What is CFTR Protein
The CFTR protein, also known as ABCC7 (ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 7), is a member of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. This transmembrane protein regulates chloride and bicarbonate ion transport across epithelial cell membranes. Synonyms for CFTR include MRP7, TNR-CFTR, and ABC35.
CFTR Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Belonging to the ABC transporter superfamily, CFTR is distinguished by its unique domain architecture. The protein consists of two membrane-spanning domains (MSDs), two nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs), and a regulatory (R) domain. The MSDs form a channel through which ions pass, while the NBDs are essential for ATP binding and hydrolysis.
Recent Research Advances about CFTR Protein
Recent research has shed light on the dynamic nature of CFTR. Advanced imaging techniques and structural studies have provided insights into the conformational changes that govern its function. Understanding these changes is crucial for developing targeted therapies for diseases associated with CFTR dysfunction.
CFTR Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The primary function of CFTR is to regulate ion transport across epithelial cell membranes, particularly the movement of chloride ions. This regulation is pivotal for maintaining the balance of salt and water on the surface of epithelial cells. CFTR achieves this by acting as a chloride channel, responding to cellular signals and opening or closing accordingly. The molecular mechanisms involve the phosphorylation of the R domain, which controls the opening and closing of the ion channel.
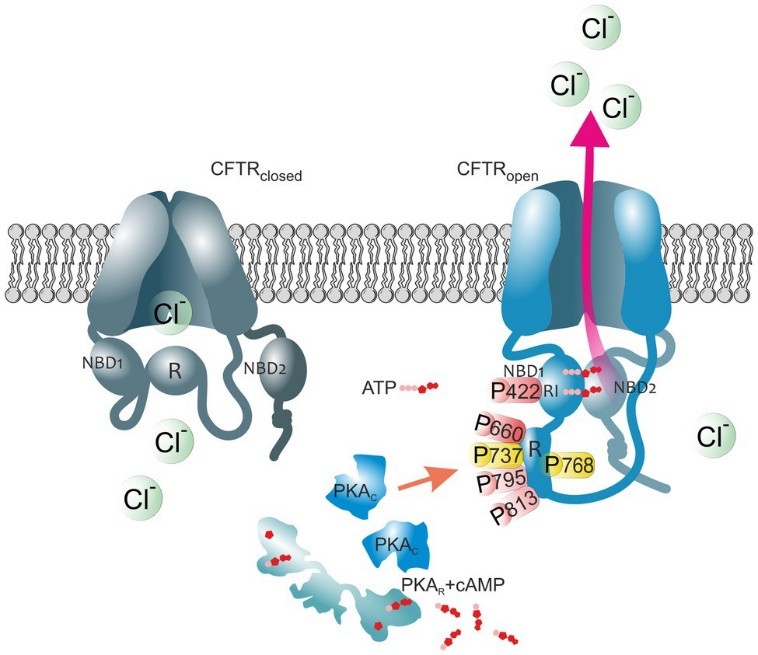
Figure 1. The impact of PKA-mediated phosphorylation on CFTR channel. (Della Sala A, et al., 2021)
CFTR Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathway of CFTR is intricately connected to cellular processes. Phosphorylation events, notably by protein kinase A (PKA) and protein kinase C (PKC), play a key role in regulating CFTR activity. These kinases modulate the conformation of the R domain, influencing the opening and closing of the ion channel. The intricate interplay of signaling molecules in this pathway highlights the sensitivity and precision of CFTR regulation.
CFTR Related Diseases
CFTR dysfunction is implicated in various diseases, with cystic fibrosis (CF) being the most well-known. In CF, mutations in the CFTR gene lead to the production of a defective protein, compromising chloride ion transport. This results in thick and sticky mucus, affecting the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems. Beyond CF, CFTR mutations are associated with conditions such as congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens (CBAVD) and pancreatitis.
CFTR's Applications in Biomedicine
- Diagnostic Development: The unique properties of CFTR make it a valuable target in diagnostic development. Assays measuring CFTR function provide insights into the cellular and molecular aspects of ion transport. These diagnostic tools are instrumental in identifying CFTR dysfunction and associated diseases, aiding in early and accurate diagnoses.
- Vaccine Development: Research exploring CFTR's role in infectious diseases has opened avenues for vaccine development. Understanding how CFTR influences host-pathogen interactions enables the design of vaccines that target specific aspects of the immune response. This holds promise for preventing infections in individuals with CF and other related conditions.
- Therapeutics: The therapeutic potential of CFTR extends to the development of drugs aimed at correcting or modulating its function. Small molecules known as CFTR modulators are being actively researched to address the underlying causes of CFTR dysfunction. These drugs hold promise for improving the quality of life for individuals with CF and other diseases linked to CFTR mutations.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFTR-276H | Recombinant Human CFTR protein, GST-tagged | Human | E. coli | GST |
| CFTR-1181H | Recombinant Human CFTR Protein, GST-Tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| CFTR-275H | Recombinant Human CFTR protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CFTR-1780H | Recombinant Human CFTR protein, His & GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/GST |
| CFTR-277H | Recombinant Human CFTR protein, His-tagged | Human | E. coli | His |
| CFTR-2664H | Recombinant Human CFTR Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| CFTR-12H | Recombinant Human CFTR Protein (Pro1181-End), N-His-tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
| CFTR-278H | Recombinant Human CFTR protein, His-tagged | Human | E. coli | His |
| CFTR-1187HFL | Recombinant Human CFTR protein, His&Flag-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His&Flag |
Reference
- Della Sala A, et al. Role of protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation in CFTR channel activity regulation. Frontiers in Physiology. 2021, 12: 690247.

