CHD4
-
Official Full Name
chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 4 -
Overview
Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding domain (CHD) proteins have been identified in a variety of organisms. This family of nine proteins is divided into three separate subfamilies: subfamily I (CHD1 and CHD2), subfamily II (CHD3 and CHD4), and subfamily III ( -
Synonyms
CHD4;chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 4;chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 4;Mi 2b;Mi2 BETA;CHD-4;ATP-dependent helicase CHD4;Mi-2 autoantigen 218 kDa protein;Mi-2b;Mi2-BETA;DKFZp686E06161
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Insect Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- HeLa
- E.coli
- His
- Non
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is CHD4 Protein?
CHD4 protein, or Chromodomain-Helicase-DNA-binding protein 4, is like the Swiss army knife of our cells. It’s part of a team called the NuRD complex that keeps an eye on DNA packaging in the nucleus. Imagine CHD4 as a backstage crew member at a concert, making sure everything is set up just right so the main act — our genes — can perform perfectly. It helps turn genes on and off by reshaping the chromatin structure, which is how DNA is wound up. Normally, CHD4 helps things run smoothly in the cell, but if it acts up, it can lead to trouble, like promoting cancer cells to grow and spread uncontrollably. Researchers are keen on figuring out how CHD4 works because it’s a potential target for cancer treatments, and unlocking its mysteries could lead to breakthroughs in medicine.What is the Function of CHD4 Protein?
CHD4 protein is key for keeping cellular operations in check. It's like a master organizer, making sure DNA is packed right in the nucleus so genes can be turned on or off as needed. Imagine it as a librarian who not only organizes books but also decides when and how they’re accessed. This helps regulate gene expression, ensuring cells run smoothly. However, when CHD4 malfunctions, it can lead to issues like uncontrolled cell growth, which is a hallmark of cancer. That's why there's a lot of scientific interest in CHD4; understanding its function better could help develop new therapies to tackle diseases where gene regulation goes awry.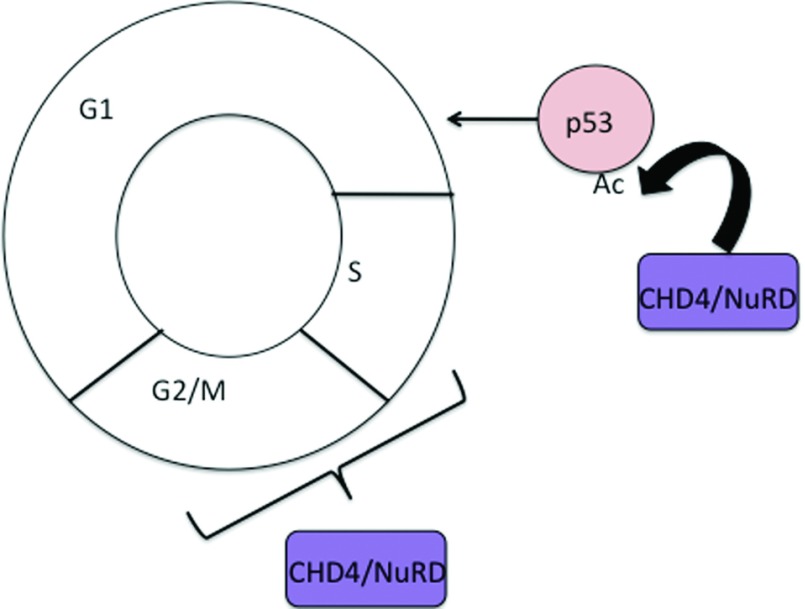
Fig1. CHD4/NuRD contribution to cell cycle control. (Aoife O'Shaughnessy, 2013)
CHD4 Related Signaling Pathway
CHD4 is part of a busy network inside our cells, and it’s deeply involved in several signaling pathways. One major pathway it taps into is the DNA damage repair pathway. Picture CHD4 as a mechanic, jumping in to help fix DNA when it gets banged up. It teams up with other proteins to make sure that any breaks in the DNA are patched up so the cell can keep running smoothly. CHD4 is also connected to pathways that control cell growth and death. By influencing these signals, CHD4 plays a role in deciding when a cell should grow or when it’s time to call it quits. These pathways are crucial because when they get off track, that’s when problems like cancer can arise. Scientists are digging into how CHD4 interacts in these pathways, hoping to uncover new ways to treat diseases related to these signaling hiccups.CHD4 Related Diseases
