Neurotransmitter Transporters
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
About Neurotransmitter Transporters
Neurotransmitter transporters are integral membrane proteins that play a crucial role in the regulation of neurotransmitter levels in the brain and other parts of the nervous system. These transporters are responsible for the reuptake of released neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft back into the presynaptic neuron, thereby terminating the synaptic transmission.
There are several types of neurotransmitter transporters, each specific to a particular neurotransmitter. Some examples include the dopamine transporter (DAT), serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and gamma-aminobutyric acid transporter (GAT). These transporters are highly selective and only transport their specific neurotransmitter.
The function of neurotransmitter transporters is essential for maintaining the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain. By reabsorbing neurotransmitters, they prevent their accumulation in the synaptic cleft, which could lead to excessive activation of postsynaptic receptors and impaired neuronal signaling.
The activity of neurotransmitter transporters is tightly regulated and can be modulated by various factors. For example, drugs such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) bind to the serotonin transporter and block its activity, increasing the concentration of serotonin in the synaptic cleft and enhancing its effects. Similarly, some drugs of abuse, like cocaine and amphetamines, target dopamine transporters and interfere with the reuptake of dopamine, leading to increased dopamine levels and prolonged activation of dopamine receptors.
Dysfunction or dysregulation of neurotransmitter transporters has been implicated in various neurological and psychiatric disorders. For instance, abnormalities in dopamine transporters have been associated with Parkinson's disease and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), while alterations in serotonin transporters have been linked to depression and anxiety disorders.
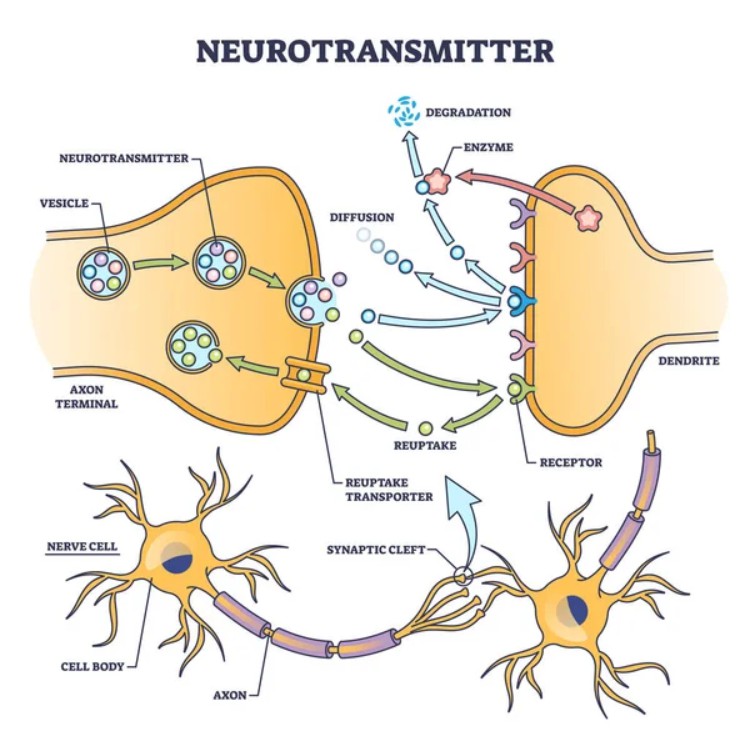
Biological Functions of Neurotransmitter Transporters
Neurotransmitter transporters are integral membrane proteins responsible for the reuptake and recycling of neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft back into the presynaptic neuron. These transporters play crucial roles in regulating neurotransmitter levels and terminating synaptic transmission. Here are some key biological functions of neurotransmitter transporters:
Reuptake of Neurotransmitters: Neurotransmitter transporters primarily function to remove neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft after release. They actively transport neurotransmitter molecules from the extracellular space back into the presynaptic neuron. This reuptake process helps terminate the signaling of neurotransmitters and allows for the recycling of neurotransmitter molecules for subsequent release.
