IL-17 Family Ligands
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for IL-17 Family Ligands Research
At Creative BioMart, we are dedicated to providing a wide range of products needed for IL-17 family ligand research. Our product line includes recombinant proteins, proteins conjugated to magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, and more.
In addition to our product line, we offer a vast array of resources on IL-17 family ligands covering multiple topics including pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related literature, and research areas. These resources are designed to enrich researchers' understanding of IL-17 family ligands and their importance in physiological processes.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL17A-26H | Recombinant Human Interleukin-17 | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| IL17A-12C | Active Recombinant Canine IL17A Protein, His-tagged | Canine | HEK293 | His |
| IL17C-14154H | Recombinant Human IL17C, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| IL17D-3185H | Recombinant Human IL17D protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| IL17F-377H | Active Recombinant Human IL17F protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| IL25-148H | Active Recombinant Human IL25 protein, hFc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | hFc |
About IL-17 Family Ligands
The IL-17 family of cytokines comprises a group of pro-inflammatory molecules that play critical roles in immune responses, inflammation, and host defense. These cytokines are primarily produced by T cells, particularly a subset known as Th17 cells, as well as other immune cells. The IL-17 family of ligands are IL-17A, IL-17B, IL-17C, IL-17D, IL-17E (IL-25), IL-17F. The IL-17 family ligands bind to five receptors: IL-17RA, IL-17RB/IL-25R, IL-17RC, IL-17RD/SEF, IL-17RE. The IL-17 family ligands are produced by T helper 17 (Th17) cells in response to IL-23 stimulation. They play an important role in fighting both intracellular and extracellular bacterial infections. The ligands act as proinflammatory mediators that can also synergize with other cytokines and interferons to increase the induction of proinflammatory responses from various target cells.
Interleukin-17A (IL-17A)
- IL-17A is the prototypical and most extensively studied member of the IL-17 family.
- It is produced by Th17 cells, γδ T cells, innate lymphoid cells, and some other immune cells.
- IL-17A acts on various cell types, including epithelial cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and immune cells.
- It promotes inflammation by inducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and antimicrobial peptides.
- IL-17A is involved in host defense against extracellular pathogens, particularly at mucosal surfaces.
Interleukin-17F (IL-17F)
- IL-17F is structurally similar to IL-17A and shares functional similarities with it.
- It is produced by Th17 cells, γδ T cells, and other immune cells.
- IL-17F acts on similar target cells as IL-17A and contributes to the induction of pro-inflammatory responses.
- It also plays a role in host defense against microbial pathogens, particularly at mucosal sites.
Interleukin-17B (IL-17B)
- IL-17B is produced by various immune cells, including Th17 cells, mast cells, and neutrophils.
- It acts on endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and immune cells, such as macrophages.
- IL-17B is involved in promoting inflammation and contributes to the recruitment of immune cells to sites of inflammation.
Interleukin-17C (IL-17C)
- IL-17C is produced by epithelial cells and some immune cells, including Th17 cells.
- It acts on epithelial cells and promotes the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
- IL-17C plays a role in the defense against bacterial and fungal infections at mucosal surfaces.
Interleukin-17D (IL-17D)
- IL-17D is produced by various immune cells, including Th17 cells and natural killer (NK) cells.
- It acts on fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and immune cells.
- IL-17D contributes to the induction of pro-inflammatory responses and may play a role in immune surveillance and tissue homeostasis.
Interleukin-17E (IL-17E, IL-25)
- IL-17E, also known as IL-25, was discovered through a bioinformatics search for proteins homologous to IL-17A. IL-17E derives from both hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells
- IL-17E is a pleiotropic cytokine, that acts on stromal, innate immune, and adaptive immune cells to orchestrate Th2-type inflammation.
- IL-17E can inhibit Th17 development through the induction of IL-13 by dendritic cells (DCs) and by inhibiting macrophage-derived IL-23 production.
The IL-17 family ligands exert their effects by binding to specific receptors on target cells, activating downstream signaling pathways, and inducing the production of inflammatory mediators. These cytokines are particularly important in the defense against microbial pathogens, regulation of inflammatory responses, and tissue repair processes. Dysregulation of IL-17 family cytokines has been implicated in various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Understanding the functions and mechanisms of IL-17 family ligands is essential for developing targeted therapies to modulate immune responses and treat related disorders.
