CEACAM6
-
Official Full Name
CEACAM6 carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (non-specific cross reacting antigen) -
Overview
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA; MIM 114890) is one of the most widely used tumor markers in serum immunoassay;determinations of carcinoma. An apparent lack of absolute cancer specificity for CEA probably results in part from the;presence in normal and neoplastic tissues of antigens that share antigenic determinants with the 180-kD form of CEA;(Barnett et al., 1988 (PubMed 3220478)). For background information on the CEA family of genes, see CEACAM1 (MIM;109770). -
Synonyms
CEACAM6;carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (non-specific cross reacting antigen);NCA;CEAL;CD66c;carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell;CD66c antigen;Non-specific crossreacting antigen;carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell;adhesion molecule 6;Sulesomab;LeukoScan;167747-19-5
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Cynomolgus
- HEK293
- C-His
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Mammalian Cells
- His
- GST
- Non
- T7
- Fc
- Avi
- SUMO
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEACAM6-664H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His | Lys35-Gly320 | |
| CEACAM6-1536C |
Recombinant Cynomolgus CEACAM6 protein, His-tagged
|
C-His | Cynomolgus | Gln35-Gly320 |
|
|
| CEACAM6-1096H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 Protein, GST-Tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| CEACAM6-221H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6, C13&N15-labeled | HEK293 | Human | Non | 35-320 a.a. |
|
| CEACAM6-27919TH | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 110 amino acids |
|
| CEACAM6-8197H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&T7 | Lys35~Pro142 |
|
| CEACAM6-2797HCL | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 cell lysate | Human Cells | Human | Non |
|
|
| CEACAM6-046C | Recombinant Cynomolgus CEACAM6 Protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Cynomolgus | His | Met1-Pro323 |
|
| CEACAM6-1308H | Active Recombinant Human CEACAM6 protein, Fc-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Fc | 35-320 a.a. |
|
| CEACAM6-179H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 Protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His | 344 |
|
| CEACAM6-199H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 protein, His-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Avi&His | Lys35-Gly320 |
|
| CEACAM6-2684H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 protein, His-SUMO-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&SUMO | 35-320aa |
|
| CEACAM6-3191H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His |
|
|
| CEACAM6-3275HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CEACAM6 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 344 amino acids |
|
| CEACAM6-3324H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Lys35~Pro142 |
|
| CEACAM6-335H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 protein, His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated | HEK293 | Human | Avi&His | Lys35-Gly320 |
|
| CEACAM6-42H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 Protein (ECD), His-tagged(C-ter) | HEK293 | Human | His | Lys35-Gly320 |
|
| CEACAM6-4661H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 Protein (Met1-Gly320), C-His tagged | Mammalian Cells | Human | His | Met1-Gly320 |
|
| CEACAM6-664HB | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 protein, His-tagged, Biotinylated | HEK293 | Human | His | 1-320 a.a. |
|
Background
What is CEACAM6 protein?
CEACAM6 gene (CEA cell adhesion molecule 6) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19q13. This gene encodes a protein that belongs to the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) family whose members are glycosyl phosphatidyl inositol (GPI) anchored cell surface glycoproteins. Members of this family play a role in cell adhesion and are widely used as tumor markers in serum immunoassay determinations of carcinoma. This gene affects the sensitivity of tumor cells to adenovirus infection. The CEACAM6 protein is consisted of 344 amino acids and CEACAM6 molecular weight is approximately 37.2 kDa.
What is the function of CEACAM6 protein?
CEACAM6 is a cell adhesion molecule belonging to the CEA family. It plays an important role in a variety of cancers, including promoting tumor proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. CEACAM6 is usually upregulated in a variety of cancers, including pancreatic, breast, non-small cell lung, gastric, and colorectal cancers, and is associated with poor prognosis. It promotes tumor cell proliferation, invasion, migration, resistance to apoptosis and chemotherapy, and angiogenesis by activating downstream signaling pathways such as ERK1/2/MAPK or SRC/FAK/PI3K/AKT, directly or through EGFR. In addition, CEACAM6 expression is regulated by a variety of factors, including the CD151/TGF-β1/Smad3 axis, multiple micrornas (such as miR-146, miR-26a, miR-29a/b/c, etc.), and DNA methylation. In terms of clinical applications, CEACAM6 is a potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target, and monoclonal antibodies and molecular therapeutic strategies targeting CEACAM6 are being developed for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer.
CEACAM6 related signaling pathway
CEACAM6 is a cell surface molecule that plays a role in a variety of biological processes, including cell adhesion, signaling, and cell migration. In cancer, CEACAM6 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by interacting with multiple signaling pathways. It can activate signaling pathways such as PI3K/AKT and ERK/MAPK, thereby promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) and increasing the migration and invasion ability of tumor cells. In addition, CEACAM6 is involved in the regulation of tumor angiogenesis and immune responses in the tumor microenvironment. Clinically, CEACAM6 expression levels are associated with the prognosis of a variety of cancers, making it a potential diagnostic marker and therapeutic target.
