TIM Family Co-Signaling Molecules
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Background
About TIM Family Co-Signaling Molecules
The TIM (T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain) family co-signaling molecules are a group of cell surface receptors that play important roles in regulating immune responses. They are predominantly expressed on T cells and are involved in modulating T cell activation, tolerance, and immune cell interactions. The TIM family members have a unique structure, comprising an extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig) domain, a mucin-like domain, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail.
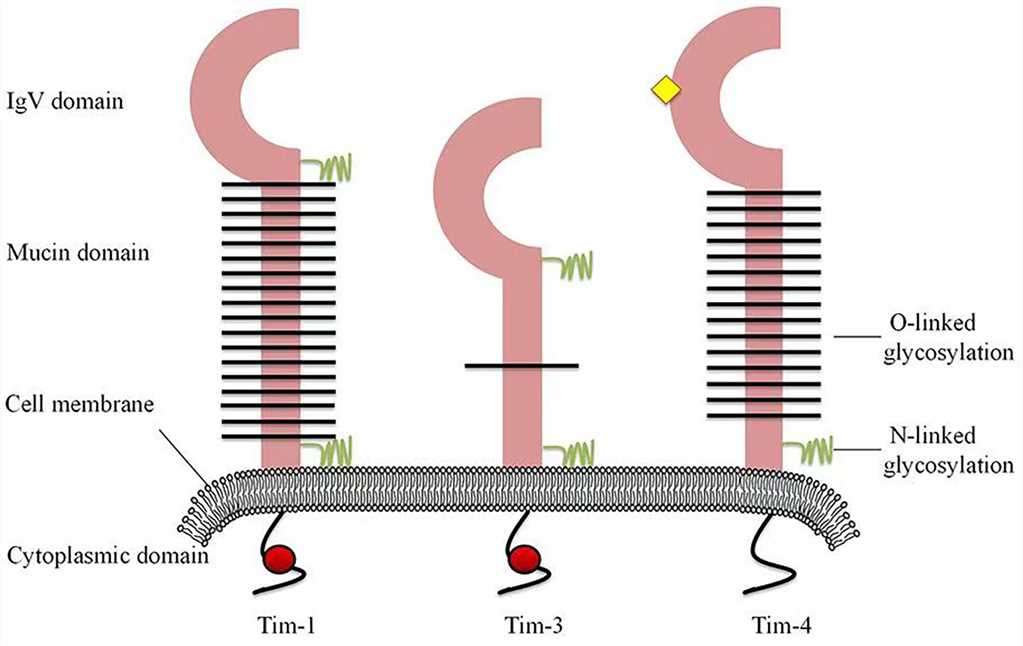 Fig.1 Structures of human Tim family members. (Liu Y, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Structures of human Tim family members. (Liu Y, et al., 2021)TIM Family History and Research Progress
The history of the TIM family dates back to the early 1990s when the first member, TIM-1, was identified. Since then, extensive research has been conducted to understand the biology, functions, and clinical implications of the TIM family molecules. Here's a brief overview of the history and research progress related to the TIM family:
| The history of the TIM family | Research progress |
|---|---|
| Discovery of TIM-1 |
|
| Expansion of the TIM Family |
|
| TIM Family in Immune Disorders and Cancer |
|
| Clinical Trials and Therapeutic Potential |
|
| Mechanistic Insights and Signaling Pathways |
|
| Future Directions |
|
The TIM Family Molecules
The TIM family co-signaling molecules play crucial roles in regulating immune responses, particularly in T cells. These cell surface receptors are involved in modulating T cell activation, tolerance, and immune cell interactions. The TIM family includes several members, such as TIM-1 (CD365), TIM-3 (CD366), TIM-4 (CD365B), and TIM-5 (CD365C). TIM-1, TIM-3, and TIM-4 are the most extensively studied members of the TIM family, while TIM-5 has been identified more recently.
