AKT2
-
Official Full Name
v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 2 -
Overview
This gene is a putative oncogene encoding a protein belonging to a subfamily of serine/threonine kinases containing SH2-like (Src homology 2-like) domains. The gene was shown to be amplified and overexpressed in 2 of 8 ovarian carcinoma cell lines and 2 of 15 primary ovarian tumors. Overexpression contributes to the malignant phenotype of a subset of human ductal pancreatic cancers. The encoded protein is a general protein kinase capable of phophorylating several known proteins. -
Synonyms
Akt2;AKT2_HUMAN;PKB;PKB beta;PKBBETA;PRKBBy;Protein kinase Akt 2;Protein kinase Akt-2;Protein kinase B beta;RAC BETA;RAC beta serine threonine protein kinase;RAC PK beta;Rac protein kinase beta;RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase;RAC-PK-beta;RACbeta;V AKT Murine Thymoma Viral Oncogene Homolog 2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Sf9 Cells
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Flag
- T7
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
- DDK
- Myc
Involved Pathway
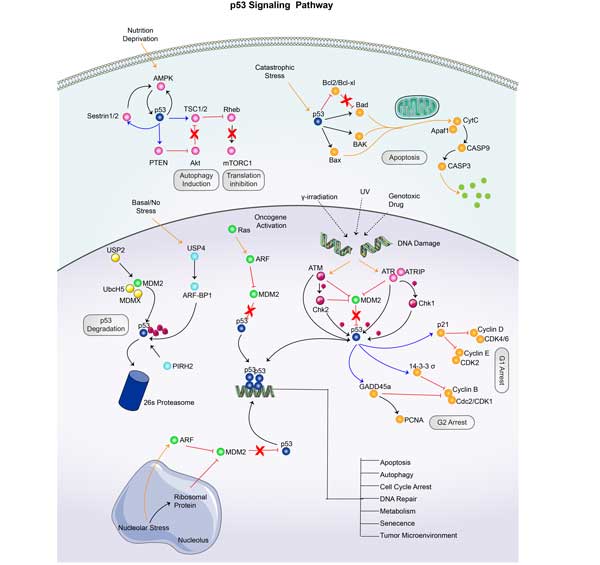
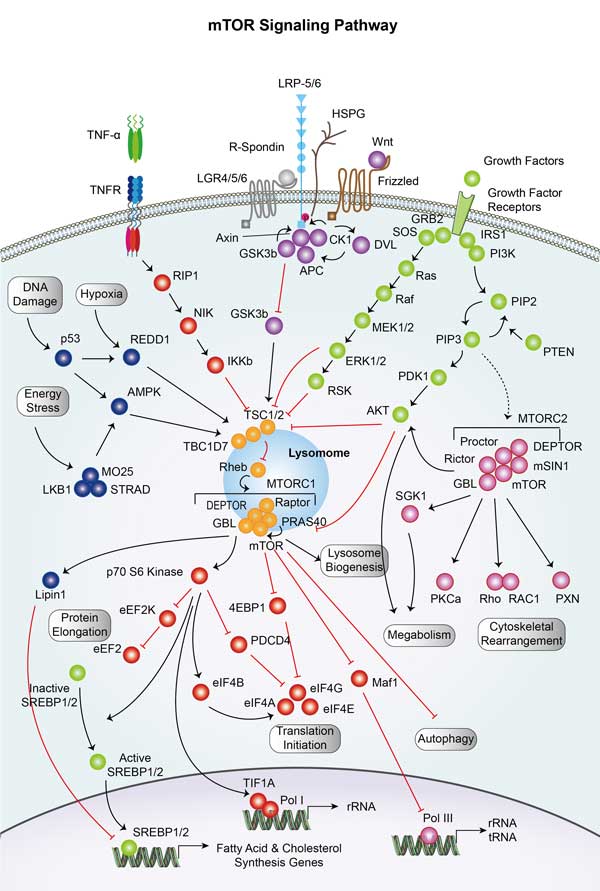
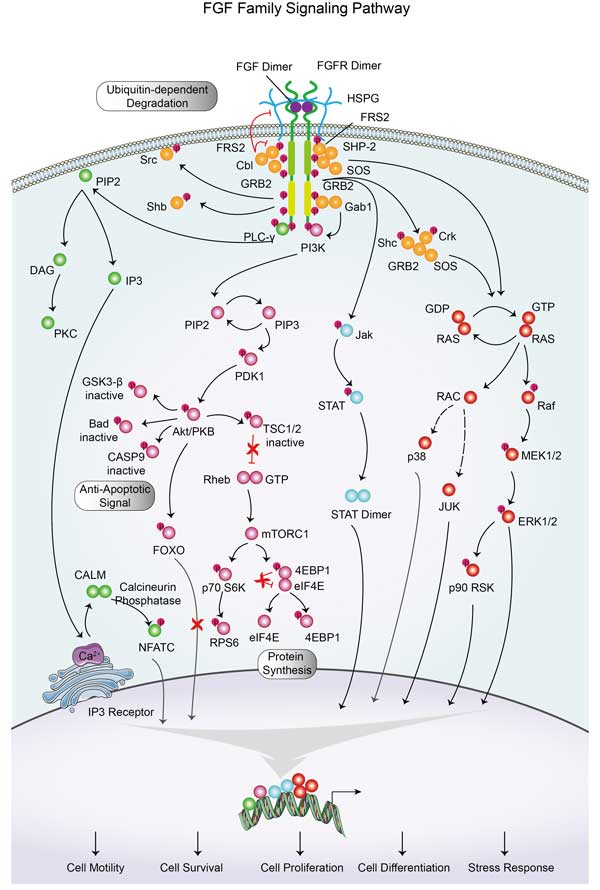
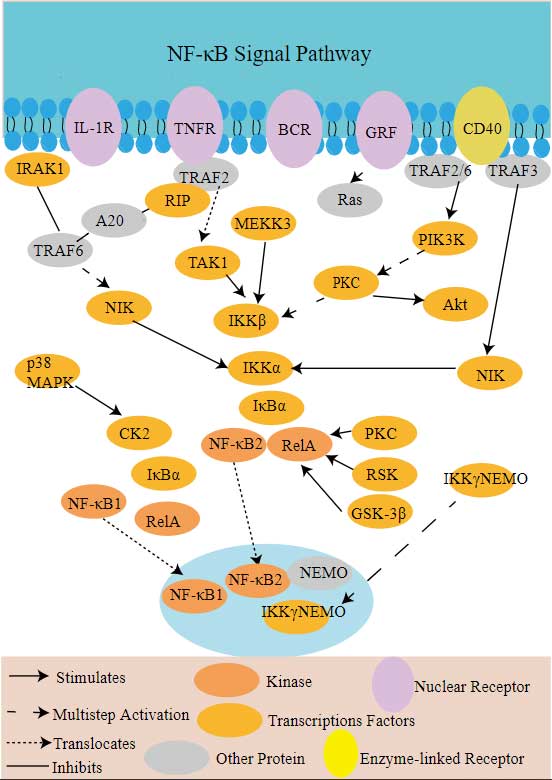
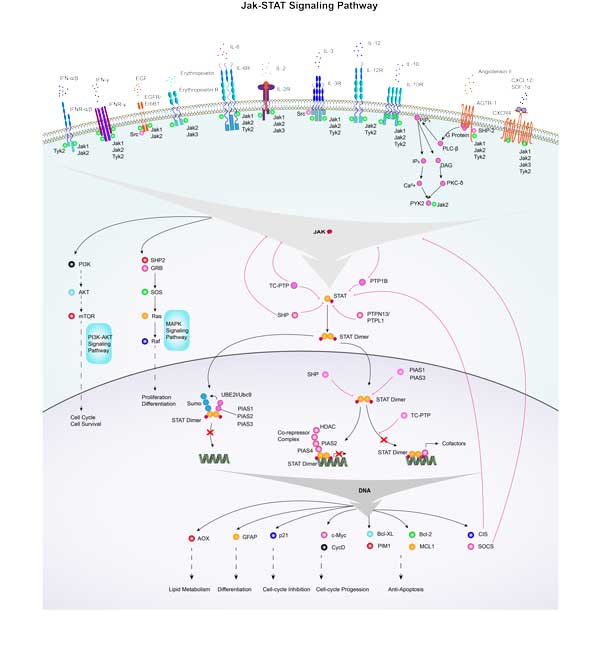
