What is ST6GAL1 Protein
What is ST6GAL1 Protein?
ST6GAL1, short for Alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 1, is a crucial enzyme encoded by the ST6GAL1 gene. This gene is responsible for the synthesis of a glycosyltransferase that plays a pivotal role in glycoprotein and glycolipid biosynthesis. Specifically, ST6GAL1 catalyzes the transfer of sialic acid, a nine-carbon monosaccharide, to the terminal positions of glycoprotein and glycolipid carbohydrates, modulating their biological activities.
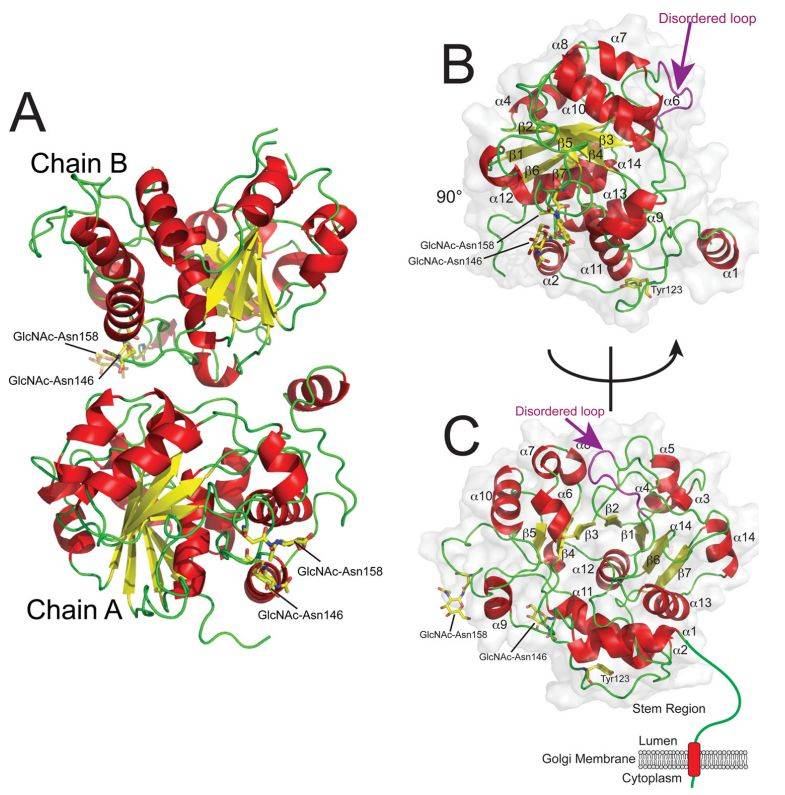
Figure 1. Schematic representations of the ST6GAL1 structure. (Meng, L., et al. 2013)
The Function of ST6GAL1 Protein
At its core, the ST6GAL1 protein's primary function lies in the realm of sialylation. Through this enzymatic process, ST6GAL1 intricately modifies glycoproteins and glycolipids, significantly influencing their biological activities. The addition of sialic acid, facilitated by ST6GAL1, modulates cell adhesion dynamics and plays a pivotal role in immune response regulation.
- Sialylation and Cell Adhesion
Sialylation's impact on cell adhesion is a testament to the functional relevance of ST6GAL1. By modifying glycoproteins on cell surfaces, this enzyme influences the binding properties of cells. The resulting alterations in cell adhesion dynamics have implications for various physiological processes, underlining the importance of ST6GAL1 in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
- Sialylation and Immune Response
The sialic acid residues added by ST6GAL1 act as signals for immune cells, contributing to the intricate balance of immune system function. The dynamic interplay between ST6GAL1-mediated sialylation and immune response highlights the enzyme's multifaceted role in cellular physiology.
ST6GAL1-Related Diseases
The dark side of ST6GAL1 emerges when its expression goes awry, contributing to various diseases. In the context of cancer, dysregulated ST6GAL1 expression has been a recurrent theme. Elevated levels of this enzyme foster increased sialylation on the cell surface, bestowing cancer cells with advantages in survival, migration, and invasion.
- Cancer Progression
The enzyme's role in modulating cell adhesion properties promotes the invasive potential of cancer cells. Aberrant sialylation patterns, orchestrated by ST6GAL1, emerge as key players in the metastatic cascade, providing a potential target for interventions aimed at impeding cancer progression.
- Neurodegenerative Disorders
Altered sialylation patterns, attributed to ST6GAL1, have been observed in conditions such as Alzheimer's disease. The interplay between ST6GAL1 and neural glycosylation adds a layer of complexity to the understanding of neurodegenerative diseases, paving the way for novel avenues of research.
ST6GAL1 Related Signaling Pathways
Delving into the signaling pathways associated with ST6GAL1 unravels the intricate tapestry of cellular regulation. Two prominent pathways—Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Notch signaling—emerge as key players influenced by ST6GAL1.
- ST6GAL1 and EGFR Pathway
ST6GAL1's impact on the EGFR pathway is a testament to its role in cancer progression. By mediating the sialylation of EGFR, ST6GAL1 can modulate downstream signaling cascades. This interaction becomes a focal point for understanding the dysregulation of cellular processes in cancer cells, offering potential avenues for targeted therapies.
