JNK
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
About JNK
JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase) is a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway that transduces extracellular signals into intracellular responses. The serine/threonine protein kinase JNK family contains three isoforms (JNK1, JNK2, and JNK3).
JNK signaling pathway is mainly activated by cytokines and stress stimuli and is involved in the regulation of cell growth, apoptosis, inflammation, and stress, etc. JNK signaling pathway is closely related to the development of many diseases, such as cancer, inflammation, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, cardiovascular disease, obesity, and diabetes, and therefore, it is of great significance to study JNK.
Mechanism of Action of JNK
JNK can directly or indirectly phosphorylate several transcription factors, the most important of which is c-Jun. Phosphorylated c-Jun forms complexes with other transcription factors enters the nucleus, and binds to DNA to regulate the transcriptional activity of specific genes. These genes are involved in a variety of biological processes such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle regulation, inflammatory response, and stress response.
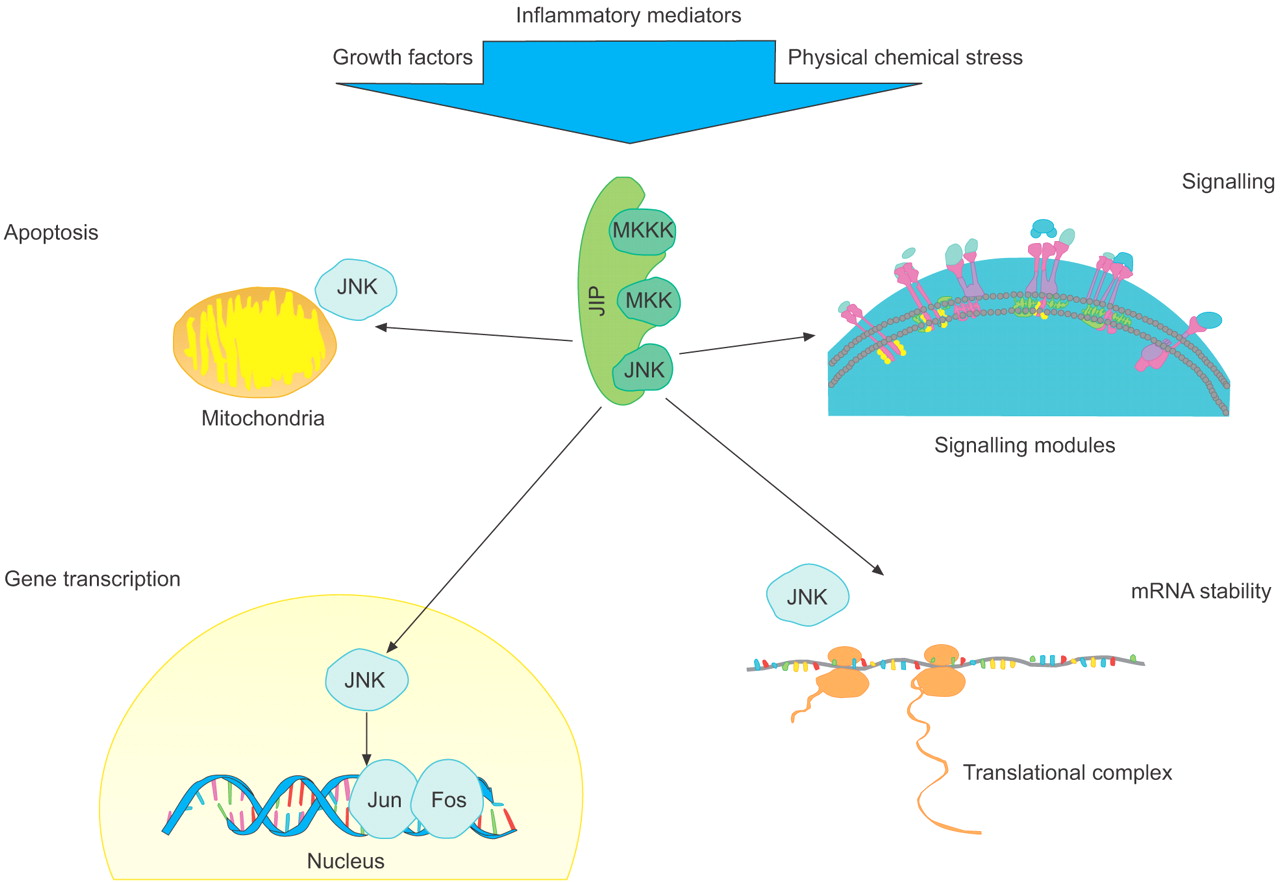 Fig.1 c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-mediated responses in the cell. (Bennett BL, et al., 2006)
Fig.1 c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-mediated responses in the cell. (Bennett BL, et al., 2006)
JNK and its upstream kinase activators are associated with scaffold proteins. Depending on the type, strength and duration of signal, JNK activation may lead to apoptosis via B-cell leukaemia/lymphoma gene product (Bcl) family proteins, gene expression via transcription factors such as activator protein-1 (Jun/Fos), increased protein expression via stabilisation of specific mRNA transcripts and modulated signalling in other pathways, such as via insulin receptor substrate 1 in insulin signalling. MKK: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MKKK: MAP kinase kinase kinase; JIP: JNK-interacting protein.
Functions of JNK
- Regulation of Apoptosis
Activated JNK promotes apoptosis by directly phosphorylating and regulating several apoptosis-related proteins, such as Bcl-2 family proteins, c-Jun, p53, etc. JNK is also involved in the regulation of apoptosis signaling pathways, such as the mitochondrial pathway, death receptor pathway, and endoplasmic reticulum stress.
- Inflammation Regulation
JNK can be activated by a variety of inflammatory factors (e.g. tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1) and further activate several inflammation-related transcription factors, such as AP-1 (activator protein-1) and NF-κB (nuclear factor-κB). These transcription factors regulate the expression of inflammation-related genes, such as inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and inflammatory mediators.
- Cytoskeleton and Cell Migration
Activated JNK phosphorylates and regulates several cytoskeletal proteins, such as cytoskeletal rearrangement protein (cofilin), F-aggregation protein (fascin), and cell adhesion molecule (integrin). These regulatory roles contribute to the onset of cellular morphological changes and cell migration.
- Stress Response
JNK can be activated by a variety of stressors (e.g. oxidative stress, heat shock, DNA damage, etc.) and is involved in the regulation of cellular stress response. Activated JNK can activate a series of stress-responsive proteins (e.g. heat shock proteins, DNA repair enzymes) to maintain cellular homeostasis and adapt to the stressful environment.
Available Resources for JNK
Aberrant activation of the JNK signaling pathway can lead to the onset and development of various diseases, including inflammatory diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, and tumors. Investigating the mechanism and regulation of the JNK signaling pathway can contribute to an in-depth understanding of these diseases and provide new directions and strategies for the treatment of related diseases. Creative BioMart offers a variety of JNK-related research products, such as recombinant proteins, cell and tissue lysates, and protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, as well as customizable services and other resources to support your research in the field of JNK. The following JNK are displayed, click to view all related molecules/targets and research reagents. For further information or to purchase products, please contact us. We are committed to providing the highest quality resources and support for your research to help you succeed.
References:
- Bennett BL. c-Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent mechanisms in respiratory disease. Eur Respir J. 2006;28(3):651-661.
- Bogoyevitch MA, Ngoei KR, Zhao TT, Yeap YY, Ng DC. c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling: recent advances and challenges. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1804(3):463-475.

