USP13
-
Official Full Name
ubiquitin specific peptidase 13 (isopeptidase T-3) -
Overview
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 13 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the USP13 gene. -
Synonyms
USP13;ubiquitin specific peptidase 13 (isopeptidase T-3);ubiquitin specific protease 13 (isopeptidase T 3);ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 13;IsoT 3;isopeptidase T-3;ubiquitin thioesterase 13;deubiquitinating enzyme 13;ubiquitin thiolesteras
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- HeLa
- GST
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is USP13 protein?
USP13 gene (ubiquitin specific peptidase 13) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3q26. Enables several functions, including BAT3 complex binding activity; chaperone binding activity; and cysteine-type peptidase activity. Involved in several processes, including maintenance of unfolded protein involved in ERAD pathway; regulation of cellular catabolic process; and regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Acts upstream of or within protein deubiquitination and protein stabilization. Predicted to be located in nucleoplasm. Predicted to be active in cytosol and nucleus. The USP13 protein is consisted of 863 amino acids and USP13 molecular weight is approximately 97.3 kDa.
What is the function of USP13 protein?
USP13 promotes the successful entry of cells into the M phase by stabilizing AuroraB and CDH1, which is critical for cell cycle regulation. In addition to its anti-apoptotic role in apoptosis, USP13 also has non-apoptotic functions such as regulatory roles in cell cycle, DNA damage response, autophagy, and endoplasmic reticulum quality control. USP13 plays a role in DNA damage response, protecting genomic stability and integrity by stabilizing effector molecules such as RAP80 and TopBP1. USP13 is associated with the process of autophagy, and it interacts with Beclin1 to promote autophagy by stabilizing the VPS34 complex, which is critical for cells to clear damaged and aging organelles. USP13 is involved in the endoplasmic reticulum associated degradation (ERAD) process, maintaining protein folding and degradation balance, and plays an important role in ER stress response.
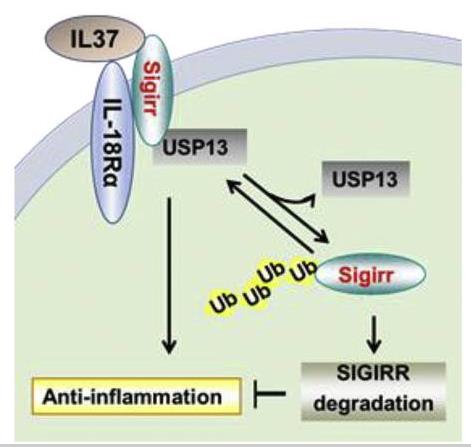
Fig1. USP13 plays an anti-inflammatory role through the stabilization of Sigirr. (Lian Li, 2019)
USP13 Related Signaling Pathway
USP13 inhibits AKT signaling by deubiquitinating and stabilizing PTEN protein, thereby affecting cell growth and metabolism. PTEN is a tumor suppressor that controls cell growth and metabolism by inhibiting the AKT signaling pathway. USP13 interacts with PTEN to protect PTEN from proteasome degradation, thereby inhibiting tumor formation and glycolysis. USP13 is involved in DNA damage response, promoting BRCA1 recruitment and DNA repair through deubiquitination and stabilization of RAP80 protein. USP13 is involved in the endoplasmic reticulum associated degradation (ERAD) process, maintaining the balance of protein folding and degradation in the ER through deubiquitination and stabilization of associated substrate proteins. USP13 promotes the smooth progression of the cell cycle by deubiquitinating and stabilizing AuroraB and CDH1. The role of USP13 in cell cycle regulation is critical for cell proliferation and division.
USP13 Related Diseases
USP13 plays an important role in a variety of cancers, including lung, ovarian, cervical, hepatocellular, glioblastoma, melanoma, and stomach cancer. The role of USP13 in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD) is closely related to the occurrence and development of neurodegenerative diseases. USP13 affects the antiviral response in viral infection by regulating the stability of STAT1 and STING. USP13 inhibits inflammation through past ubiquitination and stabilizes Sigirr and PTEN.
Bioapplications of USP13
USP13 inhibits the inflammatory response by regulating anti-inflammatory pathways, such as by stabilizing Sigirr and PTEN, which opens the possibility for the development of new anti-inflammatory drugs. The role of USP13 in modulating the antiviral response suggests that its inhibitors may help boost host defenses against viral infection. USP13's role in cell cycle regulation makes it potentially useful in cell biology research and the treatment of related diseases. The function of USP13 in response to DNA damage opens up the possibility of developing targeted therapies for specific genetic diseases or cancers. The deubiquitinating enzyme activity of USP13 makes it a promising target for drug development, especially the development of its specific inhibitors, such as Spautin-1, which have shown antitumor effects in preclinical models.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Juntae Kwon, 2023
Lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) is associated with high mortality and limited targeted therapies. USP13 is one of the most amplified genes in LUSC, yet its role in lung cancer is largely unknown. Here, researchers established a novel mouse model of LUSC by overexpressing USP13 on KrasG12D/+; Trp53flox/flox background (KPU). KPU-driven lung squamous tumors faithfully recapitulate key pathohistological, molecular features, and cellular pathways of human LUSC. They found that USP13 altered lineage-determining factors such as NKX2-1 and SOX2 in club cells of the airway and reinforced the fate of club cells to squamous carcinoma development. This study showed a strong molecular association between USP13 and c-MYC, leading to the upregulation of squamous programs in murine and human lung cancer cells.
