What is NPPB Protein
The Natriuretic Peptide B, also known as NPPB protein, first identified in pig brains during the late 1980s. NPPB is part of the natriuretic peptide family, which plays a pivotal role in cardiovascular homeostasis. The locus of the human NPPB gene is on chromosome 1 at position p36.22. It has an incredibly specific structure, comprising a 134-amino acid preprohormone, which is further processed to a 108-amino acid prohormone.
This prohormone is then cleaved into a 32-amino acid peptide, called the B-type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP), and a 76-amino acid N-terminal prohormone fragment. The B-type part is later released into circulation and serves as an essential cardiodiagnostic biomarker.
Function of NPPB Protein
Primarily secreted by the ventricles of the heart in response to excessive stretching of heart muscle cells, NPPB protein plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and fluid balance. Its functions involve inducing natriuresis, enhancing vasodilation, inhibiting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and reducing sympathetic outflow. Overall, NPPB helps to maintain cardiovascular homeostasis, and its levels within the body provide valuable information on heart functionality.
NPPB Protein-Related Signal Pathway
The signaling pathway of the NPPB protein integrates natriuretic peptide receptors (NPRs), notably NPR-A and NPR-B, which are bound by natriuretic peptides. This binding allows cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate (cGMP) to be produced, which further mediates natriuresis, vasorelaxation, inhibition of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and stimulation of myocardial relaxation. The overall process helps reduce arterial pressure all while promoting sodium excretion and enhancing renal blood flow.
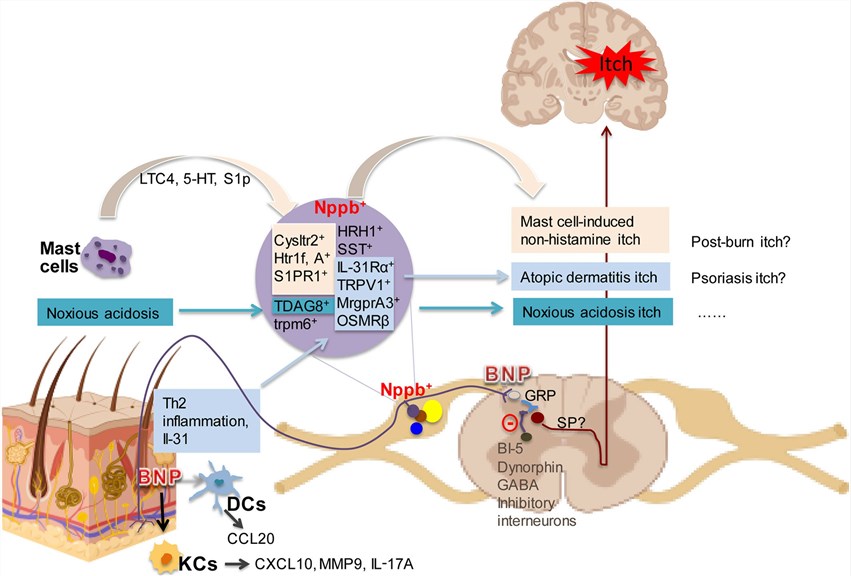
Fig1. NPPB signaling pathway (Meng, J., et al. 2020)
NPPB Protein-Related Diseases
NPPB protein and especially its hormone product B-type Natriuretic Peptide holds immense diagnostic and prognostic value in cardiovascular diseases such as heart failure. Elevated levels of BNP correspond to the severity of heart failure, making it an ideal biomarker for diagnostics and monitoring. It also plays a role in hypertension, coronary artery disease, and acute coronary syndromes.
Apart from cardiovascular diseases, NPPB protein has been implicated in certain types of cancer and neurological disorders. For example, abnormally high levels of BNP have been observed in patients with lung cancer, colorectal cancer, and melanoma.
NPPB Protein's Applications in Biomedical
The primary biomedical application of NPPB protein is as a biomarker for diagnosing heart failure and other related cardiovascular conditions. Because circulating BNP levels reflect ventricular dysfunction, it aids in diagnosing heart failures to prevent further progression.
Concurrent with this, NPPB testing has been made commercially available and has continually been employed as a rapid diagnostic tool in critical care settings, especially for patients with dyspnea.
Recently, researchers are exploring more comprehensive applications of NPPB protein, including its potential in cancer therapeutics.
In conclusion, the NPPB protein, apart from being a cornerstone of cardiovascular homeostasis, holds enormous potential in diagnostics and therapeutics in multiple medical fields. Still, further research is required to widen its horizon of clinical significance thoroughly. The future of biomedicine seems promising by tactical integration of knowledge about proteins such as NPPB in the design of preventive, diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nppb-2768M | Recombinant Mouse Nppb protein, His & GST-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His/GST |
| Nppb-2767M | Recombinant Mouse Nppb protein, His-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His |
| NPPB-10831M | Recombinant Mouse NPPB Protein | Mouse | Mammalian Cell | His |
| Nppb-389M | Recombinant Mouse Nppb Protein, His&SUMO-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | N-His&SUMO |
| NPPB-6170M | Recombinant Mouse NPPB Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| Nppb-1852M | Recombinant Mouse Nppb Protein, His&GST-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | N-His&GST |
Reference
- Meng, J., Chen, W., & Wang, J. (2020). Interventions in the B-type natriuretic peptide signalling pathway as a means of controlling chronic itch. British Journal of Pharmacology, 177(5), 1025-1040. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14952