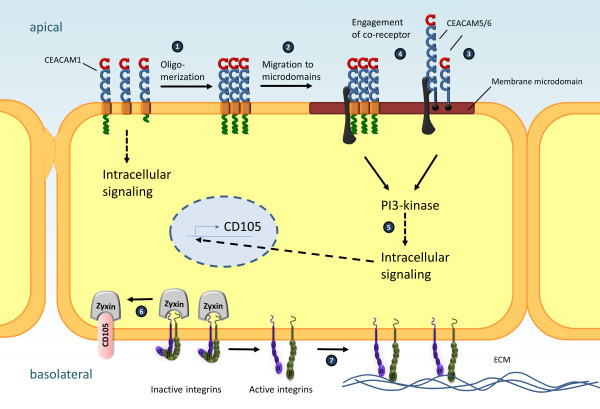
Fig1. Signaling initiated by epithelial CEACAMs. (Arnaud Kengmo Tchoupa, 2014)
CEACAM6 related diseases
CEACAM6 plays an important role in a variety of cancers, including pancreatic, lung, stomach, colorectal, breast, cholangiocarcinoma, ovarian, head and neck cancer, osteosarcoma, acute leukemia, and urinary system tumors. It is commonly upregulated in these cancers and is associated with tumor aggressiveness, metastasis, drug resistance, and poor prognosis. CEACAM6 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of tumor cells by activating various signaling pathways, such as PI3K/AKT, ERK/MAPK, etc. In addition, CEACAM6 expression is regulated by multiple factors, including miRNA, DNA methylation, and protein glycosylation. Clinically, high expression of CEACAM6 is associated with poor prognosis in a variety of cancers, making it a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target.
Bioapplications of CEACAM6
CEACAM6 plays a catalytic role in a variety of cancers, including pancreatic, stomach, lung, colorectal, and more. It plays a key role in tumor occurrence and development by promoting tumor invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis, inhibiting tumor apoptosis, and increasing tumor resistance to chemotherapy drugs. High expression of CEACAM6 is often associated with poor patient outcomes. Therapeutic strategies targeting CEACAM6, such as the development of specific antibodies, have been shown to inhibit tumor invasion and metastasis and increase the sensitivity of tumor cells to apoptosis, providing new research directions for early diagnosis and treatment of cancer. In addition, CEACAM6 also plays an important role in modulating the immune response in the tumor microenvironment, and its potential in cancer therapy is gradually being explored, including as a target for cancer therapy and as a component of immunotherapy.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Shah Kamranur Rahman, 2021
Influenza A virus (IAV) enters human lung cells by binding to the host glycoprotein CD66c, a receptor not previously identified. This study demonstrates that IAV's neuraminidase protein interacts with CD66c on the cell surface, and increasing CD66c levels enhances viral entry. CD66c's binding capacity surpasses that of other glycoproteins like EGFR and DC-SIGN, which are known to aid IAV entry. Reducing CD66c with siRNA or blocking it with antibodies inhibits viral binding and entry. CD66c specificity for IAV is confirmed by its lack of impact on Hepatitis C virus entry. Moreover, pre-incubating IAV with recombinant CD66c protein and administering it intranasally in mice reduces lung cytopathic effects, suggesting CD66c's role in IAV infection.
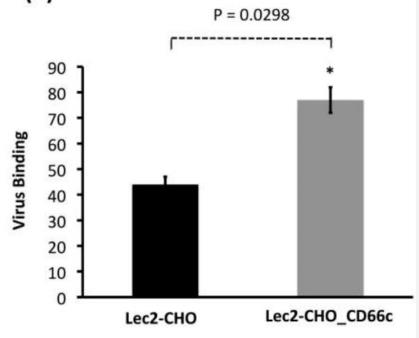
Fig1. Lec2 CHO-CD66c is CD66c overexpressing Lec2 CHO cell lines.
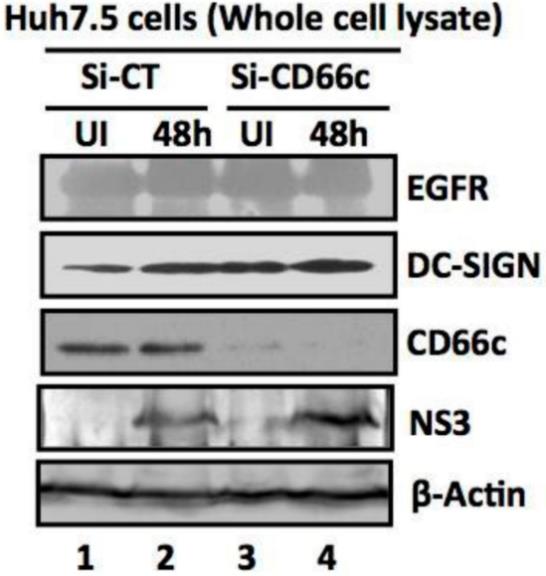
Fig2. siRNA knockdown of CD66c in Huh7.5 cells have not inhibited entry of another non-IAV virus.