Regulation of Neurotransmitter Levels: By controlling the reuptake of neurotransmitters, transporters regulate the concentration of neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft. This regulation is crucial for maintaining proper neurotransmission and preventing excessive or prolonged signaling. Dysregulation of neurotransmitter transporters can lead to abnormal neurotransmitter levels and contribute to various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Termination of Synaptic Transmission: Neurotransmitter transporters play a key role in terminating synaptic transmission. By removing neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft, transporters reduce the concentration of neurotransmitters available for binding to postsynaptic receptors. This helps to rapidly terminate the effects of neurotransmitters, allowing for precise control and temporal dynamics of synaptic signaling.
Replenishment of Neurotransmitter Vesicles: In addition to reuptake, neurotransmitter transporters participate in the recycling of neurotransmitters for future release. Once inside the presynaptic neuron, neurotransmitter molecules are transported into synaptic vesicles, where they can be stored and used for subsequent release during synaptic activity.
Modulation of Synaptic Strength: Neurotransmitter transporters can influence the strength and efficacy of synaptic transmission. By regulating the availability of neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft, transporters can modulate the amplitude and duration of postsynaptic responses. This modulation contributes to the fine-tuning of synaptic strength and the regulation of neuronal excitability.
Drug Targets: Neurotransmitter transporters are important targets for various drugs that modulate neurotransmission. Certain medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), target specific neurotransmitter transporters to increase the availability of neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft. These drugs are commonly used to treat conditions such as depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders.
Neurotransmitter Clearance: In addition to their role at synapses, neurotransmitter transporters also participate in the clearance of neurotransmitters outside the synaptic cleft. They help remove neurotransmitters that have diffused away from synapses, preventing their accumulation in the extracellular space and maintaining proper neurotransmitter homeostasis.
Overall, neurotransmitter transporters play vital roles in neurotransmission and synaptic function. Their functions extend beyond simple reuptake, encompassing the regulation of neurotransmitter levels, termination of synaptic transmission, modulation of synaptic strength, and participation in neurotransmitter recycling. Understanding the mechanisms and regulation of neurotransmitter transporters is crucial for comprehending the complexities of synaptic communication and its impact on brain function.
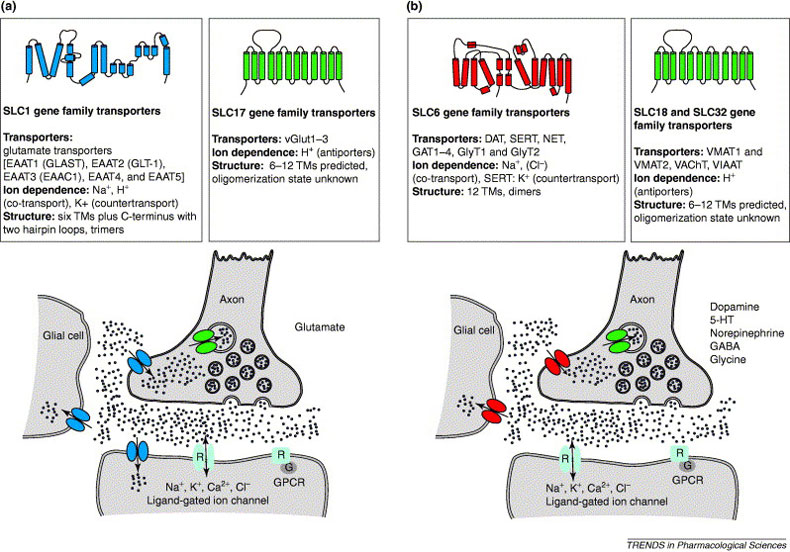 Fig.2 Neurotransmitter transporters: molecular function of important drug targets. (Gether U, 2006)
Fig.2 Neurotransmitter transporters: molecular function of important drug targets. (Gether U, 2006)
The Application Areas of Neurotransmitter Transporters
Neurotransmitter transporters have diverse applications in both research and clinical settings. Here are some key areas where neurotransmitter transporters are utilized:
Neuropharmacology and Drug Discovery: Neurotransmitter transporters are important targets for drug development and pharmacological research. By modulating the activity of neurotransmitter transporters, researchers can develop drugs that enhance or inhibit neurotransmitter reuptake, leading to altered neurotransmission. These drugs can be used to treat various neurological and psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and substance abuse.
