What is CLK1 Protein?
The CLK1 protein, scientifically known as CDC-like kinase 1, is a serine/ threonine type protein kinase that plays a crucial role in the world of biomedicine. This specific protein belongs to a family of CLKs (CDC-like kinases) proteins and this involvement in critical physiological processes has stimulated exhaustive scientific scrutiny.
The initial discovery of the CLK1 protein was borne out of the quest to understand circadian rhythms in organisms. It was identified and investigated as an integral part of the circadian clock mechanism and its genes were consequently sequenced. This discovery marked the trailhead to a new dimension in scientific research and further exploration of CLK1 could potentially address diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
In terms of the gene locus, the CLK1 gene is located on chromosome number 2(2p25.1) in humans. It spans around 117496 base pairs, starting at base pair 13711996 and ending at base pair 13837145 on the short (p) arm of chromosome 2 at a position 25.1.
The Structure of CLK1 protein
The protein structure of CLK1 reveals four sections: the serine/threonine-protein kinase catalytic domain, Protein kinase-like domain, the LAMMER-type domain and the ASKHA/TKK domain. This structure provides critical insights into the understanding of post-transcriptional gene expression regulation.
Function of CLK1 protein
The function of the CLK1 protein is primarily the regulation of pre-mRNA splicing, a mechanism vital for proper functioning at the cellular level. CLK1 phosphorylates the specific serine/arginine-rich proteins that are necessary for binding and processing of pre-mRNA, playing an instrumental role in alternative splicing regulation. Additionally, research has elucidated the direct involvement of CLK1 protein in the control of circadian rhythms, contributing to how organisms adapt to their environment's cyclical changes.
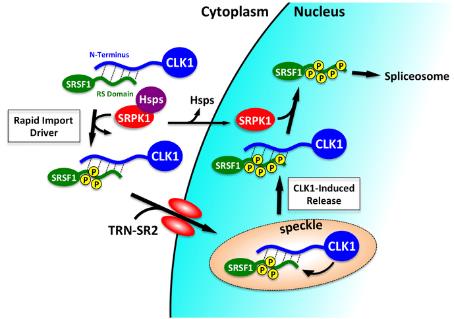
Fig1. Model showing CLK1 Entry into the Nucleus
CLK1 protein related signal pathway
The CLK1 protein is implicated in various signal pathways, most notably the spliceosome pathway. This is a critical biochemical machinery necessary for the process of splicing introns from pre-mRNA transcripts to produce mature mRNA, the dominant gene expression layer regulation. Additionally, the CLK1 protein relates to diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's, where alternative splicing regulation is often aberrantly altered.
CLK1 protein related diseases
With regards to diseases, several diseases are linked with mutations and dysfunctions in the CLK1 protein. Given its central role in alternative splicing, malfunction or mutations relating to CLK1 can lead to a vast array of complex diseases, spanning cancer, neurological disorders to autoimmune diseases. This signals the need for further exploration into the function and potential of CLK1 protein in disease management and treatments.
CLK1 protein's applications in biomedical
The critical role that CLK1 protein plays in gene expression has significant implications in the field of biomedicine. As it regulates the spliceosome pathway, a pathway critically involved in the regulation of gene expression, a better understanding of CLK1's role allows for the development of therapies for diseases associated with aberrant gene expression. For example, the development of kinase inhibitors for the CLK1 protein could disrupt atypical splicing processes, making it a potential target for cancer treatments.
Further, constant developments have seen the emergence of CLK1 inhibitors that play a crucial role in the intervention of sleep disorders, neurodegenerative, and metabolic diseases. These inhibitors function by modulating the RNA processing of pre-mRNA, a process instrumental in ensuring that genes function correctly, thereby providing an avenue for intervention in diseases largely driven by errors in gene function.
In conclusion, the CLK1 protein, with its serine/threonine kinase activity, provides pivotal control mechanisms necessary for the appropriate functioning of cellular and organ systems. Its involvement in critical physiological and metabolic processes makes it a prime target for understanding and developing novel therapeutic interventions in various disease states, thereby highlighting the relevance of comprehensively studying the CLK1 protein. There is still much potential to tap from unraveling the mysteries surrounding this protein, promising a stepping stone towards major breakthroughs in biomedical research.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLK1-284H | Recombinant Human CDC-like Kinase 1, GST-tagged, Active | Human | Sf9 Insect Cell | GST |
| CLK1-1490H | Active Recombinant Human CLK1 Protein, GST-His-tagged | Human | Insect Cell | GST/His |
| CLK1-567H | Recombinant Human CLK1 | Human | Mammalian Cell | His |
| CLK1-88HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CLK1 Protein | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | |
| CLK1-2688H | Recombinant Human CLK1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| CLK1-2203HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CLK1 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
Reference
- George, Athira & Aubol, Brandon & Fattet, Laurent & Adams, Joseph. (2019). Disordered protein interactions for an ordered cellular transition: Cdc-like kinase 1 is transported to the nucleus via its Ser-Arg protein substrate. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 294. jbc.RA119.008463. 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008463.