Case Study 2: Jacqueline I Keenan, 2014
Exclusive enteral nutrition (EEN) is a recognized first-line treatment for inducing remission in active Crohn's disease (CD), particularly in pediatric patients, yet the specific mechanisms behind its efficacy are not completely understood. This study utilized the Caco-2 human adenocarcinoma cell line to demonstrate that exposure to a polymeric formula (PF), a form of EEN, leads to a dose-dependent upregulation of CEACAM6, an adhesion molecule that plays a role in CD pathogenesis by facilitating the binding of adherent-invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC) to the intestinal lining. Notably, the increase in CEACAM6 expression was most pronounced on the cell surface. Additionally, PF treatment doubled the secretion of soluble CEACAM6 by Caco-2 cells, and this elevated release was associated with a reduced capacity of AIEC to adhere to intestinal epithelial cells.
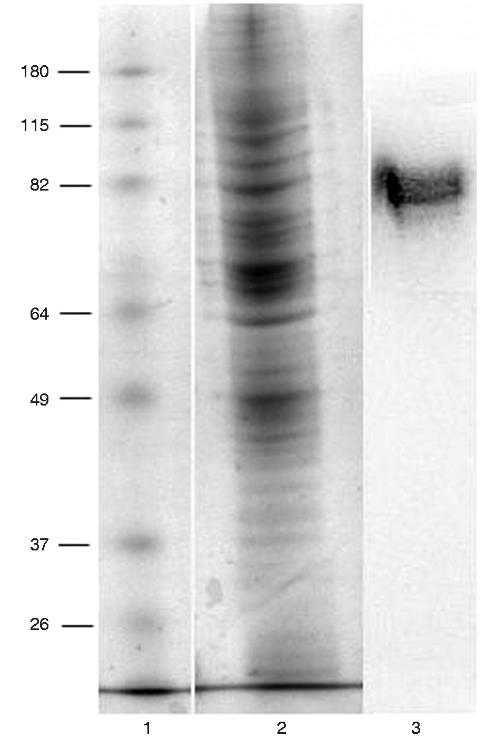
Fig3. Detection of CEACAM6 in a Caco-2 cell lysate.
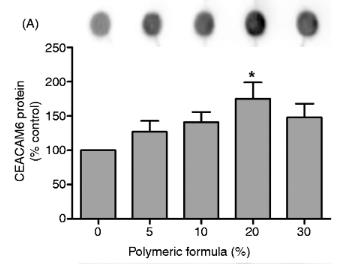
Fig4. PF added to Caco-2 cells for 24 h had a dose-dependent effect on CEACAM6 expression.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CEACAM6-664H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CEACAM6-8197H)
Involved Pathway
CEACAM6 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CEACAM6 participated on our site, such as Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall,Extracellular matrix organization,Fibronectin matrix formation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CEACAM6 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall | SLC3A2B,ANGPT2A,SIRPA,ITGB1B.1,CD177,AMICA1,GRB14,PROCR,GAS6,PPIA |
| Hemostasis | MFN1,CD84,DGKB,RHOB,IRF1B,GATA6,SERPINE2,CLEC1B,F3B,PDE10A |
| Extracellular matrix organization | FBN1,LTBP4,CTSB,BSG,COL5A3A,MATN1,SPARC,SERPINH1,MMP12,PPIB |
| Fibronectin matrix formation | CEACAM8,CEACAM1,FN1B |
Protein Function
CEACAM6 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CEACAM6 itself. We selected most functions CEACAM6 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CEACAM6. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | DES,MAP1LC3B,SPTA1,ALK,GAK,C17orf28,NTRK1,VEGFAB,STARD13,GATA1A |
Interacting Protein
CEACAM6 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CEACAM6 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CEACAM6.
CARTPT;CEACAM5;CEACAM1;CEACAM8;CEACAM7
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Lee, OJ; Son, SM; et al. CEACAM6 as detected by the AP11 antibody is a marker notable for mucin-producing adenocarcinomas. VIRCHOWS ARCHIV 466:151-159(2015).
- Aleandri, M; Conte, MP; et al. Influenza A Virus Infection of Intestinal Epithelial Cells Enhances the Adhesion Ability of Crohn's Disease Associated Escherichia coli Strains. PLOS ONE 10:-(2015).