Importance of IL-17 Family Ligands in the Immune System
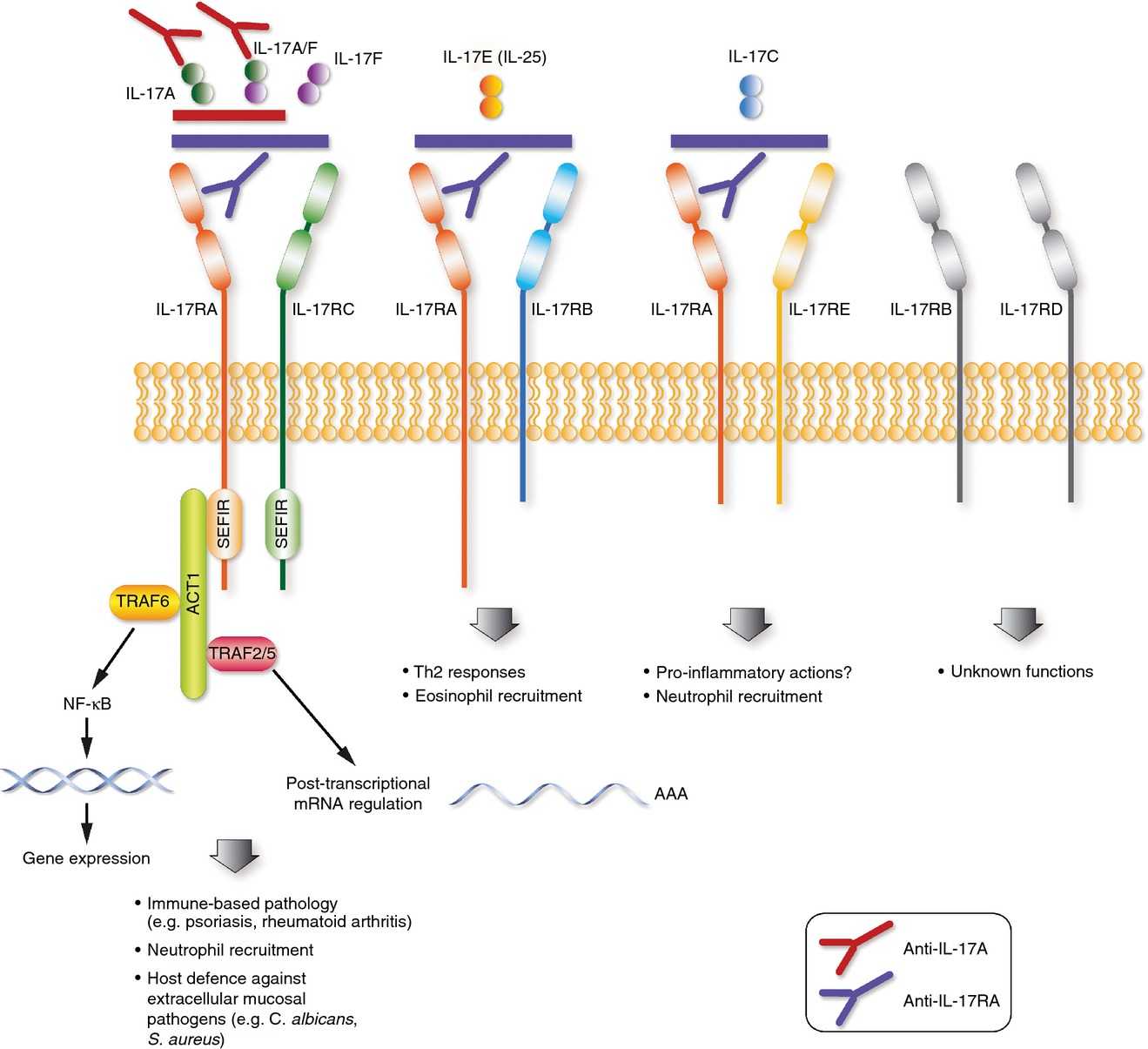 Fig.1 The IL-17 family of cytokines. (Brevi A, et al., 2020)
Fig.1 The IL-17 family of cytokines. (Brevi A, et al., 2020)
Schematic representation of the cytokines belonging to the IL-17 family, their respective receptor complexes coupled with intracellular signaling, and their target cells.
The IL-17 family of ligands has various biological functions, including driving inflammation during infections and autoimmune diseases. IL-17 is a primary pathologic cytokine and therapeutic target in several autoimmune, inflammatory illnesses, and cancers.
