What is CEACAM5 Protein
CEACAM5, officially known as Carcinoembryonic Antigen-Related Cell Adhesion Molecule 5, is a protein encoded by the CEACAM5 gene. Also referred to as CEA (Carcinoembryonic Antigen), this glycoprotein belongs to the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) family. The CEACAM5 gene is situated on the long arm of chromosome 19 (19q13.2). Its synonyms include CD66e, meconium antigen, and CEA-related cell adhesion molecule 5.
CEACAM5 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
CEACAM5, like other members of the CEA family, exhibits structural features that play crucial roles in its functions. It is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored protein, meaning it is attached to the cell membrane via a glycolipid anchor. This attachment allows CEACAM5 to participate in cell adhesion processes, a characteristic shared by many members of the CEA family.
Belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, CEACAM5 comprises immunoglobulin variable (IgV) and constant (IgC) domains. The IgV domain mediates homophilic and heterophilic interactions, facilitating cell adhesion and signaling. The protein's structural versatility enables it to engage in diverse cellular processes.
Recent Research Advances about CEACAM5 Protein
Recent research has shed light on the dynamic role of CEACAM5 in cancer progression and metastasis. Studies have explored its involvement in modulating immune responses and promoting tumor growth. Additionally, investigations into the interaction between CEACAM5 and other proteins within the tumor microenvironment have provided insights into potential therapeutic targets.
CEACAM5 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
CEACAM5 plays a pivotal role in various biological functions, primarily functioning as a cell adhesion molecule. Its involvement in cell-to-cell interactions is essential for embryonic development, immune response regulation, and maintenance of tissue integrity.
The molecular mechanisms underlying CEACAM5's functions include its ability to engage in both homophilic and heterophilic interactions. Homophilic interactions occur between CEACAM5 molecules on adjacent cells, while heterophilic interactions involve binding with other molecules, contributing to cell signaling and adhesion.
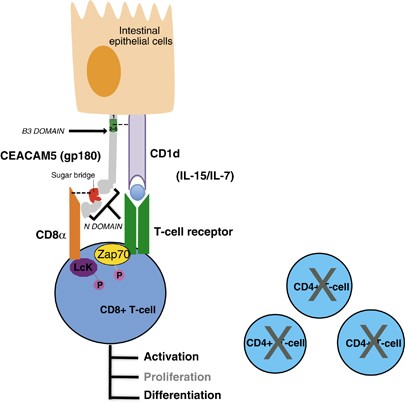
Figure 1. Interactions between CEACAM5/CD1d and CEACAM5/CD8α. (Roda G, et al., 2014)
CEACAM5 Related Signaling Pathway
CEACAM5 is implicated in diverse signal pathways that influence cell behavior. One notable pathway is the regulation of immune responses. By modulating the activities of immune cells, CEACAM5 contributes to the evasion of tumor cells from immune surveillance, promoting cancer progression.
CEACAM5 Related Diseases
CEACAM5 is notably associated with several diseases, with its most prominent connection being to various cancers. Elevated levels of CEACAM5, especially in serum, are frequently observed in patients with colorectal, pancreatic, and breast cancers. The protein's presence serves as a diagnostic marker for these malignancies, aiding in early detection and monitoring of disease progression.
CEACAM5's Applications in Biomedicine
CEACAM5's significance extends beyond its role as a diagnostic marker. In the realm of diagnostic development, the protein serves as a valuable tool for identifying and monitoring cancer. Its detection in blood samples aids in assessing the effectiveness of cancer treatments and predicting patient outcomes.
In the realm of vaccine development, CEACAM5's involvement in immune regulation makes it a potential target for therapeutic vaccines aimed at bolstering the body's natural defenses against cancer cells. Researchers are exploring ways to harness the protein's immunomodulatory properties to enhance the efficacy of cancer vaccines.
Moreover, CEACAM5 is under scrutiny for its potential in therapeutic interventions. Targeting CEACAM5 in cancer therapy holds promise for disrupting tumor growth and metastasis. Developing drugs that selectively inhibit CEACAM5 could pave the way for novel cancer treatments, offering new avenues for personalized medicine.
Recommended Products
Reference
- Roda G, et al. Characterizing CEACAM5 interaction with CD8α and CD1d in intestinal homeostasis. Mucosal Immunology. 2014, 7(3): 615-624.

