RAD51
-
Official Full Name
RAD51 recombinase -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RAD51 protein family. RAD51 family members are highly similar to bacterial RecA and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad51, and are known to be involved in the homologous recombination and repair of DNA. This protein can interact with the ssDNA-binding protein RPA and RAD52, and it is thought to play roles in homologous pairing and strand transfer of DNA. This protein is also found to interact with BRCA1 and BRCA2, which may be important for the cellular response to DNA damage. BRCA2 is shown to regulate both the intracellular localization and DNA-binding ability of this protein. Loss of these controls following BRCA2 inactivation may be a key event leading to genomic instability and tumorigenesis. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2009] -
Synonyms
RAD51;RAD51 recombinase;RECA;BRCC5;MRMV2;HRAD51;RAD51A;HsRad51;HsT16930;DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1;RAD51 homolog A;RecA-like protein;recombination protein A;RecA, E. coli, homolog of;BRCA1/BRCA2-containing complex, subunit 5
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- HeLa
- His
- Non
- GST
- Trx
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
What is RAD51 Protein?
RAD51 gene (RAD51 recombinase) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 15 at locus 15q15. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RAD51 protein family. RAD51 family members are highly similar to bacterial RecA and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad51, and are known to be involved in the homologous recombination and repair of DNA. This protein can interact with the ssDNA-binding protein RPA and RAD52, and it is thought to play roles in homologous pairing and strand transfer of DNA. This protein is also found to interact with BRCA1 and BRCA2, which may be important for the cellular response to DNA damage. The RAD51 protein is consisted of 339 amino acids and RAD51 molecular weight is approximately 37.0 kDa.
What is the Function of RAD51 Protein?
The RAD51 protein plays a crucial role in cells, mainly involved in the repair process of DNA double strand breaks (DSBS). It repairs DSBS through a homologous recombination (HR) mechanism, ensuring genome integrity and cell survival. The RAD51 protein binds to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) to form a nucleoprotein filament, in which RAD51 replaces the RPA protein to form a RAD51 nucleoprotein filament on ssDNA, a key step in the homologous recombination process. The RAD51 protein is also involved in responding to replication stress, and when the replication fork encounters DNA damage, the RAD51 protein helps stabilize the fork, preventing its collapse, and facilitating the bypass of the damage, thus protecting the cell from genomic instability. The RAD51 protein works in tandem with other proteins such as BRCA2 and RAD51 analogs, including RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D, and XRCC2, which help RAD51 form stable nuclear protein filaments on ssDNA and promote the homologous recombination process.
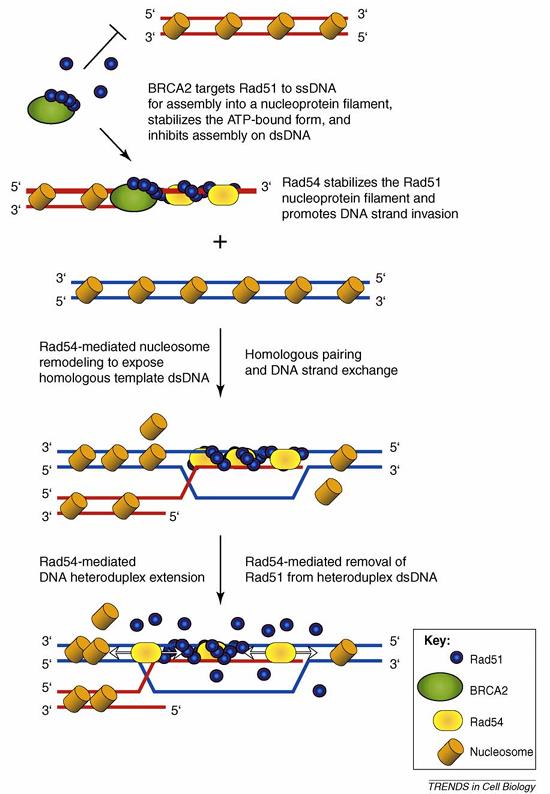
Fig1. Illustration showing protein-mediated regulation of Rad51 nucleoprotein filament assembly and disassembly. (Anthony L Forget, 2010)
RAD51 Related Signaling Pathway
The role of RAD51 protein in cells is mainly involved in the repair of DNA double strand breaks (DSBS), particularly through the homologous recombination (HR) pathway. When double-stranded DNA breaks, cells activate the DNA damage response, including the MRN complex (MRE11-RAD50-NBS1). The RAD51 protein, aided by BRCA2 and RAD51 analogs such as RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D, and XRCC2, binds to ssDNA to form RAD51 nucleoprotein filaments, which in turn perform homologous search and chain invasion, leading to the formation of D-loop (replacement ring). Proteins in the RAD51 family (RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D, XRCC2 and XRCC3) play an important role in DNA repair by transducing DNA damage signals to effector kinases and promoting break repair. RAD51 is also involved in responding to replication pressure, helping to stabilize the replication fork and facilitating the bypass of damage when DNA damage is encountered, protecting cells from genomic instability.
