Principle and Protocol of EMSA
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) is a technology to detect the interaction between protein and DNA sequence. The transcription of DNA into RNA is the key process of gene expression in organisms. The regulation of gene expression mainly occurs at the transcription level. The transcription behavior of genes is regulated by the interaction of cis-acting elements and trans-acting factors (i.e. transcription factors). In recent years, the study of gene transcriptional regulation, especially the study of gene cis-acting elements, transcription factors and their transcriptional regulation mechanism, has gradually become one of the hotspots in functional genomics.
The research on gene expression regulation can be carried out from three levels: first, isolation and identification of cis-acting elements such as the core promoter at the 5 'end of the gene, second, isolation and identification of transcription factors corresponding to each cis-acting element, and third, detection of the interaction between each cis-acting element and the corresponding transcription factor. The core function of electrophoretic mobility analysis is to verify the binding characteristics of proteins and specific nucleic acid sequences, thus indirectly inferring the target sequence of known proteins or the binding protein molecules of known sequences. However, as a technical means, electrophoretic mobility analysis itself has many shortcomings, such as the difficulty in identifying low-affinity binding. It is difficult to compare the differences of affinity between different fragments. The binding of protein complexes and DNA cannot be identified. Due to the huge difference between the external environment and the internal environment, it is difficult to really reconstruct the binding process between protein and DNA in vivo.
The purpose of this laboratory manual is to help researchers understand the principles of electrophoretic mobility analysis techniques and to master the main operational steps and precautions for gel migration.
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) is a technique for detecting the interaction between proteins and DNA sequences. It was originally used to study the interaction between DNA-binding proteins and their associated DNA-binding sequences, and can be used for qualitative and quantitative analysis. This technology has been used to study the interaction between RNA-binding proteins and specific RNA sequences and has become a classic method for the study of transcription factors.
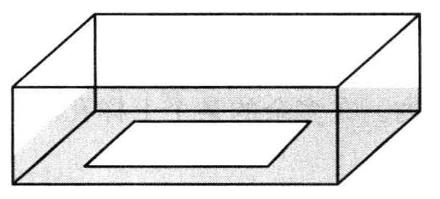
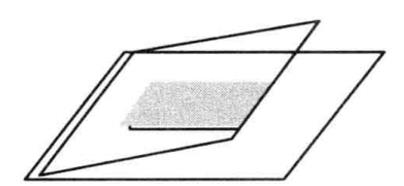
The basic principle is that the protein can combine with the end-labeled nucleic acid probe. During electrophoresis, this complex moves slower in gel than the probe without protein binding, that is, it is relatively lagging. This method can be used to detect DNA-binding proteins and RNA-binding proteins, and can detect specific proteins by adding specific antibodies, and can identify unknown proteins. The principle is shown in Figure 5-2-1.
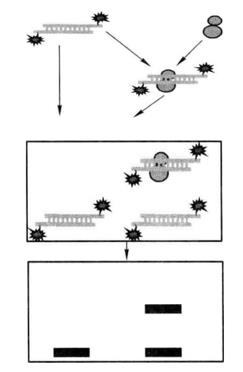 Figure 5-2-1 Schematic Diagram of Gel Retardation
Figure 5-2-1 Schematic Diagram of Gel Retardation
1. Main Instruments and Equipment
Pipette, micro centrifuge, 1.5mL centrifuge tube, 50mL centrifuge tube, thermostatic water bath, ice maker, shaker, oscillator, centrifuge, metal bath, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis device, ultraviolet analyzer, autoradiography box, X-ray film, hybrid bag, nylon membrane, filter paper.
2. Material
Protein samples to be tested, probes
3. Main Reagents
(1) 40% acrylamide storage solution (acrylamide : methylenebisacrylamide=39 :1)
(2) Poly (dI : dC)
(3) streptavidin-HRP
(4) 2×blocking buffer
(5) 5×washing buffer
(6) Equilibration Solution
(7) 10%SDS
(8) 10% ammonium persulfate
(9) Biotin-11-dUTP
(10) TdT
(11) Probe marking termination solution:0.2mol/L EDTA
1. Marking of the Probe
(1) Take out TdT buffer (5×), Biotin-11-dUTP and culture water are dissolved and put on ice bath for standby.
