Interleukins & Receptors
Creative BioMart Interleukins & Receptors Product List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for the Study of TNF Superfamily
Creative BioMart is committed to supporting research on the TNF family. We continually update our portfolio and resources to provide researchers with tools and information about the TNF family (e.g., TNF ligands and TNF receptors).
- Our broad product portfolio includes recombinant proteins, etc., which play a key role in elucidating the functions and mechanisms of various players in the TNF family.
- We have a team of experienced experts with deep knowledge in the study of the TNF family, and we are committed to providing tailored solutions to meet the unique requirements of each researcher.
- In addition, we provide comprehensive resource support including involved pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, and other valuable information. Ultimately, our goal is to increase the impact of research efforts.
Our Featured Products
About TNF Superfamily
The TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor) family is a group of proteins involved in various physiological and pathological processes, primarily related to the immune system, inflammation, and cell survival. The family consists of two main types of proteins: TNF ligands and TNF receptors.
TNF Ligands
The TNF ligands are a group of proteins that bind to specific TNF receptors and initiate signaling cascades. These ligands are typically transmembrane proteins, but some can be released as soluble forms. They play crucial roles in regulating immune responses, inflammation, and cell survival. Some well-known TNF ligands include:
- TNF-alpha (TNF-α): Also known as cachectin, TNF-alpha is one of the most extensively studied members of the TNF family. It is mainly produced by immune cells, such as macrophages and T cells, and plays a central role in inflammation, immune modulation, and host defense against infections.
- TNF-beta (TNF-β): Also called lymphotoxin-alpha (LT-α), TNF-beta is another important ligand in the TNF family. It is primarily produced by activated T cells and can regulate immune responses and inflammation.
- Fas Ligand (FasL): Fas ligand is involved in the regulation of programmed cell death, or apoptosis. It binds to the Fas receptor (CD95) and triggers apoptosis in cells expressing this receptor.
- TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL): TRAIL can induce apoptosis in cancer cells while sparing normal cells. It has shown potential as a therapeutic agent for cancer treatment.
- CD40 Ligand (CD40L): CD40 ligand is involved in immune activation and the interaction between T cells and antigen-presenting cells. It plays a crucial role in the regulation of immune responses.
TNF Receptors
TNF receptors are cell surface receptors that bind to TNF ligands and transmit signals inside the cell, initiating various cellular responses. They are typically transmembrane proteins with cytoplasmic domains that interact with intracellular signaling molecules. Some important TNF receptors include:
- TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1): TNFR1 is the primary receptor for TNF-alpha and is widely expressed on various cell types. It plays a central role in inflammation, immune responses, and cell survival.
- TNF receptor 2 (TNFR2): TNFR2 also binds to TNF-alpha but has a more restricted expression pattern compared to TNFR1. It is involved in regulating immune cell activation, tissue regeneration, and immune tolerance.
- Fas receptor (CD95): Fas receptor is the receptor for Fas ligand (FasL). Binding of FasL to the Fas receptor triggers apoptotic signaling pathways, leading to programmed cell death.
- CD40 receptor: The CD40 receptor interacts with CD40L and is mainly expressed on immune cells. It plays a crucial role in immune activation, B cell maturation, and antibody production.
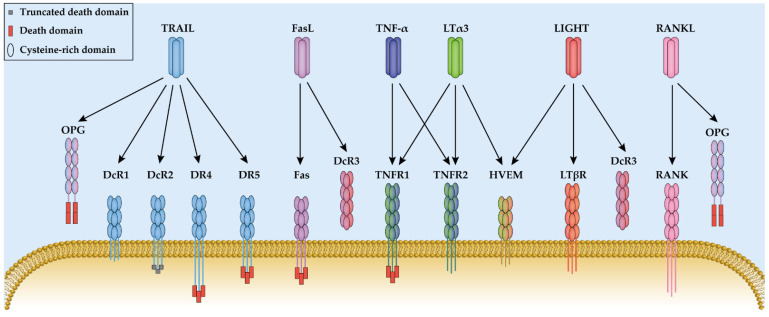 Fig.1 Interactions between multi-receptor TNF superfamily ligands (top) and their receptors (bottom). (Suo F, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Interactions between multi-receptor TNF superfamily ligands (top) and their receptors (bottom). (Suo F, et al., 2022)
Importance of the TNF Family in Disease
The TNF family and its members, including TNF ligands and TNF receptors, play significant roles in the pathogenesis of various diseases. Dysregulation of TNF family signaling has been implicated in several conditions, including autoimmune disorders, chronic inflammatory diseases, infectious diseases, and cancer. Here are some examples highlighting the importance of the TNF family in disease:
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Crohn's disease, and multiple sclerosis, involve an abnormal immune response against self-antigens. TNF-alpha, in particular, has been strongly associated with these conditions. Excessive production of TNF-alpha contributes to chronic inflammation, tissue damage, and joint destruction seen in rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune disorders. Therapies targeting TNF-alpha, such as TNF inhibitors, have revolutionized the treatment of these diseases.