CHD4 is linked to a range of diseases, primarily because of its role in how our genes are expressed. In cancer, especially, CHD4 can turn into a troublemaker. When it goes haywire, it might allow cells to grow uncontrollably, which can lead to different types of tumors. Cancers such as those of the breast, prostate, and colon have shown connections to abnormal CHD4 activity. But cancer isn't the only issue. CHD4 has also been tied to some genetic disorders where gene expression doesn't go as planned, potentially leading to developmental delays or other health problems. Scientists are keen on figuring out exactly how CHD4 contributes to these diseases, hoping that by targeting its activity, they might find new treatments or ways to prevent these conditions from taking hold.Bioapplications of CHD4
CHD4 is becoming a hot topic in scientific research because of its potential in various bioapplications. In cancer treatment, researchers are looking at CHD4 as a target for new drugs since it plays a critical role in how cancer cells grow and spread. By figuring out how to block or modify CHD4, there's hope for treatments that could slow down or even stop certain cancers in their tracks. Beyond cancer, understanding CHD4's function could also help in regenerative medicine. Since it helps control gene expression, tweaking CHD4 might improve how we use stem cells to repair damaged tissues or organs. Plus, in genetic research, CHD4 offers clues on managing conditions tied to gene regulation errors. All in all, as scientists dig deeper, CHD4 could lead the way in developing groundbreaking therapies and advances in personalized medicine.Case Study
Case Study 1: Wang J. et al. J Transl Med. 2023
The survival rate for advanced ovarian cancer hasn't changed much in years due to its tendency to spread. Here CHD4, a chromatin factor, boosts cancer spread, making it a possible target for treatment. By looking at patient data and testing treatments like romidepsin, high CHD4 levels lead to worse outcomes. When shut down CHD4, cancer cell spread slowed, thanks to less EZH2 and beta-catenin hitting the nucleus. Testing with mice showed romidepsin could curb cancer spread, offering hope for better treatments.-
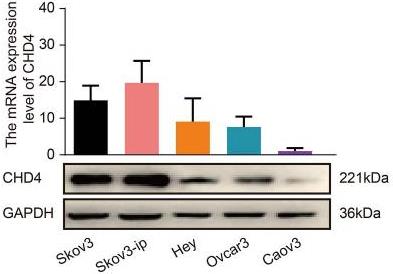 Fig1. The protein expression level of CHD4 in ovarian cancer cell lines.
Fig1. The protein expression level of CHD4 in ovarian cancer cell lines. -
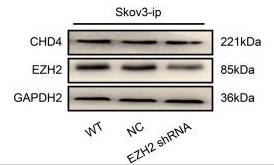 Fig2. Western blot analysis showed that inhibition of EZH2 expression had no effect on the expression level of CHD4.
Fig2. Western blot analysis showed that inhibition of EZH2 expression had no effect on the expression level of CHD4.
Case Study 2: Pratheeshkumar P. et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021
CHD4, part of the NuRD complex, is expressed in many cancers. Researchers looked at its role in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) among Middle Eastern patients. CHD4 was overexpressed in about 45% of PTC cases, linking to worse outcomes. Lab tests showed that more CHD4 led to increased growth and spread of cancer cells and pushed them towards a more aggressive state, known as EMT. Reducing CHD4 reversed these effects and reactivated E-cadherin, a crucial molecule often silenced in cancer. Shutting down factors like Snail1 or Zeb1 cut down on aggressive cancer growth, connecting EMT and cancer stemness. This info points to CHD4 as a potential target for treating aggressive PTC.-
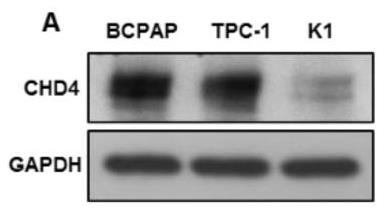 Fig3. Basal expression of CHD4 in PTC cell lines.
Fig3. Basal expression of CHD4 in PTC cell lines. -
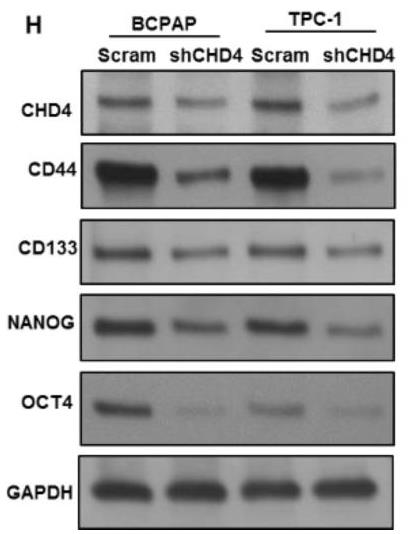 Fig4. Silencing of CHD4 reduces stemness of spheroids.