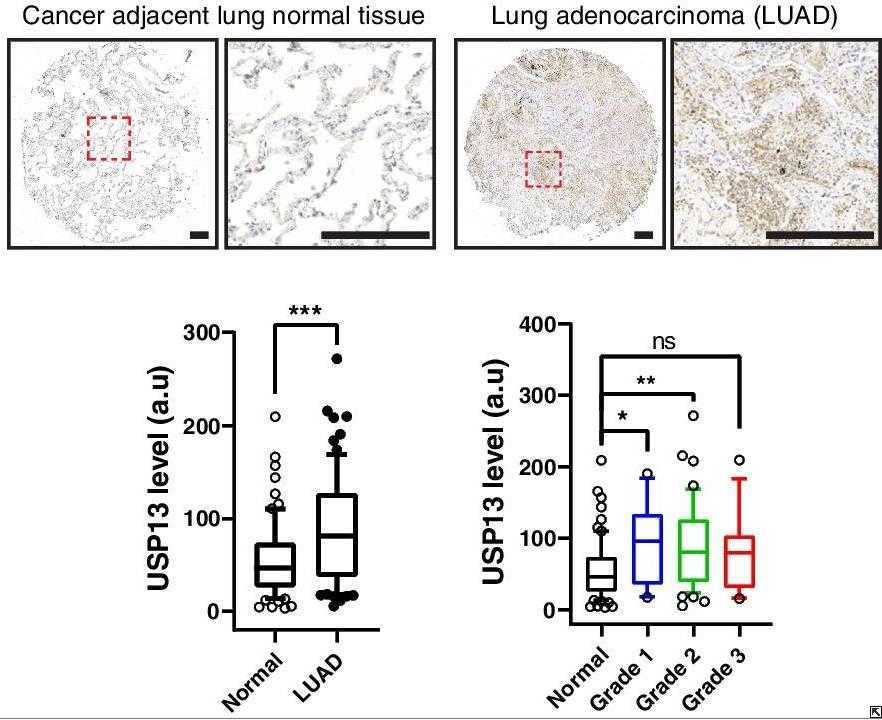
Fig1. USP13 protein level in human LUAD.
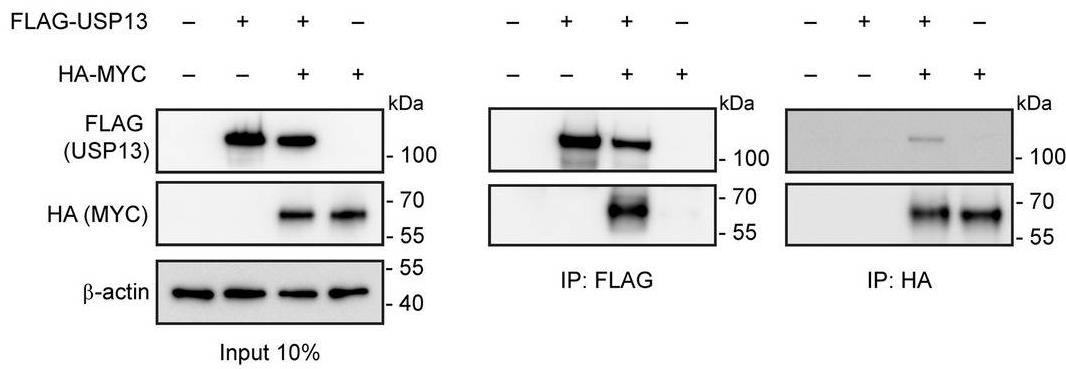
Fig2. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of exogenous FLAG-USP13 and HA-MYC in HEK293T cells.
Case Study 2: Juntae Kwon, 2022
Ubiquitin-specific Peptidase 13 (USP13) is a deubiquitinating enzyme that regulates the stability or function of its substrate. USP13 is highly amplified in human ovarian cancer, and elevated expression of USP13 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis of ovarian cancer. However, there is little known about USP13 post-translational modifications and their role in ovarian cancer. Here, researchers found that USP13 is phosphorylated at Thr122 in ovarian cancer cells. Phosphorylated Thr122 (pT122) on endogenous USP13 was observed in most human ovarian cancer cells, and the abundance of this phosphorylation was correlated to the total level of USP13. They further demonstrated that Casein kinase 2 (CK2) directly interacts with and phosphorylates USP13 at Thr122, which promotes the stability of USP13 protein.
