What is RAD51 Protein
The RAD51 protein, a linchpin in genomic maintenance, orchestrates the cellular response to DNA damage, playing a pivotal role in homologous recombination.
What is RAD51 Protein?
The RAD51 protein, an evolutionarily conserved homolog of the bacterial RecA protein, is a key player in the DNA repair machinery. Situated at the heart of homologous recombination, RAD51 is essential for maintaining genome stability by facilitating the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and promoting faithful chromosome segregation during cell division.
To comprehend the intricacies of RAD51's function, one must first grasp its structural composition. RAD51 is a member of the RecA/RadA/Rad51 protein family, characterized by a conserved core domain responsible for nucleotide binding and hydrolysis. This core domain is flanked by N-terminal and C-terminal regions, each contributing to the protein's overall stability and function.
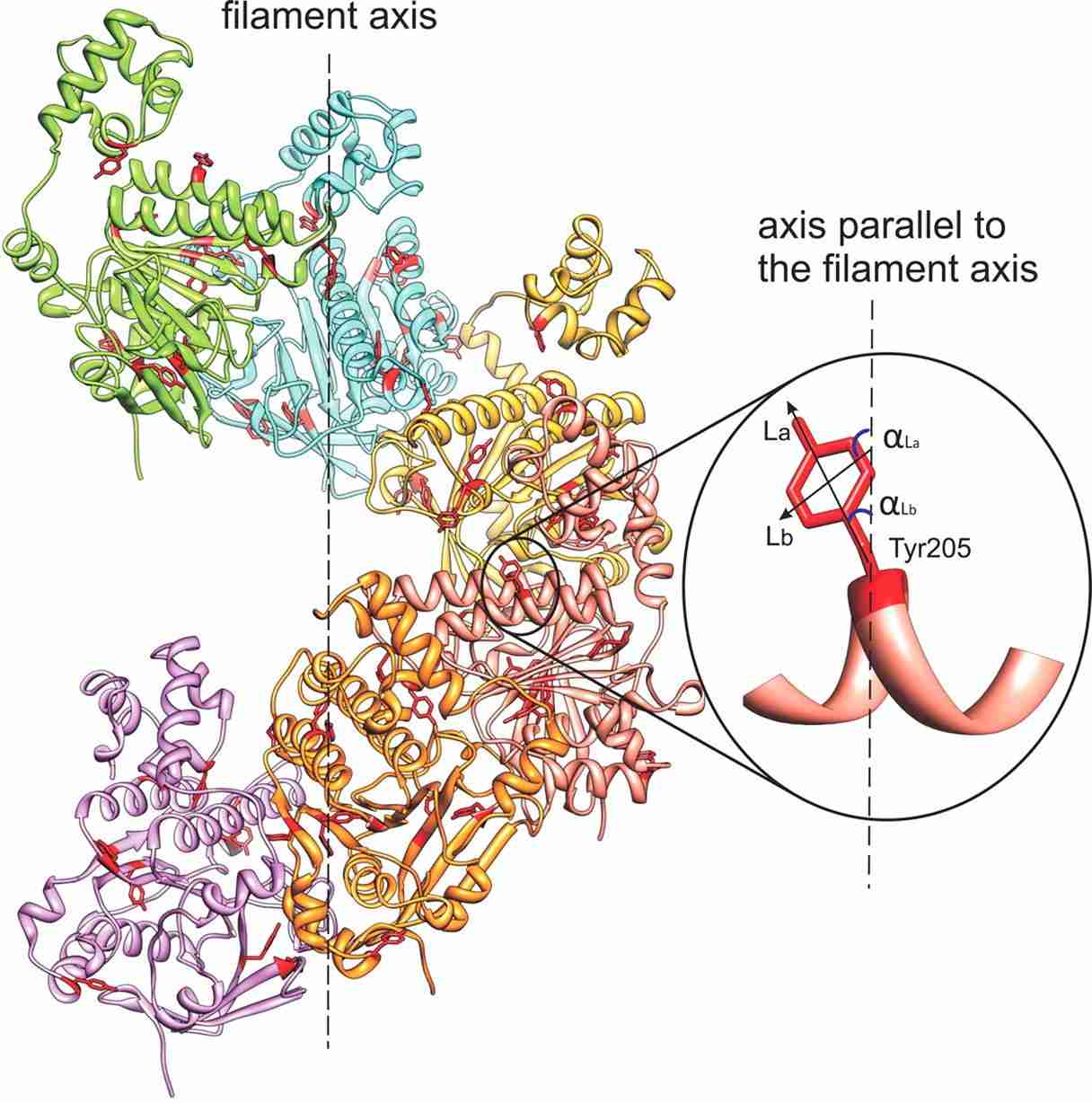
Figure 1. Model structures of the HsRad51 helical filament. (Reymer, A., et al. 2009)
The Function of RAD51 Protein
The primary function of RAD51 is to mediate homologous recombination, a complex and highly regulated process critical for the repair of DNA damage, particularly DSBs. When a DSB occurs, RAD51 is recruited to the site of damage, where it forms nucleoprotein filaments on single-stranded DNA regions. These filaments catalyze the invasion of homologous sequences, allowing the damaged DNA strand to be repaired using the intact information present in the sister chromatid or homologous chromosome.
