What is EGFR Protein
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) stands at the nexus of cellular communication, orchestrating intricate signaling cascades that govern vital cellular processes.
What is EGFR Protein?
EGFR, also known as ErbB1 or HER1, is a transmembrane receptor belonging to the ErbB family of tyrosine kinase receptors. Its architecture comprises an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain. The extracellular region engages with ligands such as epidermal growth factor (EGF), while the intracellular domain, housing kinase activity, phosphorylates tyrosine residues, setting the stage for intracellular signaling.
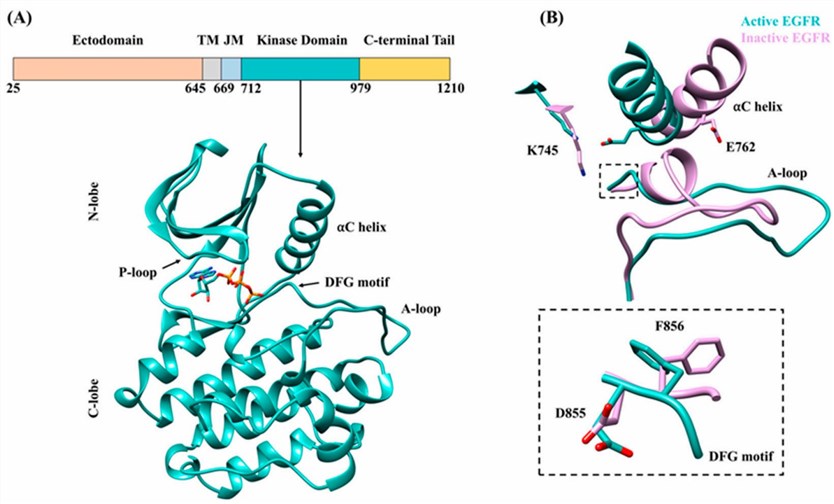
Figure 1. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and structural features of the tyrosine kinase domain. (Tamirat, M.Z., et al. 2021)
EGFR Related Signaling Pathways
The signaling pathways emanating from EGFR are intricate and diverse, each playing a distinct role in cellular responses. The Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway, a primary signaling cascade, regulates cell proliferation and survival. Simultaneously, the PI3K/Akt pathway influences cellular processes like metabolism and apoptosis. These pathways collectively form a sophisticated network modulating cellular behavior in response to EGFR activation.
Applications of EGFR in Biomedical Research
Cancer Diagnostics and Prognostics
- EGFR analysis is pivotal in cancer diagnostics, providing insights into expression levels and mutations.
- Specific EGFR mutations guide prognosis, aiding in the categorization of various cancers and informing personalized treatment approaches.
Targeted Cancer Therapies
- EGFR-targeted drugs like gefitinib, erlotinib, and cetuximab have revolutionized cancer therapy.
- These inhibitors selectively hinder EGFR activity, offering a precise and effective alternative to traditional chemotherapy.
Personalized Medicine
- EGFR mutations inform personalized medicine strategies, tailoring treatments based on an individual's genetic profile.
- This approach enhances treatment efficacy while minimizing adverse effects, marking a paradigm shift in clinical interventions.
Clinical Trials and Drug Development
- Ongoing clinical trials explore novel drugs targeting EGFR, aiming to overcome resistance mechanisms.
- Insights from EGFR research contribute to the development of cutting-edge therapies, continually advancing cancer treatment modalities.
Understanding Cellular Signaling
- EGFR serves as a key model for studying cellular signaling pathways.
- In-depth knowledge gained from EGFR research extends beyond cancer, offering valuable insights into broader cellular signaling mechanisms.
EGFR's significance in cellular processes, its association with diseases, and its applications in biomedical research underscore its prominence in the field of molecular biology. The ongoing exploration of EGFR continues to unravel its complexities, paving the way for innovative therapeutic interventions and contributing to a deeper understanding of cellular signaling dynamics.
Recommended Products for EGFR Protein
Reference
- Tamirat, M.Z., et al. Structural Basis for the Functional Changes by EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13(5): 1120.

