritic cells, and lymphocytes. Upon binding to their respective receptors on target cells, IL-1 family ligands trigger intracellular signaling pathways, leading to the production of cytokines, chemokines, and other immune modulators.
- T Helper Cell Differentiation: IL-1 family members, particularly IL-1β and IL-18, influence the differentiation of CD4+ T helper cells into different subsets. IL-1β promotes the differentiation of Th17 cells, which are involved in inflammation and host defense against certain pathogens. IL-18 promotes the differentiation of Th1 cells, which drive cellular immune responses against intracellular pathogens.
- Innate Immune Responses: IL-1 family ligands are involved in the activation of the innate immune system. They enhance the antimicrobial functions of phagocytes, such as neutrophils and macrophages, and promote the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines that recruit immune cells to the site of infection or inflammation.
- Allergic and Type 2 Immune Responses: IL-1 family ligands, such as IL-33, play essential roles in type 2 immune responses associated with allergy, asthma, and parasitic infections. IL-33 is released by damaged cells and activates immune cells, including mast cells, eosinophils, and type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s), contributing to the initiation and amplification of allergic inflammation.
- Regulation of Inflammation: IL-1 family ligands, along with their respective receptors and signaling pathways, are involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses. They interact with anti-inflammatory molecules, such as IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) and IL-36 receptor antagonist (IL-36Ra), to balance and control the intensity and duration of inflammation.
- Tissue Repair and Remodeling: Some IL-1 family ligands, including IL-33, have roles beyond inflammation. They contribute to tissue repair and remodeling processes, stimulating the activation of tissue-resident immune cells and promoting tissue healing.
Overall, IL-1 family ligands play diverse and critical roles in modulating immune responses. Their activities are tightly regulated to maintain immune homeostasis and prevent excessive inflammation. Dysregulation of IL-1 family signaling can contribute to the development of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, highlighting the importance of understanding their roles in the immune system for therapeutic interventions.
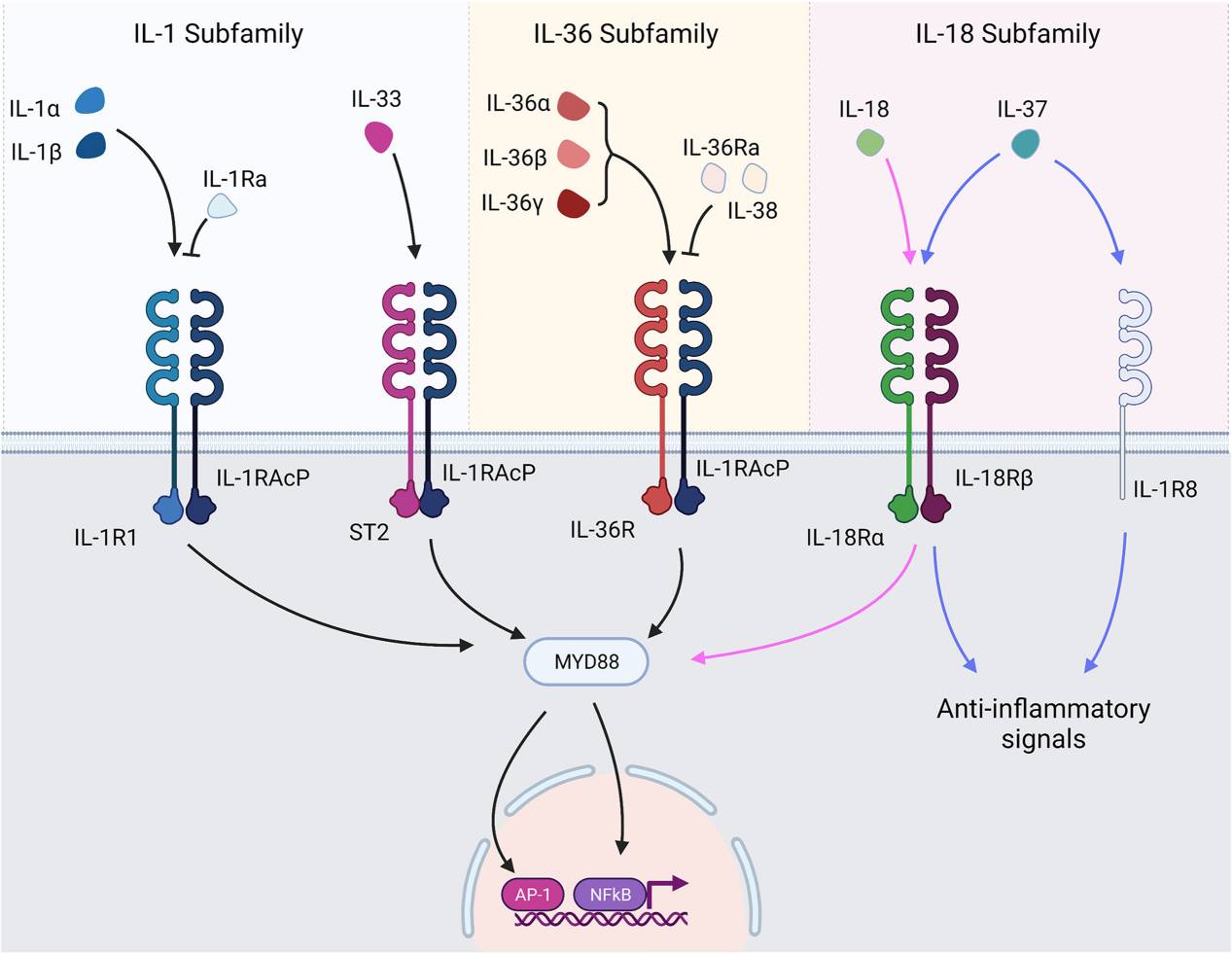 Fig.2 IL-1 superfamily cytokines and receptors. (Macleod T, et al., 2021)
Fig.2 IL-1 superfamily cytokines and receptors. (Macleod T, et al., 2021)
IL-1 family cytokines bind their respective receptors and transduce signals through TIR/MyD88 signalling pathways. The major signalling pathways result in activation of NF-κB and AP-1 and subsequent transcription of genes under their control. Receptor antagonists bind their respective receptors but prevent the recruitment of the accessory protein, thereby preventing signal transduction. IL-37 exerts anti-inflammatory signals following interaction with IL-1R8 and IL-18Rα.
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References:
- van de Veerdonk FL, Netea MG. New Insights in the Immunobiology of IL-1 Family Members. Front Immunol. 2013;4:167.
- Macleod T, Berekmeri A, Bridgewood C, Stacey M, McGonagle D, Wittmann M. The Immunological Impact of IL-1 Family Cytokines on the Epidermal Barrier. Front Immunol. 2021;12:808012.

