IL-17 Family
Creative BioMart IL-17 Family Product List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for CSF Research
Creative BioMart is your ultimate one-stop shop for all your research needs related to CSFs. Our extensive range of carefully developed products and customized services are designed to help you delve deep into the world of CSFs and their vital role in various physiological processes.
- Our product lines include top-quality recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, and others.
- We also offer a wealth of resources on CSFs, covering essential topics such as involved pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, related articles, and research areas.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSF1-565H | Active Recombinant Human CSF1 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CSF2-03H | Active Recombinant Human CSF2 protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| CSF2-4386F | Recombinant Feline CSF2 Protein | Feline | Yeast | N/A |
About Colony-Stimulating Factors (CSF)s
Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) are a group of glycoproteins that play a crucial role in regulating the production, proliferation, and differentiation of various types of blood cells in the bone marrow. They are part of the cytokine family and are primarily involved in hematopoiesis, the process by which new blood cells are formed.
CSFs are produced by various cells, including immune cells such as macrophages, monocytes, and fibroblasts. They act on hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and progenitor cells, which are responsible for generating different types of blood cells.
There are different types of CSFs, each acting on specific cell lineages:
- Granulocyte-CSF (G-CSF): G-CSF promotes the production and differentiation of granulocytes, specifically neutrophils, which are important in fighting bacterial infections. G-CSF is commonly used in clinical settings to stimulate the recovery of neutrophil counts after chemotherapy or stem cell transplantation.
- Granulocyte-Macrophage-CSF (GM-CSF): GM-CSF stimulates the production and maturation of both granulocytes and monocytes/macrophages. It also has the ability to enhance the function of these cells. GM-CSF is used therapeutically to boost immune responses in conditions such as neutropenia, myelodysplastic syndromes, and bone marrow transplantation.
- Macrophage-CSF (M-CSF): M-CSF is involved in the differentiation and survival of monocytes, promoting their maturation into tissue macrophages. It plays a role in tissue repair and inflammation, and aberrant M-CSF signaling has been associated with diseases such as arthritis and atherosclerosis.
- Erythropoietin (EPO): EPO is a CSF that primarily regulates the production of red blood cells (erythrocytes) by stimulating the differentiation and proliferation of erythroid progenitor cells. EPO is produced by the kidneys in response to low oxygen levels, and its synthetic versions have therapeutic applications in treating anemia, especially in patients with chronic kidney disease or undergoing chemotherapy.
CSFs exert their effects by binding to specific receptors on the surface of hematopoietic cells. These receptors initiate intracellular signaling pathways that lead to the activation of transcription factors and the regulation of gene expression, ultimately driving cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation.
Research on CSFs
Research on CSFs has been ongoing and has led to several advances in recent years. Here's an overview of some key areas of research and their implications:
- Discovery of novel CSFs: Scientists continue to discover and characterize new CSFs. For example, Interleukin-34 (IL-34) has been identified as a novel CSF that promotes the differentiation and survival of monocytes and macrophages. Its discovery has expanded our understanding of the regulation of myeloid cell populations and their roles in various diseases.
- Therapeutic applications: CSFs have been widely utilized in clinical settings for their therapeutic applications. For example, G-CSF and GM-CSF are commonly used to stimulate the production of white blood cells and aid in the recovery of neutrophil counts after chemotherapy or stem cell transplantation. Ongoing research aims to optimize CSF treatments, explore novel delivery methods, and investigate their potential in other conditions such as sepsis, autoimmune disorders, and chronic wounds.
- Cancer research: CSFs play complex roles in cancer development and progression. In some cases, aberrant expression and signaling of CSFs have been associated with tumor growth, angiogenesis, and immune evasion. For example, GM-CSF has been investigated as an adjuvant therapy in cancer vaccines, aiming to boost the immune response against tumor cells. Conversely, inhibiting CSF signaling has been explored as a potential therapeutic approach to hinder tumor-associated macrophages and inhibit cancer progression.
- Autoimmune disorders: Dysregulation of CSFs has been implicated in autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis. In these conditions, CSFs can contribute to the activation and recruitment of immune cells, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage. Targeting CSF signaling pathways is being explored as a potential therapeutic strategy to modulate immune responses and ameliorate autoimmune disease manifestations.
- Stem cell research: CSFs play a vital role in the regulation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and their differentiation into various blood cell lineages. Research efforts aim to better understand the molecular mechanisms underlying HSCs' self-renewal and differentiation and to identify factors that can enhance their expansion and engraftment in transplantation therapies.
- Combination therapies: Researchers are investigating the potential of combining CSFs with other therapeutic agents, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors or chemotherapy drugs, to enhance treatment outcomes. These combination approaches aim to modulate the immune response, improve the efficacy of existing therapies, and overcome resistance mechanisms.
