What is KISS1 Protein
KISS1, or Kisspeptin 1, serves as a vital player in the intricate ballet of human physiology. Officially known as KiSS-1 metastasis suppressor, it goes by various synonyms such as metastin and melanoma metastasis-suppressing activity. Belonging to the family of Kisspeptins, this protein plays a pivotal role in regulating reproductive processes.
KISS1 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Structurally, KISS1 is characterized by its conserved 54-amino acid sequence, with a distinctive amidated carboxyl terminus. Classified as a metastasis suppressor, KISS1 has recently garnered attention for its broader physiological implications, transcending its initial role in cancer research.
KISS1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of KISS1 are diverse and impactful. Primarily, it operates as a gatekeeper in the realm of reproduction, acting as a crucial regulator of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. KISS1's molecular mechanisms involve its ability to stimulate the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) – a linchpin in the orchestration of reproductive processes.
Through this mechanism, KISS1 helps regulate the secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), key players in ovulation and spermatogenesis. Not confined to the reproductive sphere, KISS1 also exerts influence over other physiological processes, such as cardiovascular homeostasis and the intricate dance of energy balance.
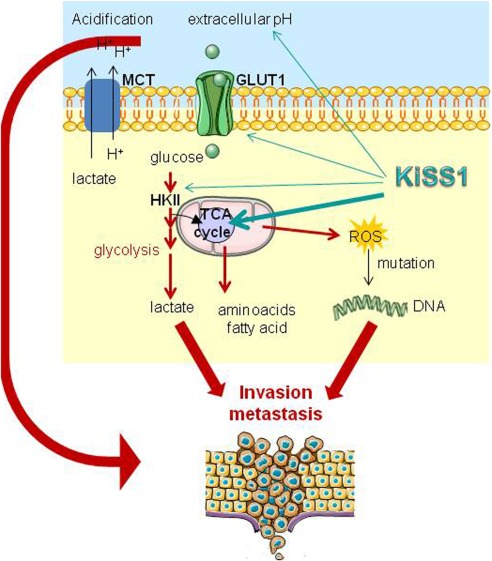
Figure 1. KiSS1 in regulation of metastasis and response to antitumor drugs. (Corno C, et al., 2019)
KISS1 Related Signaling Pathway
Delving into the molecular intricacies, KISS1 operates through the G protein-coupled receptor GPR54, also known as Kiss1R. This receptor serves as the molecular gateway for KISS1's signals, initiating downstream cascades that culminate in the modulation of GnRH release.
The Kiss1/GPR54 pathway's nuanced regulation of reproductive hormones positions it as a crucial player in the tightly choreographed dance of human fertility. Understanding these signal pathways provides a foundation for exploring therapeutic interventions and diagnostic strategies in reproductive health.
KISS1 Related Diseases
Research has unveiled the intricate links between KISS1 and various diseases. Dysregulation of KISS1 expression has been implicated in conditions such as infertility, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and certain reproductive cancers. The delicate balance maintained by KISS1 in reproductive processes underscores its potential as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target in the realm of reproductive health.
KISS1's Applications in Biomedicine
The multifaceted role of KISS1 has sparked interest in its applications within the biomedical realm. Researchers are exploring its potential in diagnostic development, seeking to leverage its role as a biomarker in conditions like infertility and reproductive cancers. KISS1's presence or absence could serve as a diagnostic indicator, guiding clinicians in tailoring personalized treatment approaches.
Furthermore, the therapeutic potential of KISS1 is being explored in the development of vaccines and targeted therapeutics. Manipulating the Kiss1/GPR54 pathway holds promise in addressing reproductive disorders and, potentially, certain cancers. The precision afforded by targeting KISS1 opens new avenues for therapeutic interventions with minimal side effects.
In vaccine development, the unique properties of KISS1 could be harnessed to stimulate specific immune responses. Research is ongoing to explore the feasibility of KISS1-based vaccines in the prevention and treatment of conditions linked to its dysregulation.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KISS1-28652TH | Recombinant Human KISS1 | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| KISS1-3825H | Recombinant Human KISS1 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| KISS1-1646H | Recombinant Human KISS1 protein, His & T7-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/T7 |
| KISS1-5077H | Recombinant Human KISS1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| KISS1-3135H | Recombinant Human KISS1 Protein (Glu20-Gly138), N-His tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
| Kiss1-7885M | Recombinant Mouse Kiss1 protein, His & GST-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His/GST |
| Kiss1-3696M | Recombinant Mouse Kiss1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| Kiss1-1070R | Recombinant Rat Kiss1 Protein, His-tagged | Rat | CHO | N-His |
| KISS1-2919R | Recombinant Rat KISS1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| KISS1-3263R | Recombinant Rat KISS1 Protein | Rat | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Corno C, Perego P. KiSS1 in regulation of metastasis and response to antitumor drugs. Drug Resistance Updates. 2019, 42: 12-21.