| Key molecules | Functions |
|---|---|
| TIM-1 (CD365) |
|
| TIM-3 (CD366) |
|
| TIM-4 (CD365B) |
|
| TIM-5 (CD365C) |
|
Table1. Known features of the Tim family. (Liu Y, et al., 2021)
| Molecules | Expressing cells | Ligand(s) | Functions | Diseases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tim-1 | Activated Th2 cells, Bregs | Tim-4, PS | Costimulation of T cell activation, modulation of Treg function, maintenance and induction of Bregs | Autoimmune diseases, infection, asthma, allergy |
| Tim-3 | Th1 cells, innate immune cells | Gal-9, HMGB1, Ceacam1, PS | Suppression of the Th1 response, increased activation of signaling pathways leading to T cell activation | Autoimmune diseases, infection, cancer |
| Tim-4 | APCs | Tim-1, PS | Regulation of T cell proliferation, clearance of apoptotic cells | Autoimmune diseases, chronic metabolic disease, infection, allergy |
Research Results of TIM Family and Diseases
Research on the TIM family has provided valuable insights into their involvement in various diseases and pathological conditions. Here are some notable research findings regarding the TIM family and disease:
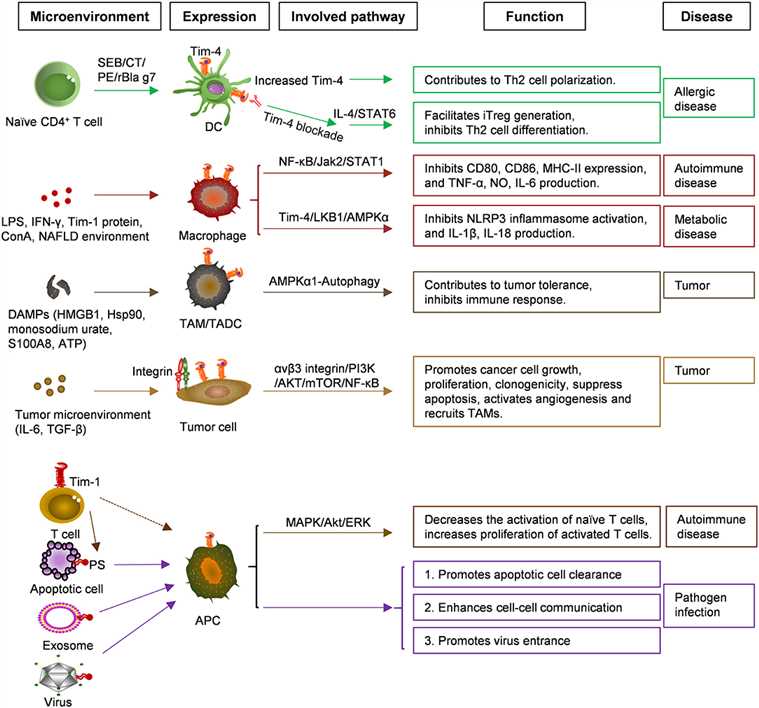 Fig.2 Functions and related signaling pathways of Tim-4 in various cells and diseases. (Liu W, et al., 2020)
Fig.2 Functions and related signaling pathways of Tim-4 in various cells and diseases. (Liu W, et al., 2020)TIM-1 and Allergic Diseases
- TIM-1 has been implicated in the development and progression of allergic diseases, such as asthma and allergic rhinitis.
- Studies have shown that polymorphisms in the TIM-1 gene are associated with increased susceptibility to asthma and allergic disorders.
- TIM-1 has been found to contribute to the pathogenesis of asthma by promoting T helper 2 (Th2) cell responses and airway inflammation.
TIM-3 and Chronic Viral Infections
- TIM-3 has been extensively studied in the context of chronic viral infections, such as HIV, hepatitis B virus (HBV), and hepatitis C virus (HCV).
- In chronic viral infections, TIM-3 is upregulated on exhausted T cells, which display impaired effector functions and contribute to viral persistence.
- Blocking TIM-3 signaling has shown promise in restoring T cell function and enhancing antiviral responses in preclinical and clinical studies.
TIM-3 and Cancer
- TIM-3 expression is frequently observed in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and is associated with T cell exhaustion in various cancers.
- High TIM-3 expression has been linked to poor prognosis and resistance to immunotherapy in cancer patients.
- Targeting TIM-3 has emerged as a strategy in cancer immunotherapy, and several TIM-3-targeted antibodies are being evaluated in clinical trials.
TIM-4 and Autoimmune Diseases
- TIM-4 has been implicated in the development of autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
- Increased expression of TIM-4 has been observed in the kidneys of lupus nephritis patients, suggesting its involvement in renal inflammation.
- TIM-4 can promote the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and influence the balance between immune tolerance and autoimmunity.
TIM-3 and Graft-versus-Host Disease (GVHD)
- GVHD is a complication that can occur after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
- Studies have shown that TIM-3 expression is upregulated on T cells during GVHD and contributes to the immune dysregulation and tissue damage seen in this condition.
- Targeting TIM-3 has shown potential in preclinical models as a strategy to mitigate GVHD and improve transplant outcomes.
These research findings highlight the significance of the TIM family members in various diseases and provide potential therapeutic targets for intervention. Further research is needed to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and develop effective strategies to modulate TIM family signaling for therapeutic benefit in these diseases.