AKT2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways AKT2 participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,ErbB signaling pathway,Ras signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with AKT2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | IL4,KRAS,MAP2K6,MAPK8,SYK,IL5,MAPK1,PDPK1,PIK3R1,MAP2K4 |
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | MAPK12,TRP53,GNAI3,RHOA,PPP2R2C,MAPK9,PRKCB,RAC1,ASAH1,DEGS1 |
| Epstein-Barr virus infection | PSMD1,ENTPD1,PSMD3,HSPA6,HLA-DRB5,POLR2D,PSMC1,NFKB1,CSNK2B,MDM2 |
| TNF signaling pathway | CASP10,CXCL2,CX3CL1,PIK3CD,CREB3L1,ICAM1,TRAF5,MAP2K1,MAPK12,BAG4 |
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | PIK3CD,MAP2K1,HIF1A,PGAM2,PFKP,MAPK1,SLC1A5,LDHA,PIK3R5,MAP2K2 |
| ErbB signaling pathway | TGFA,ERBB3,MAPK1,MAPK8,BADB,PRKCBB,PIK3CB,PRKCB,AKT1,SHC4 |
| FoxO signaling pathway | PRKAG2A,BNIP4,IL6,INSRB,SMAD2,HOMER2,PRKAA1,PLK3,SGK3,MAP2K2A |
| Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes | PDE3B,INS,NPY1R,PIK3R5,PIK3R1,PRKG1,PTGER3,NPR1,INS2,GNAI3 |
| mTOR signaling pathway | RPS6KB1,EIF4E2RS1,DDIT4,PRR5,AKT1S1,POLDIP3,RPS6KA3A,PIK3R1,RPTOR,RRN3 |
Protein Function