The IL-17 family of cytokines and their corresponding ligands play a crucial role in the immune system by regulating immune responses, inflammation, and host defense against pathogens. Here are some key aspects highlighting the importance of IL-17 family ligands:
Induction of Inflammation: IL-17 family ligands, particularly IL-17A and IL-17F, are potent inducers of inflammation. They promote the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and antimicrobial peptides by various cell types, including epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and immune cells. This pro-inflammatory response helps recruit and activate immune cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, at the site of infection or tissue damage.
Defense Against Microbial Pathogens: IL-17 family ligands are critical for host defense against extracellular microbial pathogens, such as bacteria and fungi. They enhance the recruitment and activation of immune cells at mucosal surfaces, including the gut, lungs, and skin, where these pathogens often invade. IL-17A and IL-17F promote the production of antimicrobial peptides and the clearance of pathogens.
Regulation of Adaptive Immune Responses: IL-17 family ligands, particularly IL-17A, play a role in shaping adaptive immune responses. They contribute to the differentiation and maintenance of T helper 17 (Th17) cells, a subset of CD4+ T cells that produce IL-17 cytokines. Th17 cells are involved in promoting pro-inflammatory responses and have been implicated in autoimmune diseases. IL-17A also synergizes with other cytokines, such as IL-6 and IL-23, to drive Th17 cell differentiation.
Tissue Remodeling and Repair: IL-17 family ligands contribute to tissue remodeling and repair processes. They can induce the production of factors involved in tissue remodeling, such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which aid in tissue repair and wound healing. However, excessive or dysregulated IL-17 signaling can lead to chronic inflammation and tissue damage, as observed in various autoimmune conditions.
Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases: Dysregulation of IL-17 family ligands has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Conditions such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and multiple sclerosis exhibit increased IL-17 production and signaling. Targeting IL-17 family cytokines has emerged as a therapeutic strategy for these disorders, leading to the development of IL-17 inhibitors.
Understanding the roles of IL-17 family ligands is essential for unraveling the mechanisms underlying immune responses, inflammation, and immune-related diseases. Their intricate interactions with various immune cells and signaling pathways contribute to the regulation of immune homeostasis and the balance between protective and pathological immune responses.
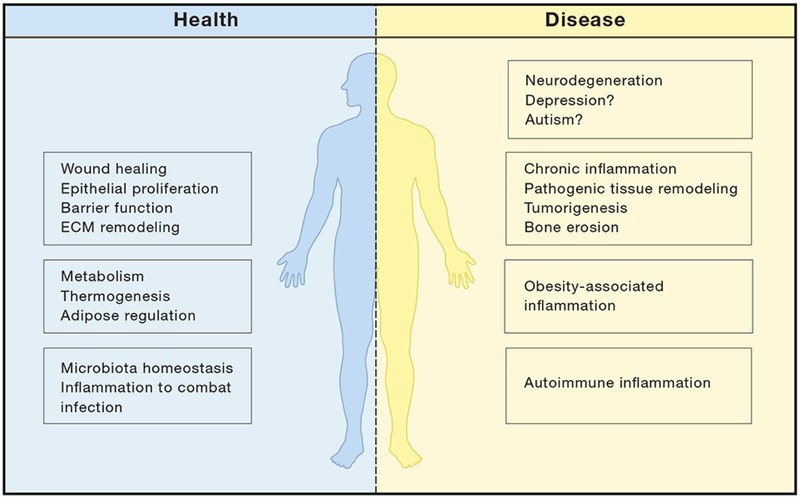 Fig.2 IL-17 protective and pathologic functions. (McGeachy MJ, et al., 2019)
Fig.2 IL-17 protective and pathologic functions. (McGeachy MJ, et al., 2019)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References:
- Monin L, Gaffen SL. Interleukin 17 Family Cytokines: Signaling Mechanisms, Biological Activities, and Therapeutic Implications. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018;10(4):a028522. Published 2018 Apr 2.
- Brevi A, Cogrossi LL, Grazia G, et al. Much More Than IL-17A: Cytokines of the IL-17 Family Between Microbiota and Cancer. Front Immunol. 2020;11:565470. Published 2020 Nov 10.
- Pappu, R., Ramirez-Carrozzi, V., Ota, N. et al. The IL-17 Family Cytokines in Immunity and Disease. J Clin Immunol 30, 185–195 (2010).
- Chang SH, Dong C. Signaling of Interleukin-17 Family Cytokines in Immunity and Inflammation. Cell Signal. 2011;23(7):1069-1075.
- McGeachy MJ, Cua DJ, Gaffen SL. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity. 2019;50(4):892-906.