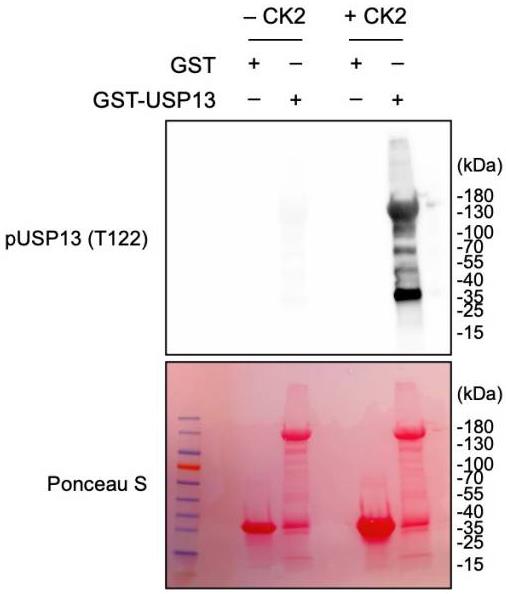
Fig3. CK2 phosphorylates USP13 in vitro.
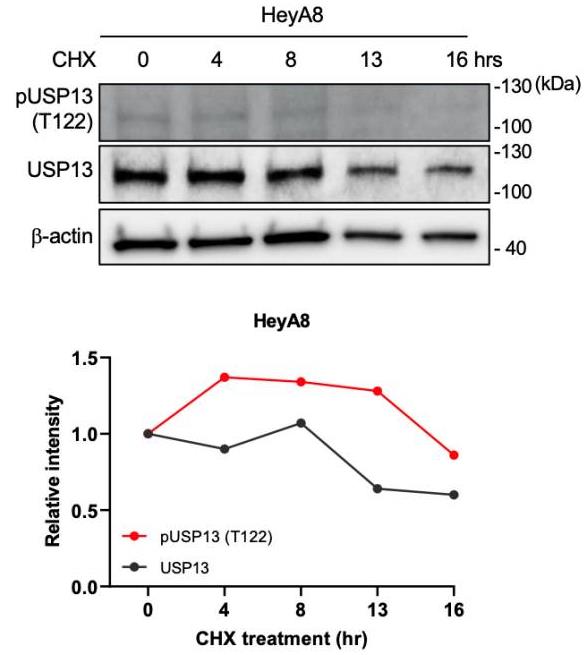
Fig4. The stability of total USP13 and pT122 USP13 was measured in Hey8A cells.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (USP13-2648H)
Involved Pathway
USP13 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways USP13 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with USP13 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
USP13 has several biochemical functions, for example, BAT3 complex binding,chaperone binding,cysteine-type endopeptidase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by USP13 itself. We selected most functions USP13 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with USP13. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | CASP2,CASP10,Casp3,CTSSA,USP9,CTS7,CTSS,USP40,USP3,USP19 |
| BAT3 complex binding | SGTA,AMFR,VCP |
| ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding | CEBPB,VCP,TRIP4,DDRGK1,CDK5RAP3 |
| chaperone binding | AHSA2,HLA-B,PACRG,AMFR,DNAJA3B,GRPEL1,SLC25A17,HSPA5,HSCB,BAG4 |
| proteasome binding | PSMG1,BAG6,UBD,PSMD14,PSMF1,USP14,ADRM1,UCHL5,DNAJB2,ID1 |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | UBE2J1,MC1R,UBE2T,SMAD5,CUL1B,SQSTM1,AKTIP,CHEK2,ANKRD32,ASB4 |
| protein binding | RAB22A,CCDC153,STAM,GAB2,MITD1,SH3BP1,KIFAP3,PDS5B,HDAC7,SENP3 |
| ubiquitin-specific protease activity | FMNL3,OTUB1A,USP31,OTUD5A,USP10,USP27X,USP1,USP2A,DUB1,OTUD6A |
| zinc ion binding | GATA3,MUL1A,NR1D2B,PHF20L1,YAF2,XRN2,CCNB1IP1,TRIM39,PDLIM5,FNTB |
Interacting Protein
USP13 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with USP13 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of USP13.
SMC1A;SMC3;UBL4A;DLST;USP5;BAG6;ATXN3;OGDH;NEDD8;NPLOC4;UFD1L;FAF2;ITCH;KCTD10;CACYBP;CYLD;DIABLO;TCAF1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Liu, YF; Soetandyo, N; et al. USP13 antagonizes gp78 to maintain functionality of a chaperone in ER-associated degradation. ELIFE 3:-(2014).
- Xiang, SJ; Fang, JQ; et al. MicroRNA-135b regulates the stability of PTEN and promotes glycolysis by targeting USP13 in human colorectal cancers. ONCOLOGY REPORTS 33:1342-1348(2015).