(2) Take out the single-chain EMSA probe to be labeled and dilute it with water to 1 μmol/L, and put it on the ice bath for standby. Set the reaction system of probe marking as follows:
| Ultrapure water | 25μL |
| TdT buffer (5×) | 10μL |
| Probes to be marked (1 μmol/L) | 5μL |
| biotin-11-dUTP (5 μmol/L) | 5μL |
| TdT*1 (2U/μL) | 5μL |
| Total volume | 50μL |
(3) Gently blow and mix with a pipette gun. Do not swirl and shake. Incubate at 37°C for 30 min.
(4) Add 2.5 μL probe labeled termination solution, mix well, and terminate probe labeling reaction.
(5) Add 50μL chloroform - isoamyl alcohol (24:1), vortex oscillation makes the organic phase and water phase fully mixed to extract TdT.
(6) 12000-14000g centrifugation for 1-2min, suck the supernatant for standby. The supernatant is a biotin-labeled single-stranded DNA probe.
2. Purification of Probes*2
(1) For 100μL of labeled probe, add 1/4 volume i.e. 25μL of 5 mol/L ammonium acetate, then add 2 times the volume i.e. 200μL of anhydrous ethanol and mix well.
(2) Precipitate for 1 h at -70°Cto -80°Cor overnight at -20°C.
(3) Centrifuge at 4°C, 12,000-16,000 g for 30 min. Carefully remove the supernatant, do not touch the precipitate.
(4) Centrifuge at 12000-16000g for 1 min at 4°C. Carefully aspirate off residual liquid. Dry the precipitate slightly, but do not over-dry.
3. Purification of Probes*2
(1) Take 5μL of oligonucleotide probe (oligo) of biotin-control (0.4 μmol/L), add 196μL TE, mix well, and dilute to 10 nmol/L oligonucleotide probe (oligo) of biotin-control (as standard). The appropriate amount of 10 nmol/L biotin-control oligonucleotide probe (oligo) was taken out and diluted to 5 nmol/L, 2.5 nmol/L, 1 nmol/L, 0.5 nmol/L and 0.25 nmol/L in order.
(2) Take 3μLof biotin-labeled DNA probe (100 nmol/L), add 27μL TE, mix well, and dilute to 10 nmol/L biotin-labeled probe (as the sample to be tested). The appropriate amount of 10 nrnol/L biotin-labeled probe was taken out and diluted to 5 nmol/L, 2.5 nmol/L, 1 nmol/L, 0.5 nmol/L and 0.25 nmol/L in that order.
(3) Take an appropriately sized nitrocellulose membrane (NC membrane) or positively charged nylon membrane and mark the membrane accordingly. For standards and samples to be tested that have undergone gradient dilution, take 2 μL and add them dropwise to the membrane respectively*3.
(4) Using a UV cross-linker, select 254 nm UV wavelength, 120 mJ/cm2, and cross-link for 30-45s.
(5) The biotin labeling efficiency of the probe was detected using a biotin assay kit*4.
4. Preparation of Biotin-labeled EMSA Probe
The sense chain and the antisense chain are mixed in equal volume (the molar ratio cannot be adjusted according to the labeling efficiency). At 95°C for 2 min, the temperature drops 0.1°C every 8s to 25°C. After the annealing reaction, the labeled EMSA probe is stored at - 20°C. At this time, the EMSA probe can be directly used for subsequent EMSA detection.
