What is NR1I2 Protein?
NR1I2, also known as the Pregnane X Receptor (PXR), was discovered in 1998 by Bertilsson et al. while investigating the regulation of CYP3A genes, a group of enzymes involved in drug metabolism. The identification of this protein indicated its paramount role in xenobiotic metabolism. Predominantly expressed in the liver and intestines, NR1I2 is a member of the nuclear receptor family that predominantly acts as a transcription factor, regulating the expression of several genes.
Located on the human chromosome 3q13.33, the NR1I2 gene is comprised of nine exons spanning approximately 35 kilobases. The protein encoded by this gene is structurally composed of several functional domains, including a ligand-binding domain (LBD), a DNA-binding domain (DBD), and a hinge region connecting these two domains. The LBD of NR1I2 is spacious and adaptable, enabling the binding of various endogenous and exogenous substances.
Function of NR1I2 protein
NR1I2 plays a significant role as a transcription regulator in response to various foreign substances, such as dietary components, drugs, and environmental pollutants. When these compounds enter the body, they bind to the NR1I2 protein. Upon binding, the protein promotes the transcription of particular detoxifying enzymes and transporters that aid in the metabolism and elimination of these substances from the body.
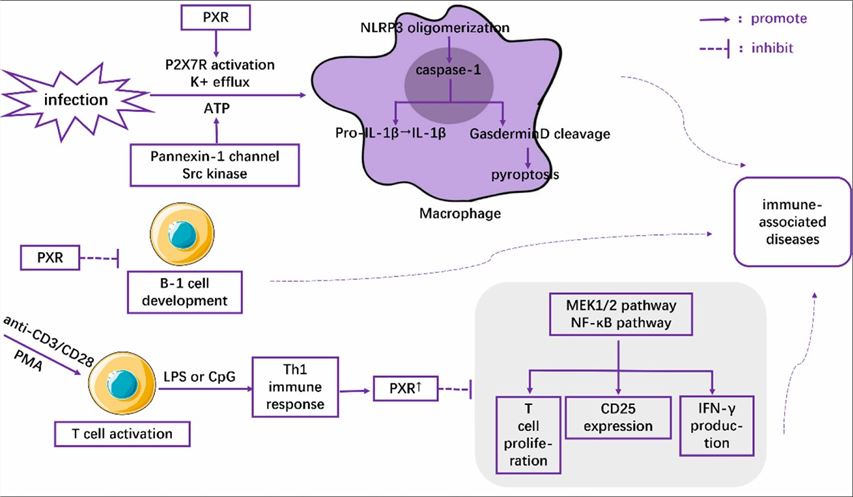
Fig1. The role of PXR in the regulation of immune cells
NR1I2 protein related signal pathway
Several signal pathways are associated with NR1I2, where it mainly acts as a ligand-activated transcription factor. These pathways include the pregnane X receptor/retinoid X receptor (PXR/RXR) activation pathway and the Farnesoid X-activated receptor (FXR) activation pathway. These pathways primarily regulate the expression of genes involved in xenobiotics metabolism and transport, glucose homeostasis, cholesterol metabolism, and bile acid biosynthesis.
NR1I2 protein related diseases
Malfunction or dysregulation of the NR1I2 protein has been connected with numerous diseases, reflecting its crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. Abnormal NR1I2 activity can lead to drug-drug interactions and affect drug clearance, fostering drug resistance in diseases like cancer. Furthermore, alterations in NR1I2 activity are linked to metabolic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia, owing to its role in lipid and glucose metabolism. Intriguingly, its association with infectious diseases such as HIV has also been documented, due to its potential interaction with antiretroviral drugs.
NR1I2 protein's applications in biomedical
In the biomedical domain, the NR1I2 protein has found various applications, predominantly in the development of therapeutic strategies. Given its role in drug metabolism, NR1I2 has been employed in predictive toxicology to anticipate possible drug-drug interactions, enhancing the safety and efficacy of pharmaceuticals. Furthermore, targeting NR1I2 has been suggested as a strategy for controlling diseases like cancer, inflammatory disorder, and HIV. Other potential applications involve using NR1I2 as a biomarker in disease diagnosis and prognosis, exploiting its differential expression in health and disease.
Therefore, NR1I2 protein is of paramount significance in the body's defense mechanism against xenobiotics and physiological metabolism regulation. Alterations in its activity substantiate the occurrence of various diseases, indicating its important role in pathological processes. In biomedicine, the protein offers a promising avenue for developing novel therapeutic strategies and enhancing drug safety and efficacy. Although considerable progress has been made, further research is crucial to explore the full potential of the NR1I2 protein in biomedical applications.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR1I2-1356H | Recombinant Human NR1I2, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| NR1I2-1300H | Recombinant Human NR1I2 Protein, His-SUMO/MYC-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/SUMO/Myc |
| NR1I2-6073H | Recombinant Human NR1I2 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| NR1I2-1114HFL | Recombinant Human NR1I2 protein, His&Flag-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His&Flag |
| NR1I2-1537H | Recombinant Human NR1I2 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| NR1I2-6702HF | Recombinant Full Length Human NR1I2 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| NR1I2-0773H | Recombinant Human NR1I2 Protein (S130-S434), Tag Free | Human | E.coli | No tag |
Reference
- Sun, L., Sun, Z., Wang, Q., Zhang, Y., & Jia, Z. (2022). Role of nuclear receptor PXR in immune cells and inflammatory diseases. Frontiers in Immunology, 13, 969399. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.969399