AKT2 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,protein binding,protein kinase C binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by AKT2 itself. We selected most functions AKT2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with AKT2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | TGFBR1,GM4922,NLK2,SRPK1A,PRKACBB,ZNF143B,PRKACAB,RIOK3,LRRK2,AURKB |
| protein kinase C binding | GRK5,TWF2,SQSTM1,YWHAG,MARCKS,ADAM9,ADD3,HDAC7,HDAC7A,DSP |
| ATP binding | MAT2AB,TSSK4,UCK2B,EGFRA,CDK9,MYO3B,GART,CKBA,ZAK,FLT1 |
| protein binding | MDM2,KCTD5,NACA,CCDC60,FAM9C,ASMTL,CLU,THOC4,TEAD1,P4HA2 |
Interacting Protein
AKT2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with AKT2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of AKT2.
HSP90AB1;crosstide;CASP3;GSK3B;LRRK2;SH3RF1;MYH13;VIM;SETDB1;CDC37;SORBS2;APOA1;APOB
AKT2 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- van de Luijtgaarden, ACM; Roeffen, MHS; et al. IGF signaling pathway analysis of osteosarcomas reveals the prognostic value of pAKT localization. FUTURE ONCOLOGY 9:1733-1740(2013).
- Marchbank, T; Mahmood, A; et al. Pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor causes autocrine-mediated migration and invasion in bladder cancer and phosphorylates the EGF receptor, Akt2 and Akt3, and ERK1 and ERK2. AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY-RENAL PHYSIOLOGY 305:F382-F389(2013).