What is TFF2 Protein
TFF2, or Trefoil Factor 2, stands as a pivotal player in the intricate symphony of proteins orchestrating biological functions within the human body. Also recognized by the moniker "Spasmolytic Polypeptide," this protein belongs to the trefoil factor family, a group characterized by the presence of trefoil motifs. Scientifically, TFF2 is encoded by the TFF2 gene, and its synonyms include "spasmolytic polypeptide/trefoil factor 2" and "intestinal trefoil factor."
TFF2 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
In terms of structural characteristics, TFF2 exhibits a unique arrangement. The trefoil motif, composed of three disulfide-bonded loops, imparts a stable and characteristic structure. Its classification places it within the trefoil factor family, which comprises mucin-associated proteins involved in mucosal protection and repair.
Recent research has unveiled exciting insights into TFF2, shedding light on its diverse roles in maintaining homeostasis within the gastrointestinal tract. The multifaceted nature of this protein has captivated researchers, leading to a deeper understanding of its implications in health and disease.
TFF2 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
TFF2's biological functions are as diverse as its structural characteristics. Primarily expressed in the gastrointestinal tract, particularly in the stomach and duodenum, TFF2 plays a crucial role in mucosal protection and repair. It is involved in maintaining the integrity of the epithelial barrier, defending against various insults such as chemical damage and inflammation.
At the molecular level, TFF2 operates through several mechanisms. It promotes cell migration and proliferation, aiding in the repair of damaged mucosa. Additionally, it contributes to the formation of the mucus gel layer, acting as a protective shield for the underlying epithelial cells. The interaction between TFF2 and mucins, the major components of mucus, further highlights its role in bolstering the defense mechanisms of the gastrointestinal tract.
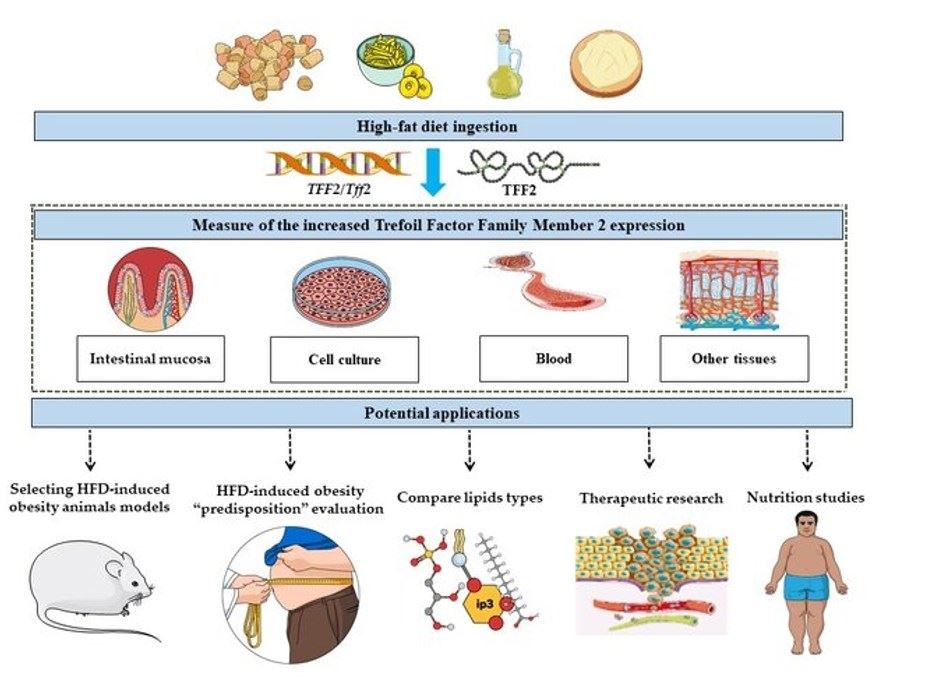
Figure 1. TFF2 expression as an indicator of the severity of the high-fat diet-induced obesity. (Ghanemi A, et al., 2021)
TFF2 Related Signaling Pathway
The intricate signaling pathways involving TFF2 further illuminate its functional relevance. TFF2 expression is influenced by various factors, including growth factors and cytokines. The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, known for its involvement in cellular responses to external stimuli, plays a crucial role in regulating TFF2 expression.
Moreover, TFF2 has been implicated in the modulation of inflammatory signaling pathways, indicating its role in the intricate interplay between the immune system and the gastrointestinal environment. Elucidating these signal pathways enhances our understanding of how TFF2 contributes to the maintenance of mucosal homeostasis.
TFF2 Related Diseases
The dysregulation of TFF2 has been linked to various diseases, emphasizing its significance in maintaining gastrointestinal health. Reduced TFF2 levels have been associated with conditions such as peptic ulcers and inflammatory bowel diseases. In these instances, the compromised mucosal defense mechanisms can lead to increased susceptibility to damage and delayed healing.
Understanding the role of TFF2 in disease pathogenesis provides valuable insights for developing targeted therapeutic interventions. Research efforts are underway to explore the potential of modulating TFF2 expression or activity to alleviate symptoms and promote mucosal healing in conditions characterized by impaired gastrointestinal function.
TFF2's Applications in Biomedicine
Beyond its physiological roles, TFF2 has garnered attention for its potential applications in biomedical research and development. In diagnostic development, TFF2 serves as a biomarker for gastrointestinal disorders, providing clinicians with valuable information about mucosal health. Its presence or absence can be indicative of underlying pathologies, aiding in the accurate diagnosis of gastrointestinal conditions.
In vaccine development, TFF2's role in mucosal immunity positions it as a potential target for enhancing vaccine efficacy. Harnessing its ability to promote mucosal defense mechanisms could pave the way for the development of vaccines that offer enhanced protection against gastrointestinal infections.
The therapeutic potential of TFF2 is also being explored, with researchers investigating its use in promoting mucosal healing and mitigating inflammation in gastrointestinal diseases. The development of TFF2-based therapeutics holds promise for improving outcomes in conditions where mucosal damage is a central feature.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFF2-1045H | Recombinant Human TFF2,His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| TFF2-30657TH | Recombinant Human TFF2 protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| TFF2-3203H | Recombinant Human TFF2, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| TFF2-659H | Recombinant Human Trefoil Factor 2 | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| TFF2-588H | Recombinant Human TFF2 Protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| TFF2-049T | Active Recombinant Human TFF2 Protein (106 aa) | Human | E.coli | |
| TFF2-5458H | Recombinant Human TFF2 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| Tff2-835R | Recombinant Rat Tff2 protein, His-tagged | Rat | E.coli | His |
| TFF2-6029R | Recombinant Rat TFF2 Protein | Rat | Mammalian Cell | His |
| TFF2-5688R | Recombinant Rat TFF2 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Ghanemi A, Yoshioka M, St-Amand J. Trefoil factor family member 2 expression as an indicator of the severity of the high-fat diet-induced obesity. Genes. 2021, 12(10): 1505.

