What is CLDN3 Protein
The CLDN3 protein, also known as Claudin-3, is a multifaceted protein with unrecognized importance until recently. Associated with certain diseases and crucial bodily processes, this protein has become a major subject of focus in the biomedical research realm.
The CLDN3 protein belongs to a large family of proteins known as claudins. The claudin gene family, identified in the late 1990s, contains 24 members, each encoding a distinct claudin protein. Claudin-3 was one of the earliest claudins discovered and characterized, providing the foundation for understanding the role and nature of this protein family.
Gene Locus and Protein Structure
Located on the chromosome 7q11.23, the CLDN3 gene is responsible for the coding of the Claudin-3 protein. The protein's structure comprises four transmembrane domains, short N- and C-terminal cytoplasmic tails, and two extracellular loops. The N-terminal end is located in the cytoplasm, while the C-terminal end extends into the extracellular space. The extracellular loops, particularly the first one, play a significant role in cell-to-cell adhesion and paracellular ion selectivity.
Function of the CLDN3 Protein
Claudin-3 protein is primarily involved in forming tight junction strands in epithelial and endothelial cells. The formation of these tight junctions contributes to controlling the paracellular permeability of ions and small molecules, acting as a crucial factor in maintaining tissue homeostasis. Therefore, it plays an essential role in regulating the movement of molecules in the intercellular space and maintaining cellular polarity.
CLDN3 Protein Related Signal Pathway
The function of Claudin-3 is closely related to multiple signal pathways. One such pathway is the ERK1/ERP2 signaling pathway, where activation can induce Claudin-3 expression. Additionally, Claudin-3 has been associated with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, impacting cell proliferation, polarity, and fate determination.
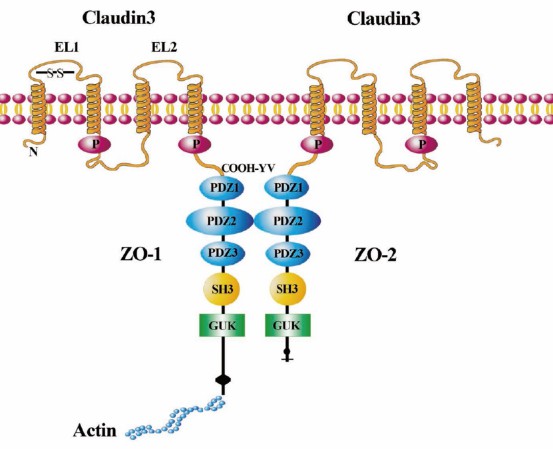
Fig1. Illustration of CLDN3 signaling in cells. (Che, Juanjuan, et al. 2018)
CLDN3 Protein Related Diseases
The aberrant expression of Claudin-3 protein is associated with multiple diseases, notably pathological conditions such as cancer. In ovarian cancer, elevated levels of the Claudin-3 protein may contribute to tumor progression and metastasis formation. A similar correlation has been observed in breast cancer, gastric cancer, and prostate cancer, where the protein often shows an increased expression.
Similarly, changes in Claudin-3 levels have also been identified in neurological disorders. Studies investigating the function of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) have found that altered Claudin-3 expression affects the BBB's integrity, potentially contributing to diseases like Alzheimer's.
Claudin-3 Protein's Applications in Biomedical research
Due to its links with cancer development, the Claudin-3 protein is an attractive target for potential cancer therapies. Research is ongoing to look into the possibility of developing drugs that can block the function of Claudin-3 and potentially halt cancer growth and metastasis.
Moreover, the Claudin-3 protein could potentially serve as a diagnostic marker for various cancer types, given its consistently increased expression in cancer tissues. Furthermore, its involvement in maintaining the BBB integrity implies possible implications for treating neurological disorders.
Lastly, on a more general note, continuing to unravel the mysteries surrounding Claudin-3 contributes to a broader understanding of cellular biology, particularly cell-cell adhesion, cellular polarity, and the regulation of paracellular transport.
In summary, the Claudin-3 protein has evolved from its initial findings as a constituent of tight junctions to becoming a major subject of investigation due to its implications in various diseases. From exploring potential therapeutic targets to providing crucial insights into the mechanisms involved in various pathological conditions, the biomedical research on Claudin-3 promises to become even more relevant in the future.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLDN3-11295H | Recombinant Human CLDN3, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CLDN3-10H | Active Recombinant Human CLDN3 Full Length Full Length Transmembrane protein, His-tagged(VLPs) | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CLDN3-2055HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CLDN3 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| CLDN3-1537H | Recombinant Human CLDN3 Full Length Transmembrane protein, His-tagged | Human | In vitro E. coli expression system | His |
| CLDN3-0298H | Active Recombinant Human CLDN3 Full Length Transmembrane protein(Nanodisc) | Human | HEK293 | N/A |
| CLDN3-84HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CLDN3 Protein | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System |
Reference
- Che, Juanjuan & Yue, Dongsheng & Zhang, Bin & Zhang, Hua & Huo, Yansong & Gao, Liuwei & Zhen, Hongchao & Yang, Yan & Cao, Bangwei. (2018). Claudin-3 Inhibits Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition and Invasion via Suppression of the Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Medical Sciences. 15. 339-351. 10.7150/ijms.22927.

