What is FGFR2 Protein?
Proteins play essential roles in the biological processes occurring in all living organisms. One critical protein controlling various processes in a human body is the fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2).
Background and Discovery of FGFR2 Protein
The FGFR2 protein became recognized as a critical entity in biological processes in the early 1990s. It is a tyrosine kinase receptor for fibroblast growth factors(FGF). Research shared by Miki et al. (1992) showcased the presence of FGFR2 in keratinocytes, illustrating its role in stimulating cell proliferation and cell motor activity.
The FGFR2 gene is located on chromosome 10q26, an area associated with various cancers. FGFR2 is part of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, which includes four members: FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4. The receptor proteins share 55-72% amino acid sequence similarity and contain three immunoglobulin-like (Ig-like) domains, a transmembrane segment, and a tyrosine kinase domain. FGFR2 protein specifically consists of an extracellular region for ligand (FGF) interaction, a transmembrane region, and an intracellular region with a tyrosine kinase function.
Function of FGFR2 Protein
The FGFR2 protein functions as a cell-surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors. FGFR2 regulates a multitude of biological processes, such as cellular proliferation, differentiation, and migration, through its cell surface receptor function. Besides, FGFR2 plays a crucial role in embryonic development, tissue regeneration, and angiogenesis.
FGFR2 Protein-Related Signal Pathway
FGFR2 protein takes part in multiple signal transduction cascades, including the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt pathway, and phospholipase C gamma (PLCγ) pathway. Once FGFR2 binds with a suitable FGF ligand, it triggers these pathways, commencing several cellular responses, influencing cellular proliferation, survival, migration, and differentiation.
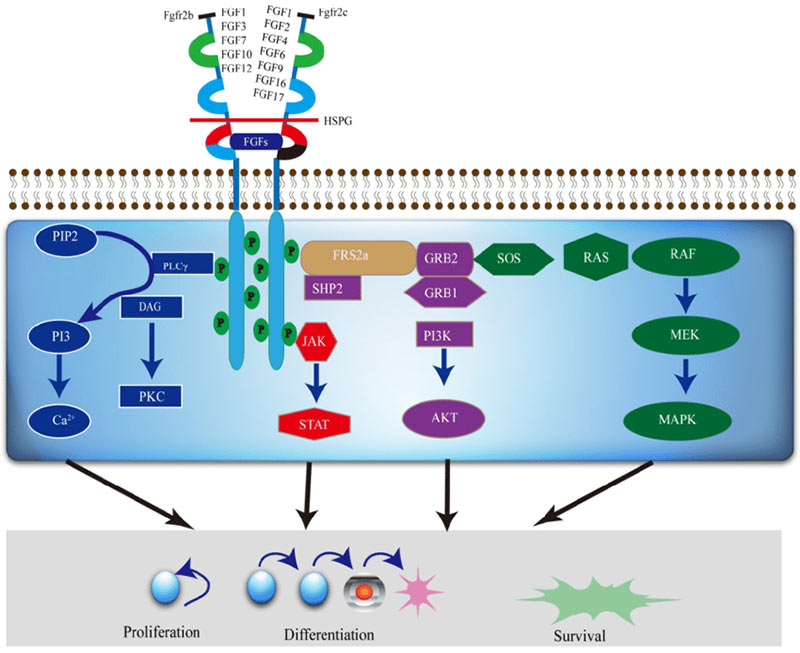
Fig1. FGFR2 mediated signaling pathways
FGFR2 Protein-Related Diseases
The mutation or overexpression of FGFR2 is linked to several diseases. Alterations in the FGFR2 gene are known to result in craniosynostosis syndromes, conditions resulting in abnormal head shapes due to premature fusion of the cranial sutures. Pfeiffer, Apert, Crouzon, and Beare-Stevenson Cutis Gyrata syndromes are some of the syndromes linked to FGFR2 mutations.
Moreover, recent studies associate FGFR2 gene mutations with many cancer types, such as breast, endometrial, and gastric cancers. These are often coupled with an increased likelihood of cancer cell proliferation, survival, and spread due to the overactivation of FGFR2 protein-mediated pathways.
FGFR2 Protein's Applications in Biomedical Field
Due to its role in disease development and progression, FGFR2 and its pathway have become potential therapeutic targets in the biomedical field, particularly in oncology. Various inhibitors targeting FGFR2, such as dovitinib and AZD4547, have been studied in clinical trials for treating specific cancers.
FGFR2 also has diagnostic significance in some diseases. For example, FGFR2 gene amplification or overexpression can serve as a diagnostic biomarker for some cancers.
In conclusion, the FGFR2 protein, as a part of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, plays a significant role in numerous biological processes and disease developments. Understanding the FGFR2 protein mechanisms and pathways is crucial for disease diagnosis and the development of targeted therapeutic strategies, reinforcing its importance to the biomedical field. However, much remains to be explored about FGFR2 to fully utilize its potential in disease diagnostics and therapeutics.
Our Featured Products
Reference
- Lei, Josh & Deng, Chu-Xia. (2017). Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2 Signaling in Breast Cancer. International Journal of Biological Sciences. 13. 1163-1171. 10.7150/ijbs.20792.

