What is DHFR Protein
DHFR, or Dihydrofolate Reductase, is a pivotal enzyme essential for cellular processes and is intricately involved in folate metabolism. Its official full name is "Dihydrofolate Reductase," and it is also known by the synonym DHFR. Belonging to the enzyme family of reductases, DHFR plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. In terms of structure, DHFR is characterized by its compact, globular shape, and it falls under the classification of oxidoreductases due to its involvement in reduction-oxidation reactions. Recent research advances in understanding the nuances of DHFR have illuminated its significance in various cellular functions.
DHFR Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of DHFR are diverse and pivotal for cellular survival. Its primary role is to catalyze the conversion of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate, a crucial step in the synthesis of purines, pyrimidines, and certain amino acids. By participating in these biosynthetic pathways, DHFR ensures the availability of essential building blocks for DNA and RNA synthesis. The molecular mechanism involves the reduction of dihydrofolate using NADPH as a cofactor, highlighting the enzyme's role in maintaining cellular nucleotide pools. This function places DHFR at the crossroads of cellular metabolism, making it an indispensable player in the intricate dance of cellular processes.
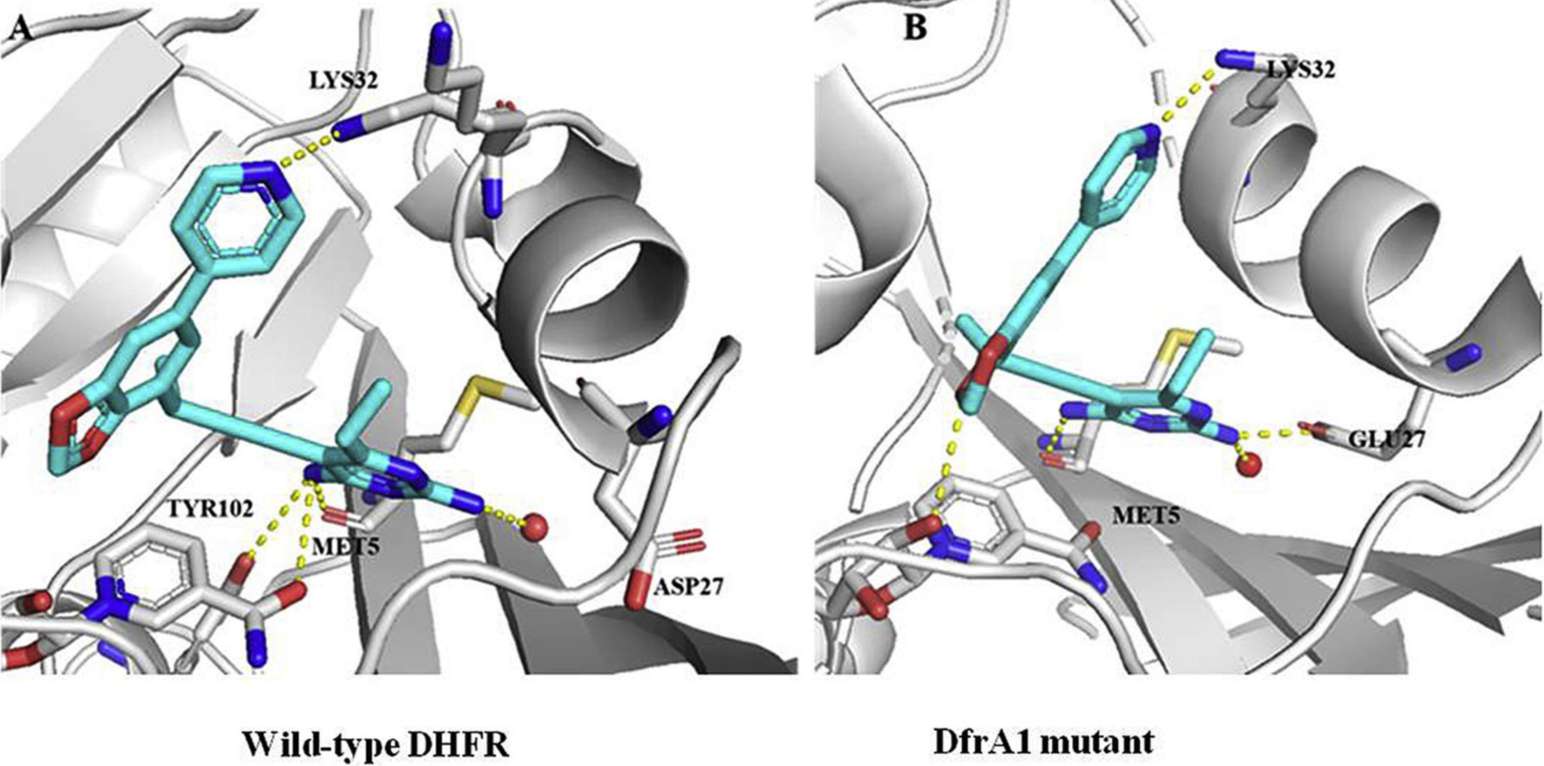
Figure 1. DHFR is increasingly important for combating against drug-resistant bacteria. (He J, et al., 2020)
DHFR Related Signaling Pathway
Understanding the signal pathways involving DHFR is crucial for unraveling its role in cellular processes. DHFR is intricately connected to the folate cycle, where it collaborates with other enzymes to maintain balanced levels of folate derivatives. This interconnected network regulates nucleotide synthesis and influences cellular responses to environmental stimuli. The dysregulation of DHFR signaling pathways has been implicated in various pathological conditions, highlighting the need for targeted therapeutic interventions.
DHFR Related Diseases
While DHFR is vital for normal cellular function, its dysregulation or mutations can lead to various diseases. One notable example is cancer, where aberrant DHFR expression is associated with uncontrolled cell proliferation. Methotrexate, a widely used anticancer drug, exerts its effects by inhibiting DHFR, disrupting the cancer cells' ability to synthesize essential nucleotides. Additionally, mutations in the DHFR gene have been linked to congenital disorders, emphasizing the importance of this enzyme in embryonic development and normal physiology.
DHFR's Applications in Biomedicine
The significance of DHFR extends beyond its role in cellular processes, finding applications in the realm of biomedicine. In diagnostic development, DHFR has been exploited as a target for imaging agents, allowing for the visualization of folate metabolism in vivo. Moreover, in vaccine development, DHFR has been utilized as a platform for antigen delivery, enhancing the immune response to specific targets. In therapeutics, the enzyme serves as a key target for drugs, with methotrexate being a prime example. The versatility of DHFR in biomedical applications underscores its importance as a molecular tool for advancing diagnostics, vaccines, and therapeutic strategies.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHFR-11966H | Recombinant Human DHFR, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| DHFR-2586H | Recombinant Human DHFR Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| DHFR-0618H | Recombinant Human DHFR Protein (M1-D187), His tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| DHFR-2818H | Recombinant Human DHFR protein, His-SUMO-tagged | Human | E.coli | His-SUMO |
| DHFR-28331TH | Recombinant Human DHFR, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| DHFR-6261H | Recombinant Human DHFR Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| DHFR-1960H | Recombinant Human DHFR Protein (Met1-Asp187), N-His tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
| DHFR-2526HF | Recombinant Full Length Human DHFR Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| DHFR-1590HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human DHFR Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| DHFR-0617H | Recombinant Human DHFR Protein (M1-D187), Tag Free | Human | E.coli | No tag |
Reference
- He J, et al. Dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors for use as antimicrobial agents. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2020, 195: 112268.

