What is NR2F2 Protein
In the intricate landscape of molecular biology, the NR2F2 protein, also known as COUP-TFII, emerges as a key player, orchestrating various cellular processes.
NR2F2, a transcription factor encoded by the NR2F2 gene, belongs to the nuclear receptor superfamily. Comprising a DNA-binding domain and a ligand-binding domain, its structural characteristics are emblematic of nuclear receptors. These receptors serve as molecular switches, regulating gene expression and influencing cellular functions.
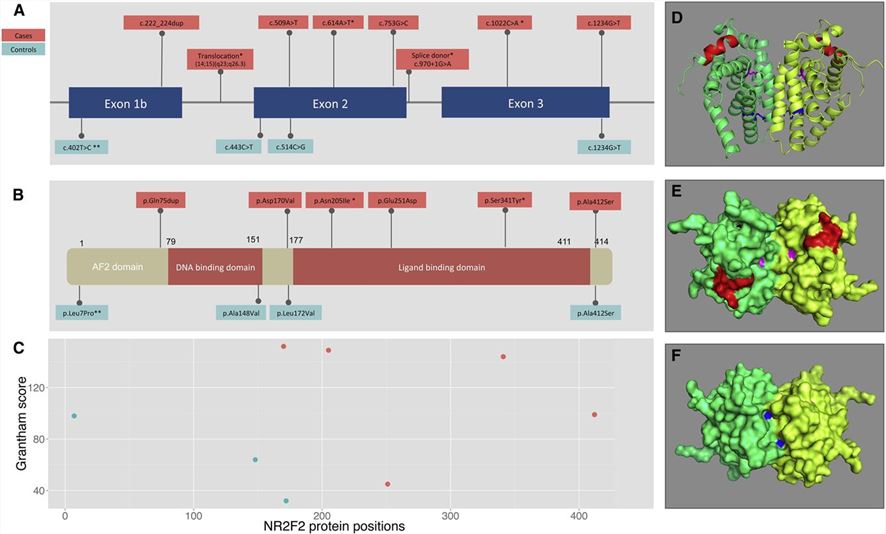 Figure 1. Structure of NR2F2 and the Encoded Protein. (Al Turki, S., et al. 2014)
Figure 1. Structure of NR2F2 and the Encoded Protein. (Al Turki, S., et al. 2014)The Function of NR2F2 Protein
- Embryonic Development
NR2F2 plays a pivotal role in embryonic development, steering the intricate process of cell fate determination. It acts as a molecular conductor, ensuring the precise differentiation of cells into specialized tissues. Notably, NR2F2 influences the formation of vital organs such as the heart, lungs, and central nervous system, underscoring its significance in the foundational stages of life.
- Vascular Development
In addition to its role in embryogenesis, NR2F2 emerges as a key player in vascular development. Through the regulation of angiogenesis, NR2F2 contributes to the formation of new blood vessels, a process critical for both embryonic development and postnatal life.
- Metabolic Regulation
NR2F2 extends its influence to metabolic processes, serving as a metabolic sensor that responds to fluctuations in nutrient levels. Dysregulation of NR2F2 has been associated with metabolic disorders, including obesity and insulin resistance, highlighting its intricate involvement in maintaining metabolic homeostasis.
NR2F2-Related Diseases
- Cardiovascular Diseases
Dysregulation of NR2F2 has been implicated in cardiovascular diseases, particularly congenital heart defects. The impact on heart development emphasizes its role in maintaining the structural and functional integrity of the cardiovascular system.
- Cancer
The versatile nature of NR2F2 is evident in its association with various cancers. Depending on the context, NR2F2 can act as both a tumor suppressor and an oncogene. Its influence on cell proliferation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis makes it a potential target for cancer therapy.
- Metabolic Disorders
Beyond its role in cardiovascular health and cancer, NR2F2 dysregulation has been linked to metabolic disorders. Understanding its contribution to conditions such as obesity and insulin resistance opens avenues for therapeutic interventions targeting metabolic pathways.
NR2F2 Related Signaling Pathways
- Interaction with Transcription Factors
NR2F2 engages in complex interactions with other transcription factors, forming a regulatory network that modulates gene expression patterns. These interactions influence crucial cellular functions, including differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis.
- Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
The crosstalk between NR2F2 and the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway unveils another layer of its regulatory capabilities. This interaction is pivotal for cell fate determination and tissue development, with dysregulation contributing to the pathogenesis of diseases, including cancer.
Applications of NR2F2 in Biomedical Research
- Cancer Therapeutics
The dual role of NR2F2 in cancer—acting as both a tumor suppressor and an oncogene—positions it as a compelling target for cancer therapeutics. Unraveling the context-dependent functions of NR2F2 in different cancer types holds promise for the development of targeted therapies.
- Cardiovascular Regeneration
Harnessing NR2F2's regulatory functions in cardiovascular development presents opportunities for cardiac regeneration. Manipulating NR2F2 for promoting vascularization and tissue repair could offer innovative approaches for treating cardiovascular diseases.
- Metabolic Interventions
The involvement of NR2F2 in metabolic regulation opens avenues for interventions in metabolic disorders. Strategies aimed at modulating NR2F2 activity hold potential for managing conditions like obesity and insulin resistance.
- Drug Development
Understanding NR2F2-related signal pathways provides a foundation for drug development. Small molecules targeting specific interactions or modulating NR2F2 activity could serve as therapeutic agents for diseases associated with NR2F2 dysregulation.
NR2F2 emerges as a pivotal protein with far-reaching implications in cellular processes, from embryonic development to metabolic regulation. Its involvement in various diseases and signal pathways highlights its importance in maintaining cellular homeostasis. The ongoing research into NR2F2 not only deepens our understanding of fundamental biological processes but also opens up new possibilities for therapeutic interventions in diseases where NR2F2 dysregulation plays a role. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of NR2F2, the potential for groundbreaking discoveries in biomedical research remains high, holding promise for improved treatments and a better understanding of human health and disease.
Recommended Products for NR2F2 Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR2F2-3323HF | Human | Recombinant Full Length Human NR2F2 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| NR2F2-25H | Human | Recombinant Human NR2F2 Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | GST |
| NR2F2-10867M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse NR2F2 Protein | Mammalian Cell | His |
| NR2F2-6187M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse NR2F2 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| NR2F2-4067R | Rat | Recombinant Rat NR2F2 Protein | Mammalian Cell | His |
| NR2F2-3726R | Rat | Recombinant Rat NR2F2 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| NR2F2-8789Z | Zebrafish | Recombinant Zebrafish NR2F2 | Mammalian Cell | His |
| NR2F2-5991C | Chicken | Recombinant Chicken NR2F2 | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Al Turki, S., et al. Rare variants in NR2F2 cause congenital heart defects in humans. Am J Hum Genet. 2014, 94(4): 574-85