5. EMSA Gel Preparation
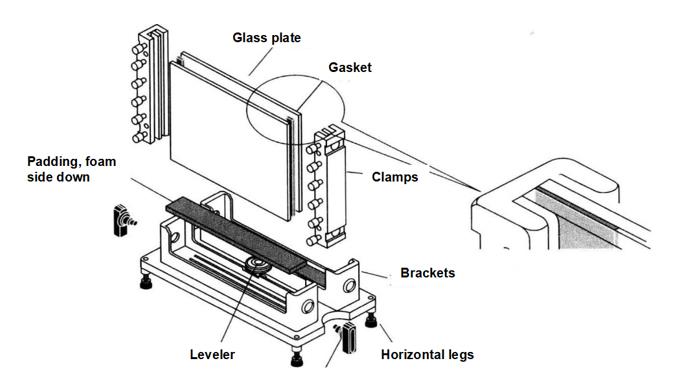
(1) Prepare the mold for pouring glue.
(2) Prepare 20 mL 4% polyacrylamide gel*5 according to the formula in Table 5-2-1.
Table 5-2-1 Preparation of 4% polyacrylamide gel
| Reagent | Dosage |
| TBE buffer (10×) | 1mL |
| Double-distilled water | 16.2mL |
| 39 : lacrylamide/bisacrylamide(40%) | 2mL |
| 80% glycerol | 625 μL |
| 10% ammonium persulfate | 150 μL |
| TEMED | 15 μL |
Add each solution in the above order, mix well before adding TEMED, mix well immediately after adding TEMED, and add immediately to the mold for glue making to avoid air bubbles and add comb teeth.
6. EMSA Gel Bonding Experiment
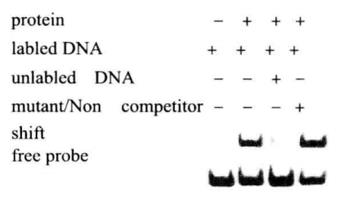
(1) Set up the EMSA binding reaction as follows
| Negative control | |
| Nuclease-free water | 7μL |
| EMSA/gel-shift bonding (5X) | 2μL |
| Glycerin nuclear protein or purified transcription factor | 0μL |
| Marked probe | 1μL |
| Total volume | 10μL |
| Sample reaction | |
| Nuclease-free water | 5μL |
| EMSA/gel-shift bonding (5X) | 2μL |
| Glycerin nuclear protein or purified transcription factor | 2μL |
| Marked probe | 1μL |
| Total volume | 10μL |
| Probe cold competition reaction | |
| Nuclease-free water | 4μL |
| EMSA/gel-shift bonding (5X) | 2μL |
| Glycerin nuclear protein or purified transcription factor | 2μL |
| Marked probe | 1μL |
| Unmarked probe | 1μL |
| Total volume | 10μL |
| Cold competition reaction of mutation probe | |
| Nuclease-free water | 4μL |
| EMSA/gel-shift bonding (5X) | 2μL |
| Glycerin nuclear protein or purified transcription factor | 2μL |
| Marked probe | 1μL |
| Unmarked mutation probe | 1μL |
| Total volume | 10μL |
| Super-shift reaction | |
| Nuclease-free water | 4μL |
| EMSA/gel-shift bonding (5X) | 2μL |
| Glycerin nuclear protein or purified transcription factor | 2μL |
| Marked probe | 1μL |
| Antibodies specific to target proteins | 1μL |
| Total volume | 10μL |
(2) Add the reagents in order as described above, mix well, and leave at room temperature (20-25°C) for 20 min.
(3) Add EMSA/gel-shift loading buffer, mix well and load the sample immediately.
7. Electrophoretic Analysis
(1) Use 0.5 × TBE is used as electrophoresis solution. Pre-electrophoresis is conducted at a voltage of 10V/cm for 30min.
(2) Add the sample mixed with the loading buffer into the loading hole. Add the same volume of diluted 1 into one of the excess loading holes × EMSA/gel-shift loading buffer.
(3) According to the voltage of 10V/cm, stop electrophoresis when bromophenol blue reaches 1/4 of the lower edge of the gel.
