What is SP1 Protein?
The Specificity Protein 1, commonly referred to as SP1, is a transcription factor that was first discovered in the 1980s. This protein was initially identified due to its ability to specifically bind to the SV40 early promoter, a viral gene regulator, and activate transcription, the process of copying genetic information from DNA to RNA. The SP1 protein belongs to the Sp/KLF (Kruppel-Like Factor) family of transcription factors, whose members share a highly conserved DNA-binding domain.
With regards to its gene locus, the SP1 gene is located on chromosome 12q13.1 in humans. It spans an area of approximately 42 kb and is composed of three exons and two introns.
What Is The Structure of SP1 Protein?
The SP1 protein is known for its three zinc finger motifs found in its DNA-binding domain, which provide a structure for the protein to bind to specific gene promoter regions. Additionally, SP1 contains a glutamine-rich transactivation domain, allowing for the recruitment of other transcriptional machinery and proteins to aid in gene transcription. The protein interacts with other cellular proteins through its inhibitory domain, facilitating protein-protein interactions that regulate its transcriptional activity.
What Is The Function of SP1 Protein?
Functionally, SP1 is a versatile protein. It has been implicated in controlling a variety of biological processes such as cell differentiation, cell growth, apoptosis, immune responses, and response to DNA damage. This protein has a unique ability to bind to GC-rich promoter regions in a plethora of genes, hence playing a critical role in the regulation of these genes. Interestingly, it is known to modulate the transcription of over 12,000 genes, as indicated by bioinformatics analysis.
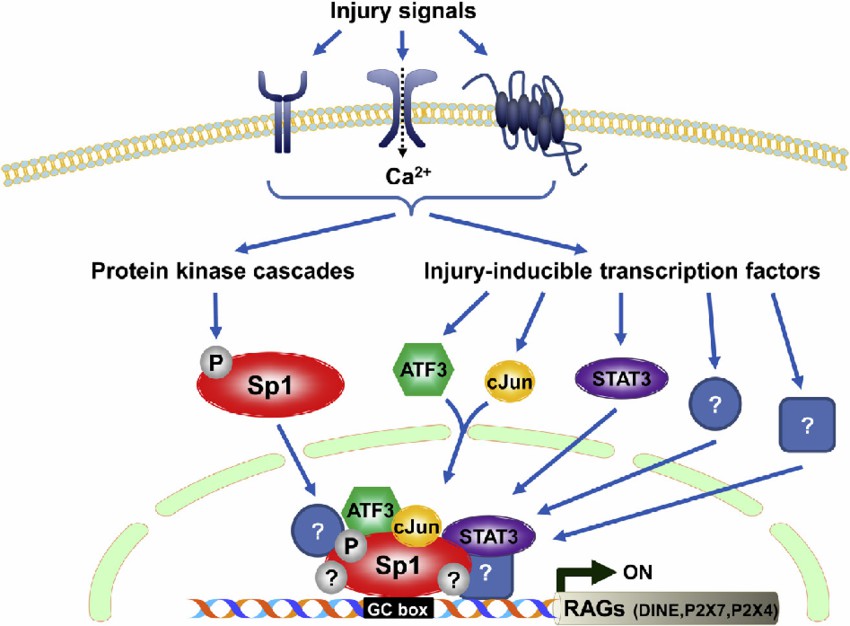
Fig1. Sp1-mediated transcriptional complex to induce the expression of regeneration-associated genes (RAGs) in response to nerve injury
SP1 protein related signal pathway
Various signaling pathways influence the function and behavior of the SP1 protein. For instance, it can be activated or inhibited by phosphorylation, acetylation, glycosylation, and sumoylation, among others, depending on the particular pathway involved. Furthermore, many growth factors and hormones can modulate SP1 activity, exemplifying the protein's central role in diverse biological processes.
SP1 protein related diseases
Given its crucial role in gene transcription regulation, it's not surprising that abnormalities in the function or expression of SP1 have been linked to a variety of diseases. Overexpression of SP1 has been observed in numerous types of cancer, including lung, breast, gastric, and colorectal cancer. This overexpression has often been associated with tumor progression and poor patient prognosis. Moreover, SP1 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's due to its involvement in the transcription of genes associated with these disorders.
Additionally, SP1 is also implicated in other conditions such as diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular diseases. The global role of SP1 protein in diverse biological processes underscores its importance and potential as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target for different diseases.
SP1 protein's applications in biomedical
In terms of its applications in biomedicine, the SP1 protein offers many opportunities. One of the most notable is its potential as both a therapeutic target and prognostic marker in various types of cancer, given its frequent overexpression in these diseases. Accordingly, multiple SP1 inhibitors have been developed and studied in the context of cancer. For instance, mithramycin and its derivatives have shown promise in preclinical and clinical studies. Furthermore, the use of gene therapy techniques to modulate SP1 expression is under exploration.
In the field of neurodegenerative diseases, controlling SP1 protein function might offer a way to modify disease progression, as it plays a pivotal role in the transcription of genes implicated in these disorders.
In conclusion, the SP1 protein, being a versatile transcription factor, plays a critical role in several biological processes. Its association with various diseases, in particular with cancers, highlights its potential as both a diagnostic tool and a therapeutic target. Indeed, while we have made significant strides in understanding the biology of the SP1 protein, there is still much to unravel about this fascinating molecule. Particularly in understanding its full spectrum of gene targets and the downstream effects they mediate in health and disease.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP1-8511H | Active Recombinant Human SP1, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| SP1-2093H | Active Recombinant Human SP1, HA & Flag-tagged | Human | Insect Cell | HA/Flag |
| SP1-590H | Recombinant Human Sp1 Transcription Factor | Human | Sf9 Insect Cell | N/A |
| SP1-30987TH | Recombinant Human SP1, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| SP1-5677R | Recombinant Rat SP1 Protein | Rat | Mammalian Cell | His |
| SP1-5336R | Recombinant Rat SP1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Miras-Portugal, M. Teresa & Gomez-Villafuertes, Rosa & Gualix, Javier & Díaz-Hernandéz, Juan & Artalejo, Antonio & Ortega, Felipe & Delicado, Esmerilda & Pérez-Sen, Raquel. (2016). Nucleotides in neuroregeneration and neuroprotection. Neuropharmacology. 104. 243-254. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.09.002.