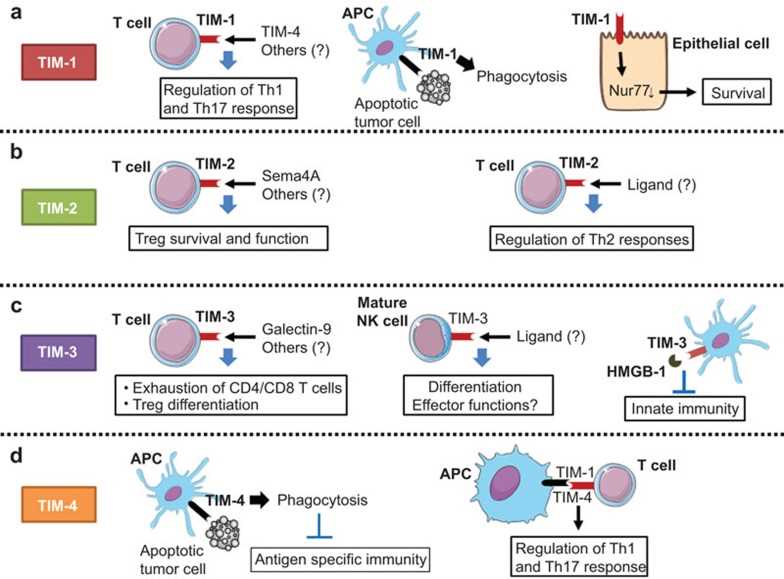 Fig.3 The role of the TIM gene family in antitumor immune responses. (Baghdadi M, et al., 2013)
Fig.3 The role of the TIM gene family in antitumor immune responses. (Baghdadi M, et al., 2013)Case Study
Case 1:Jia K, He Y, Dziadziuszko R, et al. T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3 in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2019;8(6):895-906.
The aim of this research was to evaluate TIM-3 expression status on tumor cells and TILs in NSCLC tumor tissue. This study that underlined that TIM-3 expression level on TILs was associated with the expression of other immune checkpoints and the survival time of NSCLC patients. We found TIM-3 was expressed on tumor cells and lymphocytes in both adenocarcinoma and squamous carcinoma. More importantly, high level of TIM-3 on lymphocytes was correlated with early relapse and shorter survival time on NSCLC patients.
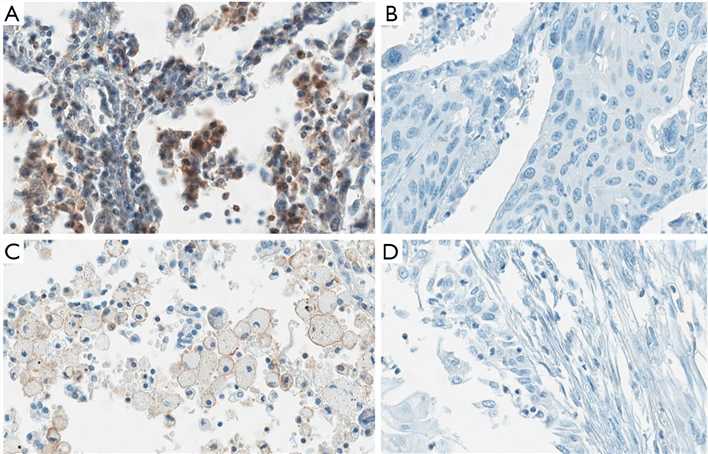 Fig.1 Expression of TIM-3 on tumor cells and TILs.
Fig.1 Expression of TIM-3 on tumor cells and TILs.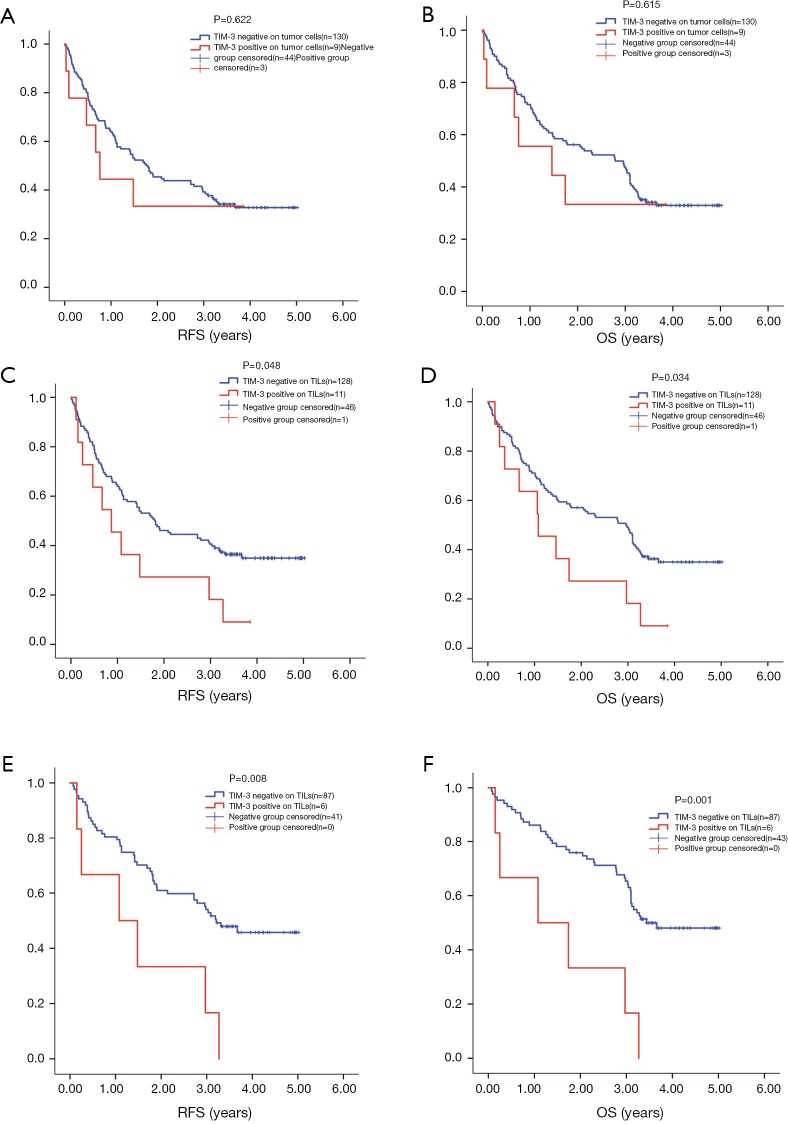 Fig.2 Survival analysis by TIM-3 level on TILs and tumor cells.
Fig.2 Survival analysis by TIM-3 level on TILs and tumor cells.Case 2: Zheng Y, Wang L, Chen M, et al. Inhibition of T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-1 (TIM-1) protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury Cell Commun Signal. 2019;17(1):103.
To determine the mechanism of T cell-mediated damage on neurons, the authors knocked down TIM-1 and used a Western blot to detect the interference efficiency (a). The ELISA results indicated that the expression of LDH in the CD3 group was higher than that in the Control group. There was no significant difference