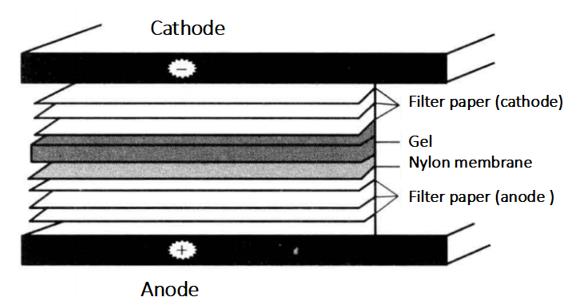
8. Film Transfer (Semi-Dry Transfer)
(1) Prepare electric transfer buffer 0.5 × TBE 200 mL.
(2) Cut 6 Whatman 3 mm filter paper and a nylon film (marked with a pencil at one corner of the film) which are exactly the same size as the gel × Immerse in TBE for 10min.
(3) Cover the bottom graphite electrode (anode) of the electromotor with 3 Whatman 3 mm filter paper, nylon film, gel and 3 Whatman 3 mm filter paper*6 in turn.
(4) Install the upper electrode (cathode) of the electrometer, connect the power supply, and turn the film. The membrane current (mA) is the membrane area (cm2) 4-5 times, and the film transfer time is 30min.
9. UV fixation for 30s
10. Chemiluminescence reaction
(1) Prepare the assay reagents: remove 2 × closure solution from 4°C with 5 × washing solution and place in a 37°C warm bath to dissolve the white precipitate*7.
(2) Close the binding membrane: immerse the binding membrane in 15mL1 × Incubate at room temperature for 15min in closed solution.
(3) Discard the blocking solution and incubate the binding membrane with the newly prepared 15mL streptavidin-HRP reaction solution at room temperature for 15min.
(4) Discard the reaction liquid with 1 × Wash the membrane at room temperature for 4 times, 15mL each time, 5min each time.
(5) Immerse the binding membrane in 15mL equilibrium solution for 5min at room temperature, and put the membrane face up into the hybrid bag.
(6) 600μL of luminol/enhancer solution and stable peroxide solution were mixed and evenly added to the surface of the film for 1-4 min. The film was sealed in a glass test tube to remove air bubbles, placed in a radiographic autoradiography cassette, pressed onto an X-ray film, and exposed for 2-30 min*8.
(7) Prepare developing solution and fixing solution. Prepare the developing solution and fixing solution according to the package instructions of developing powder and fixing powder, put the X-ray film into the developing solution in the dark room until the stripes appear, rinse once with water and put into the fixing solution, remove the film when the rest of the film is transparent, and observe the results.
1. There is a white precipitate in the Closure Solution and Washing Solution at low temperature, please put them in a 37°C warm bath and wait for the precipitate to dissolve completely before preparing 1×Closure Solution and 1×Washing Solution according to the operation instructions. Put the remaining storage solution back to 4°C for storage.
2. Pay attention to keep the membrane moist during operation, otherwise it will lead to high background.
*1 Take out TdT from - 20°C before use and put it back immediately after use.
*2 It is often not necessary to purify the labeled probe for experimental simplicity. In some cases, purification should be performed in order to reduce the interference of unreacted excess biotin-11-dUTP in subsequent experiments. Purified probes will improve the electrophoretic results of EMSA.
*3 When adding standards or samples to be tested dropwise on the membrane, take care that the droplets are sufficiently absorbed by the membrane to form a small, wet, circular spot on the membrane. If conditions permit, equipment specifically designed for spot hybridization or slit hybridization can be used for the detection of probe labeling efficiency. After all standards and samples have been added dropwise, leave the membrane to dry at room temperature.
*4 The labeling efficiency of the samples was obtained by comparison with the standard curve made by the standard markers.
*5 The use of different ratios of Acr/Bis does not affect the results much.
*6 Pay attention to the order of nylon membranes and gels.
*7 Since the closure solution and washing solution will appear as white precipitate at 4°C, put them at room temperature or 37°C in advance to dissolve them completely.
*8 Depending on the strength of the signal, decide the length of the exposure time.

