What is DSG1 Protein
The Desmoglein 1 (DSG1) protein, known for its pivotal role in cell adhesion, stands as a cornerstone in the intricate web of molecular interactions within our bodies. Officially classified as a member of the desmoglein protein family, DSG1 has earned various aliases, including desmosomal glycoprotein 1 and cadherin family member 4. Belonging to the cadherin superfamily, DSG1 exhibits distinctive structural characteristics that define its essential functions.
DSG1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
DSG1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein primarily expressed in the epidermis, where it contributes significantly to the structural integrity of epithelial tissues. Functionally, it serves as a critical component of desmosomes – specialized cell structures that facilitate strong cell-to-cell adhesion. In these desmosomes, DSG1 forms complexes with other desmosomal proteins, fostering the cohesion necessary for tissue integrity.
Molecularly, DSG1 engages in homophilic interactions, binding with other DSG1 molecules on neighboring cells. This adhesive property, driven by calcium-dependent binding, creates a robust network that reinforces cell adhesion. The molecular mechanisms underlying DSG1 function involve the recruitment of various intracellular proteins, orchestrating signaling cascades that fortify the stability of cell junctions.
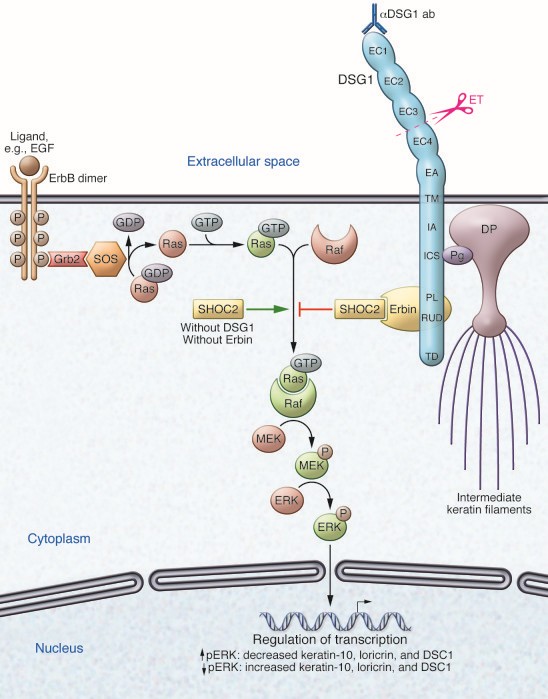
Figure 1. Keratinocyte structure, adhesion, and signaling modulated by Erbin and/or DSG1. (Hammers C M, et al., 2013)
DSG1 Related Signaling Pathway
Unraveling the signal pathways associated with DSG1 unveils the complexity of cellular communication. DSG1-mediated signaling involves the recruitment of plakoglobin and desmoplakin, which, in turn, link to the cytoskeleton. This intricate interplay reinforces cell adhesion, promoting tissue stability. Disruptions in these signaling pathways, as observed in pemphigus foliaceus, highlight the fragility of the equilibrium maintained by DSG1.
DSG1 Related Diseases
The importance of DSG1 becomes strikingly apparent when considering diseases linked to its dysfunction. Pemphigus foliaceus, a blistering skin disorder, often arises from autoantibodies targeting DSG1, leading to the compromised integrity of epidermal tissues. The autoimmune nature of this condition underscores the delicate balance maintained by DSG1 in preserving tissue architecture.
DSG1's Applications in Biomedicine
Beyond its fundamental role in cellular adhesion, DSG1 holds promise in various biomedical applications. In diagnostic development, the detection of DSG1 autoantibodies serves as a crucial marker for pemphigus foliaceus, aiding in timely and accurate disease diagnosis. Additionally, the protein's involvement in cell adhesion mechanisms positions it as a potential target for therapeutic interventions aimed at reinforcing tissue integrity.
In the realm of vaccine development, a nuanced understanding of DSG1's structure and function enables the exploration of strategies to modulate immune responses. Targeting DSG1-related pathways could hold the key to developing vaccines that mitigate autoimmune reactions, providing a novel avenue for therapeutic advancement.
Therapeutically, the intricate involvement of DSG1 in cell adhesion opens avenues for targeted interventions. Developing drugs that selectively modulate DSG1-related signaling pathways could offer innovative approaches for treating conditions characterized by compromised tissue integrity, such as autoimmune blistering disorders.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSG1-8319H | Recombinant Human DSG1 | Human | Mammalian cells | N/A |
| DSG1-820H | Recombinant Human DSG1 protein, His & GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/GST |
| DSG1-1601H | Recombinant Human Desmoglein 1 | Human | Mammalian cells | N/A |
| DSG1-2890H | Recombinant Human DSG1 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| DSG1-144HF | Recombinant Full Length Human DSG1 Protein | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | |
| DSG1-2457H | Recombinant Human DSG1 protein, His&Myc-tagged | Human | E.coli | His&Myc |
| DSG1-26581TH | Recombinant Human DSG1 | Human | Wheat Germ | N/A |
| DSG1-1994H | Recombinant Human DSG1 Protein (Glu50-Pro548), N-His tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
| DSG1-12178H | Recombinant Human DSG1 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| DSG1-1388H | Recombinant Human DSG1 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
Reference
- Hammers C M, Stanley J R. Desmoglein-1, differentiation, and disease. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2013, 123(4): 1419-1422.