Beyond DNA repair, RAD51 is also implicated in the maintenance of genomic stability during meiosis, where it aids in the proper alignment and segregation of homologous chromosomes. This ensures the generation of genetically diverse gametes, essential for the continuation of species.
RAD51-Related Diseases
Given its pivotal role in maintaining genomic integrity, dysregulation or malfunction of RAD51 is associated with various diseases, including cancer. DNA repair mechanisms is essential to prevent the accumulation of mutations that can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and tumorigenesis.
Several studies have identified aberrant RAD51 expression or function in various cancer types, including breast, ovarian, prostate, and pancreatic cancers. Elevated RAD51 levels are often linked to increased resistance to chemotherapy, as cancer cells exploit the protein's DNA repair capabilities to survive treatment-induced damage.
Furthermore, mutations in the RAD51 gene itself have been implicated in hereditary breast and ovarian cancers. Individuals carrying these mutations exhibit an increased predisposition to developing these cancers, underscoring the importance of RAD51 in maintaining the integrity of the genome.
RAD51 Related Signaling Pathways
The involvement of RAD51 in DNA repair extends beyond its direct role in homologous recombination. RAD51 is intricately woven into a network of signal pathways that coordinate the cellular response to DNA damage. One such pathway is the well-studied ATM (ataxia-telangiectasia mutated) pathway.
In response to DSBs, the ATM kinase is activated and phosphorylates key players in the DNA damage response, including RAD51. This phosphorylation not only enhances RAD51's DNA binding affinity but also regulates its assembly into nucleoprotein filaments at the site of damage. This orchestrated series of events ensures the efficient and precise repair of DNA lesions.
Additionally, RAD51 is closely associated with the BRCA1 and BRCA2 proteins, both of which play critical roles in homologous recombination. Mutations in these genes are linked to hereditary breast and ovarian cancers, further highlighting the interconnectedness of RAD51 with various signal pathways governing genomic stability.
Applications of RAD51 in Biomedical Research
- Therapeutic Interventions
RAD51 is an attractive therapeutic target. Small molecules modulating RAD51 activity enhance cancer treatment efficacy. Inhibitors, when coupled with radiation or chemotherapy, overcome treatment resistance. This approach offers potential breakthroughs in cancer therapy.
- Personalized Medicine
Identification of RAD51 mutations allows personalized interventions. Tailored strategies mitigate cancer predisposition, showcasing the potential for precision medicine in hereditary cancers.
- Diagnostic Biomarker
RAD51 expression levels serve as diagnostic biomarkers. Assessing its functional status predicts treatment responses in cancer patients. Detection of RAD51 mutations in high-risk individuals aids early intervention, reshaping cancer diagnostics.
Targeting RAD51 for cancer treatment, exploring its diagnostic potential, and understanding its role in hereditary cancers represent just a fraction of the vast landscape waiting to be explored. As research advances, RAD51 is likely to remain at the forefront of scientific endeavors, providing insights that may reshape our understanding of cellular biology and revolutionize approaches to disease management.
Recommended Products for RAD51 Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAD51-128H | Human | Active Recombinant Human RAD51, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| RAD51-134H | Human | Recombinant Human RAD51 | E.coli | N/A |
| RAD51-2155H | Human | Recombinant Human RAD51, GST-tagged | E.coli | GST |
| RAD51-125H | Human | Recombinant Human RAD51 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| RAD51-279HFL | Human | Recombinant Full Length Human RAD51 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| RAD1-01H | Human | Recombinant Human RAD51 (G151D) Mutation Protein, Trx/His-tagged | E.coli | Trx/His |
| RAD51-1851H | Human | Recombinant Human RAD51 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| Rad51-5350M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Rad51 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| RAD51-12414Z | Zebrafish | Recombinant Zebrafish RAD51 | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Reymer, A., et al. Structure of human Rad51 protein filament from molecular modeling and site-specific linear dichroism spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009, 106(32): 13248-53.

