What is SNAI1 Protein
The Snail Family Transcriptional Repressor 1, or SNAI1, is a pivotal protein that plays a crucial role in various cellular processes. Also known by its aliases, such as Snail, SNA, and dJ710H13.1, this protein is a member of the Snail superfamily. Structurally, SNAI1 is characterized by its C2H2-type zinc finger domain, which is essential for its transcriptional regulatory functions. Belonging to the Snail/Slug zinc finger family, SNAI1 is classified as a transcription factor, exerting control over the expression of numerous target genes.
In recent research, advances in understanding the regulatory mechanisms of SNAI1 have unfolded. Scientists have delved into its intricate interactions within cellular pathways, shedding light on its multifaceted functions.
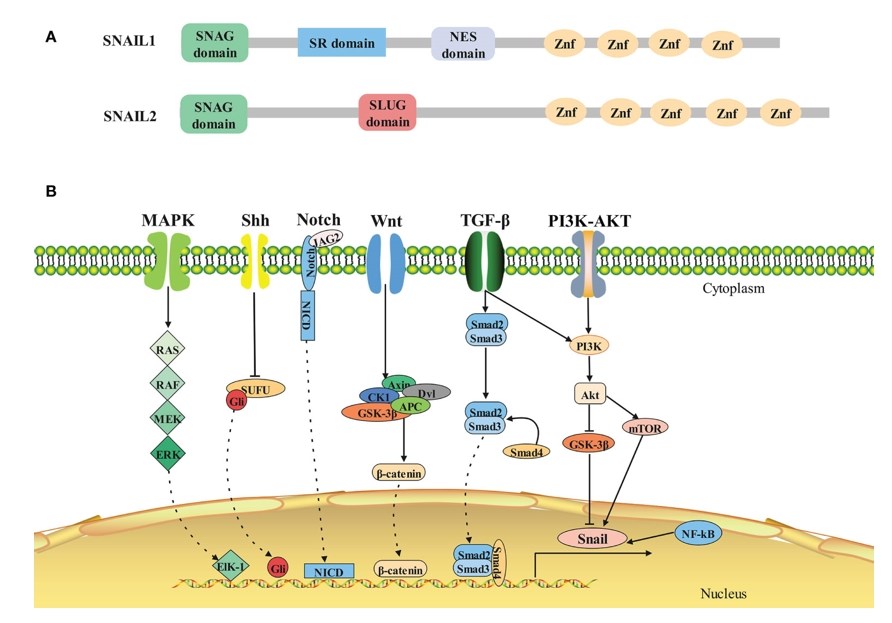
Figure 1. Structure and signaling pathways of SNAIL1. (Tang X, et al., 2021)
SNAI1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
SNAI1 primarily acts as a transcriptional repressor, orchestrating the suppression of specific target genes involved in crucial cellular processes. Its influence extends across diverse biological functions, including embryonic development, tissue differentiation, and maintenance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). EMT is a pivotal process in embryogenesis and wound healing, during which cells undergo a transformation from epithelial to mesenchymal states. At the molecular level, SNAI1 operates by binding to E-box motifs in the promoter regions of target genes, thereby inhibiting their transcription. This repression is instrumental in governing cellular plasticity, allowing cells to adapt to changing environmental cues.
SNAI1 Related Signaling Pathway
The Wnt signaling pathway stands out as a key player in regulating SNAI1 expression. Activation of Wnt signaling leads to the stabilization and nuclear translocation of β-catenin, a co-factor that collaborates with SNAI1 in promoting EMT. The interplay between Wnt signaling and SNAI1 underscores the intricate web of molecular events governing cellular behavior.
In addition to Wnt, other pathways, such as TGF-β and Notch signaling, also intersect with SNAI1, amplifying its impact on cellular processes. Deciphering these signal pathways provides a holistic understanding of SNAI1's regulatory network.
SNAI1 Related Diseases
Aberrant expression and dysregulation of SNAI1 have been implicated in various diseases, with cancer at the forefront. In cancer progression, SNAI1 contributes to the acquisition of invasive and metastatic phenotypes by promoting EMT. Elevated SNAI1 expression is often associated with poor prognosis in cancer patients, emphasizing its role as a potential biomarker.
Beyond cancer, SNAI1 has been implicated in fibrosis, where its activation contributes to tissue scarring and organ dysfunction. Understanding these pathological links provides valuable insights for developing targeted therapeutic interventions.
SNAI1's Applications in Biomedicine
Harnessing the unique properties of SNAI1 has opened new frontiers in biomedical research and development. In diagnostics, the detection of SNAI1 expression levels serves as a potential biomarker for predicting cancer prognosis and assessing disease severity. The identification of SNAI1 in tissue samples provides valuable information guiding personalized treatment strategies.
Furthermore, SNAI1's involvement in EMT makes it a promising target for vaccine and therapeutic development. Strategies aimed at modulating SNAI1 activity could potentially impede cancer metastasis and alleviate fibrotic conditions. The exploration of SNAI1 as a therapeutic target underscores its significance in combating various diseases.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNAI1-330H | Recombinant Human snail family zinc finger 1, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| SNAI1-30016TH | Recombinant Human SNAI1 | Human | Wheat Germ | N/A |
| SNAI1-178H | Recombinant Human SNAI1 protein, T7/His-tagged | Human | E.coli | T7/His |
| SNAI1-16H | Recombinant Human SNAI1, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| SNAI1-4718H | Recombinant Human SNAI1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| SNAI1-3405H | Recombinant Human SNAI1 Protein (Met1-Arg264), His tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| SNAI1-2376HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human SNAI1, Flag-tagged | Human | Mamanlian cells | Flag |
| SNAI1-15660M | Recombinant Mouse SNAI1 Protein | Mouse | Mammalian Cell | His |
| SNAI1-8511M | Recombinant Mouse SNAI1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| Snai1-5989M | Recombinant Mouse Snai1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
Reference
- Tang X, et al. SNAIL1: linking tumor metastasis to immune evasion. Frontiers in Immunology. 2021, 12: 724200.

