What is CLEC7A Protein
The CLEC7A protein belongs to a category of proteins known as C-type lectin receptors, which are typically involved in the body's immune response to infections and other diseases. Specifically, CLEC7A (C-Type Lectin Domain Family 7 Member A), also known as Dectin-1, primarily contributes to the immune system's capacity to recognize and respond to fungal pathogens, particularly those that characterize a beta-glucan polysaccharide structure. This protein, expressed predominantly in myeloid cells, facilitates the initiation of innate and adaptive immune responses.
Function of CLEC7A Protein
CLEC7A protein plays an indispensable role in immune surveillance and control of pathogens, particularly fungal ones. It achieves this by triggering a variety of cellular responses, including endocytosis, phagocytosis, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and the activation of several signaling pathways which encourage the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
Most notably, the CLEC7A protein exhibits unique pattern recognition capabilities, allowing it to identify beta-glucan components present on the fungal cell wall. Upon recognizing these components, it will induce signaling cascades, thereby influencing an array of immune responses. This biological function has critical clinical implications given that dysfunctional variants of the CLEC7A gene can result in compromised immune responses, leading to severe infection and disease states.
CLEC7A Protein Related Signal Pathway
The multiple functions of the CLEC7A protein are largely credited to its integration in several signal pathways. The central signaling pathway connected with CLEC7A involves the collaboration with signaling molecule spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk). This association induces the activation of the CARD9-BCL10-MALT1 signaling complex, leading to the activation of major mechanisms such as MAPK and NF-kB pathways that promote inflammatory gene expression.
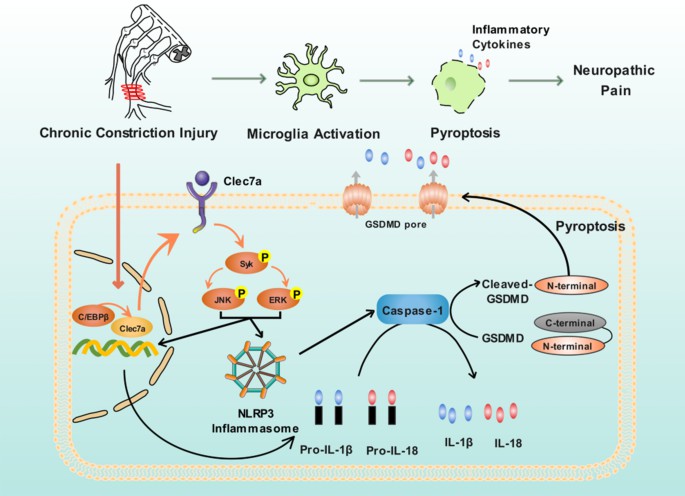
Fig 1. The critical role of C/EBPβ-Clec7a axis in neuropathic pain progression (Dan Wu et al. 2022)
Additional to the Syk pathway, recent studies have identified the induction of the Raf-1 pathway by CLEC7A, which independently triggers the NF-kB and inflammasome activation, leading to IL-1beta production. This CLEC7A protein's ability to activate both Syk-dependent and Syk-independent pathways only further underscores its complexity and far-reaching implications on immune responses.
CLEC7A Protein Related Diseases
Given CLEC7A's foundational role in immune response, it is unsurprising that mutations in the CLEC7A gene or dysfunctions in the CLEC7A pathway can facilitate various diseases. Deficiency or faulty variations of CLEC7A have been linked to chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis and invasive fungal infections. Moreover, studies have revealed associations between the CLEC7A protein and autoimmunity, septic shock, and various forms of cancer, including lung and colorectal cancer.
Interestingly, the CLEC7A protein is not merely a bystander but also participates in disease progression. For instance, in the cancer context, CLEC7A can infiltrate tumor microenvironments, thereby fostering tumor growth and suppressing anti-tumor responses. It is pertinent to note, however, that research is ongoing, and our understanding of the intricate relationship between CLEC7A and these diseases continues to evolve.
CLEC7A Protein's Applications in Biomedical
The CLEC7A protein's critical involvement in immunity and disease response opens up multiple avenues for biomedical applications. It can serve as both a therapeutic target and a prognostic indicator given its role in various disease processes. For instance, targeted therapy through CLEC7A can help modulate immune response against specific pathogens, particularly in individuals prone to invasive fungal infections.
In the context of cancer, the manipulation of CLEC7A expression could influence the tumor microenvironment to encourage anti-tumor responses. Moreover, based on the correlation between CLEC7A expression and certain disease outcomes, this protein has the potential to be developed as a biomarker for the prognosis of these diseases. As is evident, the CLEC7A protein, due to its multifaceted role in immunity, poses a substantial prospect for therapeutic interventional strategies.
In conclusion, the CLEC7A protein functions as an invaluable component of the body's defense mechanism. Its involvement in multiple signaling pathways underscores its comprehensive role in mediating immune responses. Furthermore, the CLEC7A protein is a significant factor in several diseases and can be harnessed for a variety of biomedical applications. However, it is clear that our understanding of this protein remains in its nascent stages, warranting further studies to unravel its full potential for clinical applications.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLEC7A-11322H | Recombinant Human CLEC7A, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| Clec7a-2204M | Recombinant Mouse Clec7a, His tagged | Mouse | Human Cell | His |
| CLEC7A-1793R | Recombinant Rhesus Monkey CLEC7A Protein | Rhesus monkey | HEK293 | N/A |
| CLEC7A-732R | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque CLEC7A Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rhesus monkey | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| CLEC7A-2172HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CLEC7A Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| CLEC7A-2686H | Recombinant Human CLEC7A Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Wu, D., Zhang, Y., Zhao, C. et al. Disruption of C/EBPβ-Clec7a axis exacerbates neuroinflammatory injury via NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in experimental neuropathic pain. J Transl Med 20, 583 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-022-03779-9