- ST6GAL1 and Notch Signaling
The intricate crosstalk between ST6GAL1 and the Notch signaling pathway adds another layer of complexity to cellular regulation. Sialylation of Notch receptors by ST6GAL1 influences their interactions and activation, contributing to the intricate web of cellular fate determination and development.
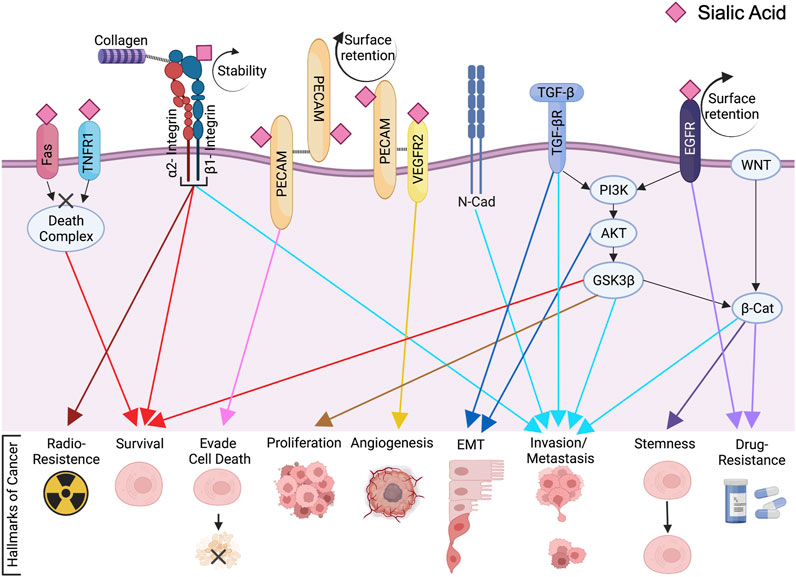
Figure 1. ST6Gal1-mediated Signaling Cascades in Cancer. (Gc, S., et al. 2022)
Applications of ST6GAL1 in Biomedical Research
The therapeutic potential of modulating ST6GAL1 activity and its diagnostic significance are garnering increasing attention.
- ST6GAL1 Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy
The development of ST6GAL1 inhibitors emerges as a promising strategy in the fight against cancer. Targeting aberrant sialylation patterns mediated by elevated ST6GAL1 expression holds the potential to disrupt pro-metastatic properties, providing a novel avenue for anticancer drug development.
- ST6GAL1 as a Diagnostic Biomarker
Aberrant ST6GAL1 expression in diseases, particularly cancer, positions it as a potential diagnostic biomarker. Detecting altered ST6GAL1 levels in patient samples offers a window into disease presence and progression, enhancing diagnostic precision and early intervention strategies.
- ST6GAL1 in Glycoengineering for Therapeutics
The manipulation of sialylation patterns by ST6GAL1 is gaining traction in glycoengineering for therapeutic purposes. This approach aims to enhance the efficacy of biopharmaceuticals by optimizing their glycosylation profiles. The potential impact on pharmacokinetics, stability, and immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins presents a frontier in personalized medicine.
From its fundamental functions to its involvement in diseases and burgeoning applications in biomedicine, ST6GAL1 stands as a captivating subject of study. As research progresses, the tantalizing prospect of leveraging ST6GAL1 for targeted therapies and diagnostic innovations beckons, ushering in a new era of precision medicine.
Recommended Products for ST6GAL1 Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST6GAL1-27H | Human | Active Recombinant Human ST6GAL1 Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian cells | His |
| ST6GAL1-1122H | Human | Recombinant Human ST6GAL1, His tagged | HEK293 | His |
| ST6GAL1-2720H | Human | Recombinant Human ST6GAL1 Full Length Transmembrane protein (1-406 aa), His-tagged | In vitro E. coli expression system | His |
| ST6GAL1-4147H | Human | Recombinant Human ST6GAL1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| ST6GAL1-2739H | Human | Recombinant Human ST6GAL1 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | N-His |
| St6gal1-7036M | Mouse | Active Recombinant Mouse St6gal1, His tagged | HEK293 | His |
| ST6GAL1-961R | Rat | Recombinant Rat ST6GAL1 Protein (Lys27-Cys403), His-tagged | HEK293 | His |
| ST6GAL1-4501R | Rhesus Macaque | Recombinant Rhesus monkey ST6GAL1 Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian Cell | His |
| ST6GAL1-1140Z | Zebrafish | Recombinant Zebrafish ST6GAL1 | Mammalian Cell | His |
| ST6GAL1-6794C | Chicken | Recombinant Chicken ST6GAL1 | Mammalian Cell | His |
References
- Meng, L., et al. Enzymatic basis for N-glycan sialylation: structure of rat α2,6-sialyltransferase (ST6GAL1) reveals conserved and unique features for glycan sialylation. J Biol Chem. 2013, 288(48): 34680-98.
- Gc, S., et al. ST6Gal1: Oncogenic signaling pathways and targets. Front Mol Biosci. 2022, 9: 962908.