between TIM-1 expression in the siRNA group and TIM-1 in the siRNA + CD3 group (b). The EdU assay showed that the level of TIM-1 siRNA combined with CD3 could enhance the decrease in cellular proliferation observed in the CD3 group (c-d). Light microscopy was used to examine the morphology of the total neuronal cells in each treatment group (e). The authors performed an ELISA to examine the changes in cytokine secretion, including the level of TNF-α, IL-6, NO, and MIP-1α in each group with an ELISA. The authors found that CD3 stimulation could increase the expression of TNF-α, MIP-1α, NO, and IL-6, whereas blocking TIM-1 decreased such production (f-i). These findings indicate that the knockdown of TIM-1 could significantly reduce the T cell-mediated damage to neurons when T cells and neurons were co-cultured in vitro.
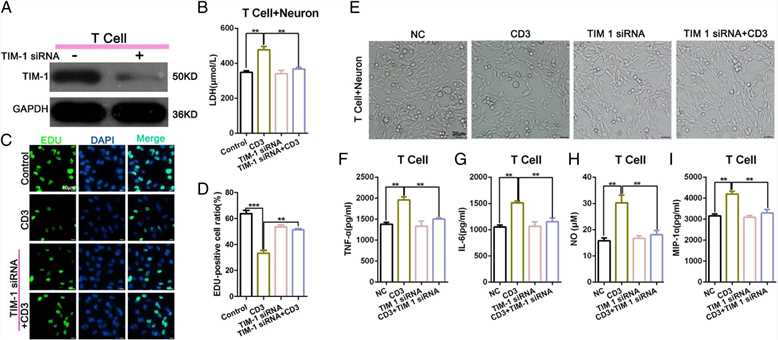 Fig.3 The level of T cell-mediated damage on neurons was significantly reduced following an in vitro TIM-1 knockdown in co-cultured T cells and neurons.
Fig.3 The level of T cell-mediated damage on neurons was significantly reduced following an in vitro TIM-1 knockdown in co-cultured T cells and neurons.References
- Liu Y, Chen H, Chen Z, Qiu J, Pang H, Zhou Z. Novel roles of the Tim family in immune regulation and autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2021;12:748787.
- Kuchroo VK, Dardalhon V, Xiao S, Anderson AC. New roles for TIM family members in immune regulation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(8):577-580.
- Liu W, Xu L, Liang X, et al. Tim-4 in health and disease: friend or foe? Front Immunol. 2020;11:537.
- Baghdadi M, Jinushi M. The impact of the TIM gene family on tumor immunity and immunosuppression. Cell Mol Immunol. 2014;11(1):41-48.