RAD51 Related Diseases
RAD51 expression is upregulated in a variety of malignancies and is associated with poor prognosis. RAD51 plays an important role in tumor metabolism, metastasis and chemotherapy drug resistance, and its high expression is associated with the occurrence and development of a variety of tumors, such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer and prostate cancer. Mutations in the RAD51 gene have been linked to the development of Fanconi anemia, an inherited bone-draining disease. RAD51 plays an important role in liver development, liver regeneration and tumorigenesis. RAD51 plays a central role in homologous recombination repair, and its abnormal function may lead to defects in DNA repair, thereby increasing the sensitivity of cells to DNA damage and promoting the occurrence and development of tumors.
Bioapplications of RAD51
The function of RAD51 in liver development and regeneration, as well as its role in tumorigenesis, provides an important genetic model for the study of the pathological mechanisms of liver aging, liver fibrosis, and eventually hepatocellular carcinoma. Overexpression of RAD51 is associated with tumor metabolism, metastasis and drug resistance. Studying the role of RAD51 in these processes is helpful to develop new cancer treatment strategies, and RAD51 has become a potential target for the development of anti-cancer drugs. Drug development targeting RAD51 is ongoing, such as CYT-0851, developed by Cyteir, an oral RAD51 inhibitor designed to treat cancer by inhibiting RAD51-mediated homologous recombination repair mechanisms.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jonathan J Wilde, 2021
Searching for factors to improve knockin efficiency for therapeutic applications, biotechnology, and generation of non-human primate models of disease, the strand exchange protein RAD51 can significantly increase Cas9-mediated homozygous knockin in mouse embryos through an interhomolog repair (IHR) mechanism. IHR is a hallmark of meiosis but only occurs at low frequencies in somatic cells, and its occurrence in zygotes is controversial. Using multiple approaches, researchers provide evidence for an endogenous IHR mechanism in the early embryo that can be enhanced by RAD51. This process can be harnessed to generate homozygotes from wild-type zygotes using exogenous donors and to convert heterozygous alleles into homozygous alleles without exogenous templates. Furthermore, additional IHR-promoting factors and describe features of IHR events.
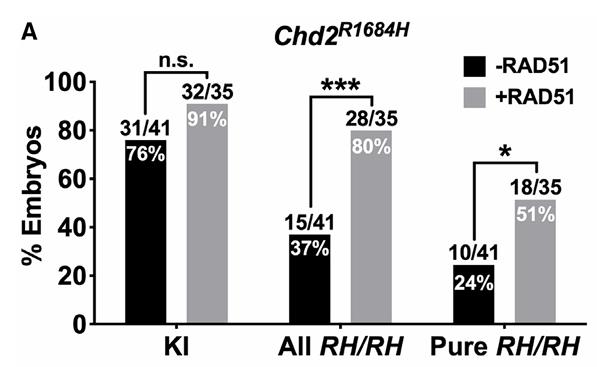
Fig1. Quantification of KI efficiency (left) and homozygous KI efficiency in embryos generated by Chd2RH PNI with or without RAD51.