Overall, research on CSFs continues to expand our understanding of hematopoiesis, immune regulation, and their implications in various diseases. Ongoing studies are focused on identifying novel CSFs, exploring their therapeutic potential, and elucidating the complex interactions between CSFs and immune cells in both physiological and pathological conditions.
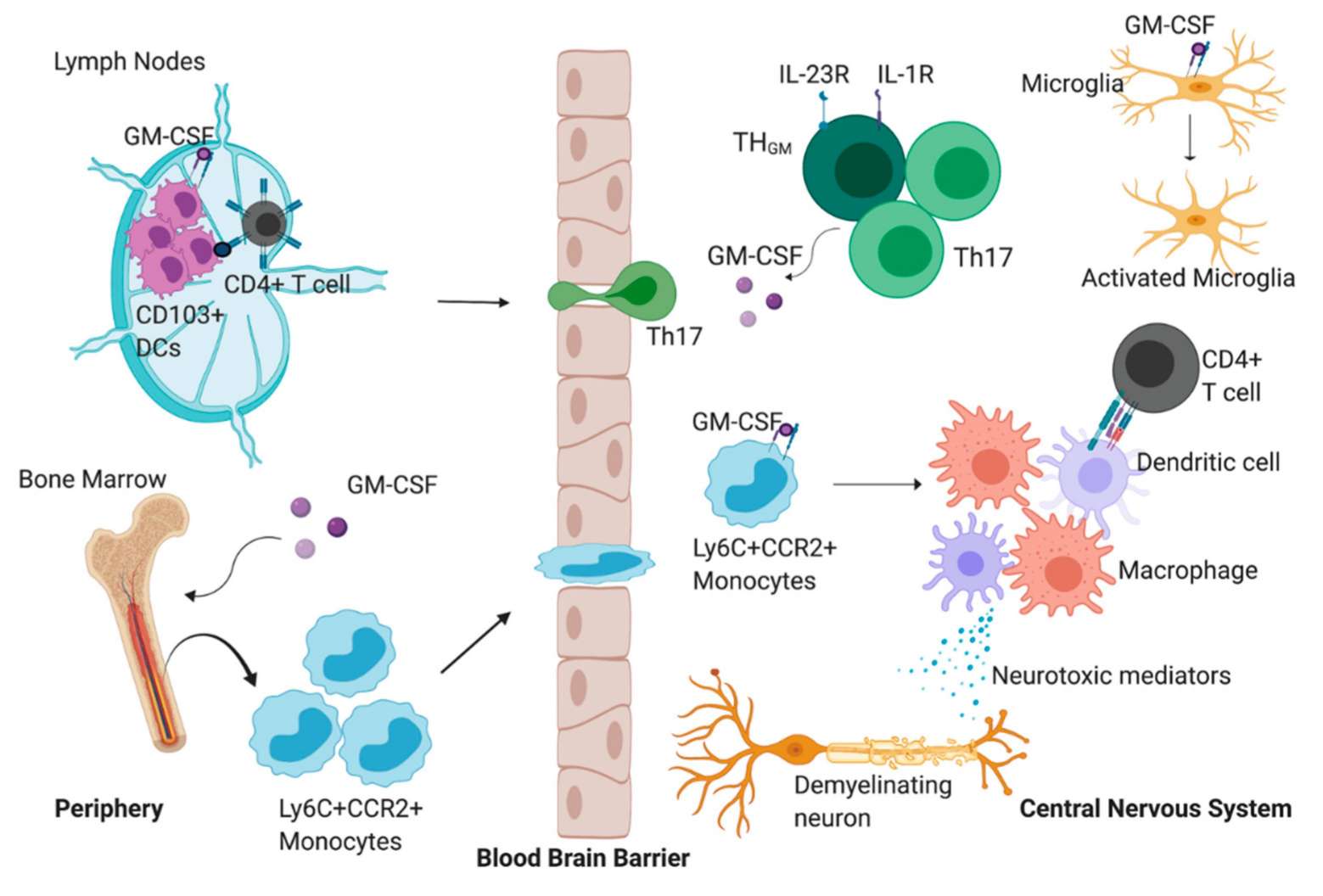 Fig.2 The proposed role of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). (Monaghan KL, et al., 2020)
Fig.2 The proposed role of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). (Monaghan KL, et al., 2020)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Monaghan KL, Wan ECK. The role of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in murine models of multiple sclerosis. Cells. 2020; 9(3):611.
- Park M, Vaikari V P, Dhandhukia J P, et al. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor fused to elastin-like polypeptides assembles biologically-active nanoparticles[J]. Bioconjugate chemistry, 2020, 31(5): 1551-1561.

