What is LOXL2 Protein?
The study of proteins and their extensive roles in the body offers immense insights into the systems of life. Proteins are critical for sustaining life, encompassing a vast range of biological functions, from catalyzing reactions to serving as signaling molecules. One such protein, known as lysyl oxidase-like 2 (LOXL2), has attracted considerable scientific attention due to its various roles in physiology and pathological processes.
The Discovery and Background of LOXL2 Protein
The LOXL2 protein was initially identified in a cDNA library from human placenta in 1998. Subsequent investigations have since recognized LOXL2 as a member of the lysyl oxidase (LOX) family. This family also includes LOX, LOXL1, LOXL3, and LOXL4, all involved in catalyzing the crosslinking of collagen and elastin in the extracellular matrix, thereby contributing to tissue structure and integrity.
Gene Locus and Protein Structure
The human LOXL2 gene is located on chromosome 8p21.3-p21.2 and is compounded by ten exons spanning roughly 70 kbp. This gene codes for a protein of ~87kDa, possessing a highly conserved C-terminal catalytic domain similar to all LOX family members. This catalytic domain harbors the copper-binding site and lysyl-tyrosyl-quinone (LTQ) cofactor necessary for the catalytic function of LOX proteins. Aside from the similarities, LOXL2 also carries a unique N-terminal domain, a four scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domain, absent in the original LOX enzyme.
Function of LOXL2 Protein
LOXL2 plays significant roles in multiple physiological and pathological processes. In normal physiology, it takes part in the formation and remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM) by oxidizing lysine residues in collagen and elastin, an essential step in the biogenesis of connective tissues. Moreover, it is involved in embryonic development, more specifically in the correct formation and differentiation of certain tissues.
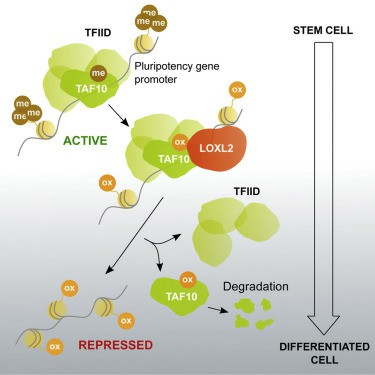
Fig1. LOXL2 Oxidizes Methylated TAF10
LOXL2 Protein Related Signal Pathway
In cellular signal transduction, LOXL2 contributes significantly. It interacts with multiple signal pathways, including transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), focal adhesion kinase (FAK), and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) pathways. It regulates TGF-β signaling by controlling the formation of a key intermediate on the pathway—latent TGF-β binding protein-1 (LTBP-1)—implicating LOXL2 as an essential player in the profibrotic activity of TGF-β.
LOXL2 Protein Related Diseases
Aberrant expression or overexpression of LOXL2 has been connected with various disease conditions, particularly cancer and fibrosis. Its involvement in ECM remodeling renders it crucial in cancer metastasis as it enhances the invasion ability of cancer cells. Observed elevated levels of LOXL2 in many aggressive cancers solidify its adverse role. In addition, the dysregulated LOXL2 contributes to the pathogenesis of fibrotic diseases by enhancing pathologic ECM accumulation, including lung, liver, and kidney fibrosis.
LOXL2 Protein's Applications in Biomedical
The critical role of LOXL2 in disease pathology establishes it as an attractive therapeutic target. Numerous LOXL2 inhibitors are in development or undergoing clinical trials for treating fibrotic diseases and tumors, suggesting promising applications in therapeutic interventions. Also, LOXL2 serves as a valuable biomarker for LOXL2-associated diseases, particularly in predicting tumorigenesis or disease progression.
In conclusion, LOXL2 is a fascinating protein, with crucial roles in the physiological and pathological processes. Its involvement with disease pathology presents great possibilities in therapeutics, benefiting from advancements in molecular biology and medical technology. Further understanding of LOXL2 will undoubtedly offer more insights into the intricate processes within our bodies.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOXL2-3923H | Recombinant Human LOXL2, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| LOXL2-3920H | Recombinant Human LOXL2 Protein, Avi/His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Avi/His |
| LOXL2-29651TH | Recombinant Human LOXL2 protein, FLAG-tagged | Human | Insect Cell | FLAG |
| LOXL2-150H | Recombinant Human LOXL2, GST-tagged | Human | Sf9 Insect Cell | GST |
| LOXL2-2748H | Recombinant Human LOXL2 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| LOXL2-272H | Recombinant Human LOXL2 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| Loxl2-274M | Recombinant Mouse Loxl2 Protein, His-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His |
| Loxl2-275R | Recombinant Rat Loxl2 Protein, His-tagged | Rat | E.coli | His |
Reference
- Iturbide, A., Pascual-Reguant, L., Fargas, L., Cebrià, J. P., Alsina, B., García de Herreros, A., & Peiró, S. (2015). LOXL2 Oxidizes Methylated TAF10 and Controls TFIID-Dependent Genes during Neural Progenitor Differentiation. Molecular Cell, 58(5), 755-766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.04.012