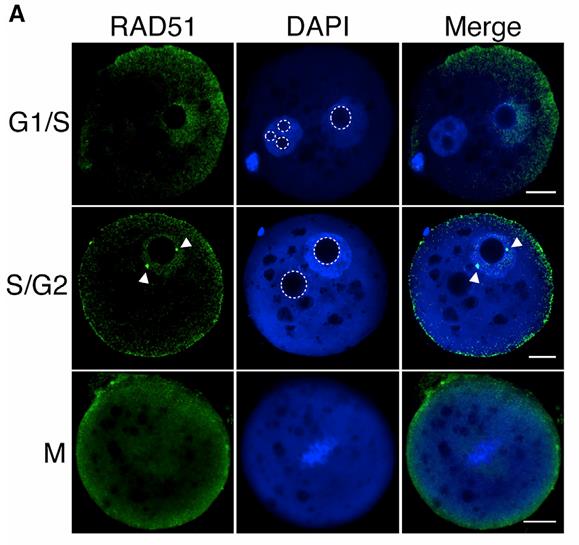
Fig2. Representative images of RAD51 immunocytochemistry in G1/S, S/G2, and M-phase zygotes injected with Cas9 and RAD51.
Case Study 2: Marinella Roberti, 2019
Olaparib is a PARP inhibitor (PARPi). In BRCA2-defective patients, PARPi inhibits DNA single-strand break repair, while BRCA2 mutations hamper double-strand break repair. Recently, researchers identified a series of triazole derivatives that mimic BRCA2 mutations by disrupting the Rad51-BRCA2 interaction and thus double-strand break repair. Here, they have computationally designed, synthesized, and tested over 40 novel derivatives. Additionally, they designed and conducted novel biological assays to characterize how they disrupt the Rad51-BRCA2 interaction and inhibit double-strand break repair. These compounds synergized with olaparib to target pancreatic cancer cells with functional BRCA2. This paradigm could be exploited in other genetic pathways to discover innovative anticancer targets and drug candidates.
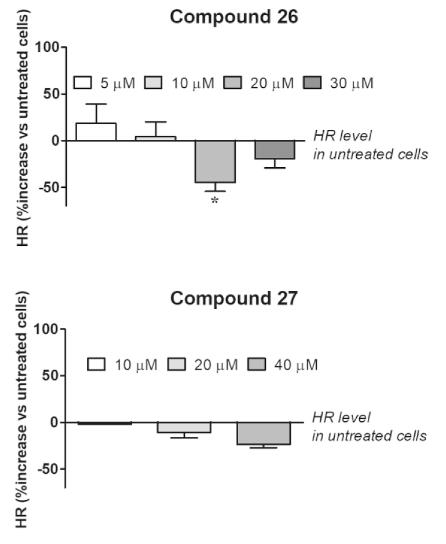
Fig3. Estimation of homologous recombination efficiency in BxPC-3 cells treated (16 h) with the newly identified BRCA2-Rad51 disruptors 26 and 27.