Chronic Inflammatory Diseases
Chronic inflammatory conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are characterized by persistent inflammation. TNF-alpha and other TNF family members play a crucial role in driving and sustaining the inflammatory response in these conditions. TNF inhibitors have demonstrated efficacy in reducing inflammation, relieving symptoms, and improving quality of life in patients with IBD and COPD.
Infectious Diseases
TNF-alpha and other TNF family members are involved in the immune response against infectious agents. While TNF-alpha contributes to the defense against pathogens by activating immune cells and promoting inflammation, excessive production can lead to tissue damage and septic shock. In some cases, pathogens have evolved mechanisms to manipulate TNF signaling for their own benefit. For instance, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium causing tuberculosis, can inhibit TNF-alpha production to evade immune responses. Understanding the complex interactions between TNF family members and pathogens is crucial for developing strategies to combat infectious diseases.
Cancer
Dysregulation of TNF family signaling has been implicated in cancer development and progression. TNF-alpha can promote tumor growth and angiogenesis in some contexts. On the other hand, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and Fas ligand (FasL) have shown potential as therapeutic agents in selectively inducing apoptosis in cancer cells while sparing normal cells. Targeting TNF signaling pathways has been explored as a strategy for cancer therapy.
Other Diseases
The TNF family has also been implicated in other diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, and bone disorders. For example, TNF-alpha has been linked to neuroinflammation and neuronal cell death in conditions like Alzheimer's disease. TNF family members are involved in bone remodeling and can contribute to the pathogenesis of osteoporosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Understanding the role of the TNF family in disease pathogenesis has led to the development of targeted therapies, such as TNF inhibitors, which have significantly improved the management of several inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. Further research into the complex interactions and signaling pathways of the TNF family holds promise for the development of novel therapeutic approaches for various diseases.
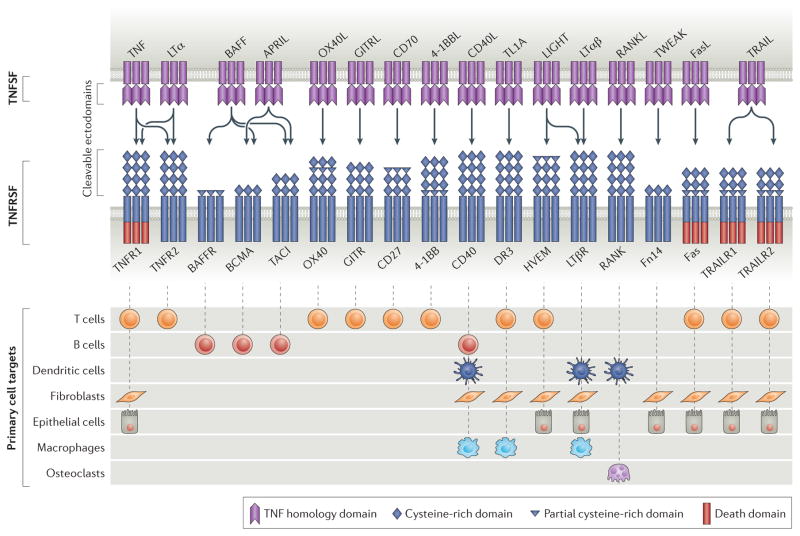 Fig.2 Select members of the TNF and TNFR superfamily implicated in rheumatic diseases. (Croft M, et al., 2017)
Fig.2 Select members of the TNF and TNFR superfamily implicated in rheumatic diseases. (Croft M, et al., 2017)
We are committed to helping you achieve your scientific goals and make meaningful contributions to research on the roles of the various components of the Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Superfamily and their role in disease. Contact us today to learn more about our products and resources.
References:
- Suo F, Zhou X, Setroikromo R, Quax WJ. Receptor Specificity Engineering of TNF Superfamily Ligands. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(1):181. Published 2022 Jan 13.
- MacEwan DJ. TNF ligands and receptors--a matter of life and death. Br J Pharmacol. 2002;135(4):855-875.
- Siegmund D, Wajant H. TNF and TNF receptors as therapeutic targets for rheumatic diseases and beyond. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023;19(9):576-591.
- Croft M, Siegel RM. Beyond TNF: TNF superfamily cytokines as targets for the treatment of rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(4):217-233.