Neurotransmitter Uptake Assays: Neurotransmitter transporters are utilized in vitro to study the kinetics and mechanisms of neurotransmitter uptake. These transporters can be heterologously expressed in cell lines or incorporated into membrane vesicles to perform uptake assays. These assays help researchers understand the transport properties of neurotransmitter transporters, evaluate drug interactions, and screen potential therapeutic compounds.
Neurotransmitter Release and Recycling Studies: Neurotransmitter transporters are involved in the recycling of neurotransmitters by facilitating their reuptake into presynaptic neurons. Researchers use techniques such as neurotransmitter release assays, synaptic vesicle preparations, and imaging methods to investigate the release and recycling processes mediated by neurotransmitter transporters. These studies provide insights into synaptic transmission, synaptic plasticity, and neuronal communication.
Neuroimaging: Positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging techniques can utilize specific radioligands that bind to neurotransmitter transporters. By labeling these radioligands with radioactive tracers, researchers can visualize and quantify the density and distribution of neurotransmitter transporters in the brain. Neuroimaging of neurotransmitter transporters has applications in the diagnosis and monitoring of various neurological disorders, including Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and mood disorders.
Biomarker Research: Alterations in neurotransmitter transporter expression and function have been associated with several neurological and psychiatric disorders. Researchers investigate changes in neurotransmitter transporter levels, trafficking, and activity as potential biomarkers for disease diagnosis, progression, and treatment response. These studies contribute to a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms of neurological disorders and aid in the development of personalized therapeutic approaches.
Neurological Disease Research: Studies involving genetically modified animal models with altered neurotransmitter transporter expression or function help elucidate the role of these transporters in normal brain function and disease pathology. By manipulating neurotransmitter transporter genes, researchers can investigate the consequences of transporter dysfunction, assess its impact on neurotransmission, and study the development of neurological disorders.
Neurotoxicology: Neurotransmitter transporters are involved in the uptake and clearance of neurotransmitters, including excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters. Neurotoxicology studies employ neurotransmitter transporters to assess the effects of exogenous chemicals, drugs, or environmental toxins on neurotransmitter systems. These investigations provide insights into the mechanisms of neurotoxicity and aid in the development of strategies to mitigate adverse effects.
The application areas of neurotransmitter transporters are diverse and span from basic research to clinical settings. They contribute to our understanding of neurological disorders, drug development, biomarker identification, and diagnostic imaging techniques. Continued research on neurotransmitter transporters holds promise for advancing our knowledge of brain function and improving treatments for neurological and psychiatric conditions.
Available Resources for Neurotransmitter Transporters
Creative BioMart offers a variety of products related to neurotransmitter transporters, including recombinant proteins, cell and tissue lysates, and protein pre-coupled magnetic beads. At the same time, we offer customized services designed to meet your specific needs for neurotransmitter transporters and related research. In addition, we provide a wide range of educational and technical resources, including knowledge related to neurotransmitter transporters, as well as product application notes or experimental protocols to help optimize your research. Feel free to view the following neurotransmitter transporter-related molecules and click to view a comprehensive resource. If you need more details or have other questions, please feel free to contact us.
Reference:
- Gether U, Andersen PH, Larsson OM, Schousboe A. Neurotransmitter transporters: molecular function of important drug targets. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27(7):375-383. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2006.05.003.