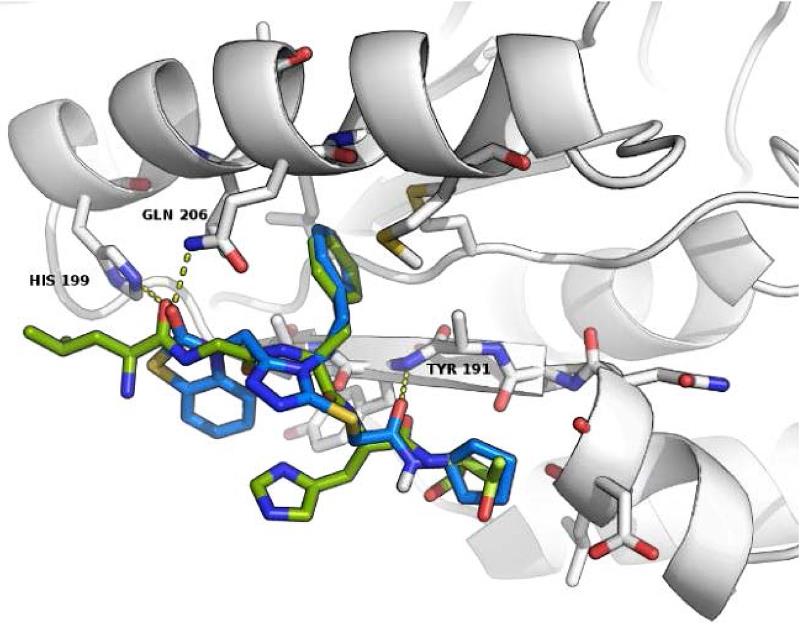
Fig4. Compound 1 docked into the FxxA domain of Rad51.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RAD51-128H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (RAD51-125H)
Involved Pathway
RAD51 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RAD51 participated on our site, such as Homologous recombination,Fanconi anemia pathway,Pathways in cancer, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RAD51 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Fanconi Anemia Pathway | FANCC,FANCE,RPA4,RMI2,TELO2,HES1,EME2,FANCG,REV1,FANCL |
| Homologous recombination | NBN,RPA3,RAD51L3,SYCP3,TOP3B,XRCC3,POLD4,MUS81,EME1,RPA4 |
| Pathways in cancer | RALB,MAX,STAT3,RXRA,LAMB1,BAX,STAT5A,LAMB3,TGFA,GNG10 |
| Pancreatic cancer | TGFBR1,RAC3,NFKB1,CDC42,TRP53,TGFBR2,PIK3CG,BCL2L1,PLD1,MAP2K1 |
Protein Function
RAD51 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,DNA polymerase binding,chromatin binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RAD51 itself. We selected most functions RAD51 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RAD51. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| single-stranded DNA-dependent ATPase activity | DNA2,RAD18 |
| protein C-terminus binding | VPS36,PQBP1,ERCC1,KCNJ11,HIC2,ZBTB16,PHB2,BLOC1S2A,NEIL1,PCGF1 |
| double-stranded DNA binding | TDP1,RAD51D,CRY1,APTX,SAFB,HLF,SMAD2,MCM10,XRCC2,MTERFD1 |
| ATP binding | CSNK1G2A,PTK6B,GRK7,SMOK2B,SYN2A,ERCC6L2,ATAD1B,ALDH18A1,GM711,PIK3C2A |
| single-stranded DNA binding | HMGB1,CDC45,TDP1,PURB,XRCC3,TDP2B,TDP2,C10orf2,RAD51AP1,TREX1 |
| chromatin binding | JUB,MORF4L1,DHX30,Trl,PRKCBP1L,PYGO2,FOSL2,CITED2,TCF7L2,PBRM1L |
| protein binding | VPS53,PSG5,CORO1C,MYO10,KIF6,RAB11FIP5,IGF2BP1,PXMP4,TNFRSF6B,TMEM140 |
| DNA polymerase binding | HMGB1,ACD,PCNA,FANCD2,SMARCA4,LONP1,CDK2AP1,FANCI |
| identical protein binding | SNX33,SLK,ASS1,STXBP1,GOT1L1,E2F7,GLUL,APOE,UAP1,S100A4 |
Interacting Protein
RAD51 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RAD51 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RAD51.
BRCA2
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Liu, H; Yang, WF; et al. Nimotuzumab abrogates acquired radioresistance of KYSE-150R esophageal cancer cells by inhibiting EGFR signaling and cellular DNA repair. ONCOTARGETS AND THERAPY 8:509-518(2015).
- Le Cigne, A; Menil-Philippot, V; et al. Transient expression of RAD51 in the late G2-phase is required for cell cycle progression in synchronous Physarum cells. GENES TO CELLS 19:755-765(2014).