Fig4. Silencing of CHD4 reduces stemness of spheroids.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CHD4-1180H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CHD4-1180H)
Involved Pathway
CHD4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CHD4 participated on our site, such as Chromatin modifying enzymes,Chromatin organization,Gene Expression, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CHD4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| RNA Polymerase I Promoter Clearance | MTA1,TAF1B,CHD4A,UBTF,MBD3B,TAF1C,TAF1D,MTA2,EFCAB11,TAF1A |
| Chromatin organization | ASH2L,MBD3,KDM5D,CHD4A,PADI6,RBBP7,KIAA1267,MSL1,EP400,MTA3 |
| RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation | MBD3B,RRN3,GATAD2B,UBTF,MTA3,CHD4A,MBD3,GATAD2A,MTA1,MBD3A |
| Gene Expression | GTF3AA,RXRBB,GTF3C4,TAF1L,PHF1,ZNF620,CDK9,ZNF561,PTRF,IPO8 |
| RNA Polymerase I, RNA Polymerase III, and Mitochondrial Transcription | CRCP,BRF2,TFB2M,SNAPC2,CBX3,SNAPC1B,SNAPC1A,ZFP143,ZNF143B,SNAPC1 |
| RNA Polymerase I Transcription | MTA1,MBD3A,GATAD2AB,RRN3,MBD3,GATAD2B,PTRF,CD3EAP,PTRFB,CHD4A |
| Chromatin modifying enzymes | HMG20B,MORF4L2,COPRS,KDM1B,SMARCC1B,KAT7B,TAF6L,ARID5B,KAT7,SETD3 |
| HDACs deacetylate histones | SAP18,MBD3A,GATAD2AB,CHD4A,KDM1A,SAP30,GATAD2B,PHF21A,SUDS3,GATAD2A |
-
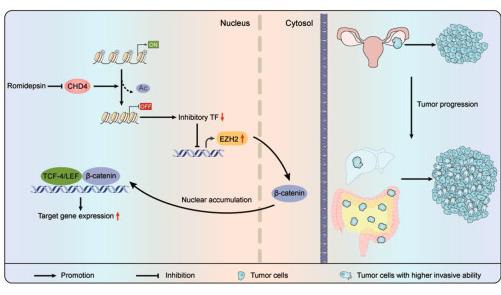 Fig1. Diagram of the mechanism by which CHD4 activates the EZH2/β-catenin pathway to promote ovarian cancer invasion and metastasis. (Jieyu Wang, 2023)
Fig1. Diagram of the mechanism by which CHD4 activates the EZH2/β-catenin pathway to promote ovarian cancer invasion and metastasis. (Jieyu Wang, 2023) -
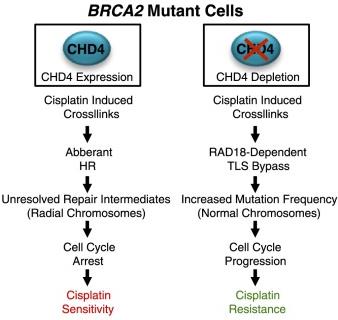 Fig2. Model depicting the response to cisplatin-induced cross-links in BRCA2 mutant cells expressing or depleted of CHD4. (Shawna Guillemette, 2015)
Fig2. Model depicting the response to cisplatin-induced cross-links in BRCA2 mutant cells expressing or depleted of CHD4. (Shawna Guillemette, 2015)
Protein Function
CHD4 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,ATP-dependent DNA helicase activity,DNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CHD4 itself. We selected most functions CHD4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CHD4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| contributes_to RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding | SMARCB1,GATAD2B,ACTL6A,ACTB,SMARCC1,SMARCA4,HDAC1,SMARCE1,MTA2,RBBP4 |
| contributes_to nucleosomal DNA binding | ACTB,MBD3,MTA2,SMARCC2,HDAC1,RBBP4,HDAC2,SMARCA4,GATAD2B,SMARCB1 |
| ATP binding | MARK2,KDR,BCR,DGUOK,HSPA8,SMC6,NEK8,STK11,HIPK2,GLULB |
| RNA polymerase II repressing transcription factor binding | BBS1,PPARA,GTF2A2,BBS4,HDAC2,SIN3A,BBS2,GSC,TBP,RBPJ |
| protein binding | DVL2,TTC6,CCDC50,ALG2,SSX2IP,NHP2L1,SUGT1,MEF2D,CCND2,FAM32A |
| zinc ion binding | MEP1A.2,RBM14B,SETDB1B,MID2,PTPN1,TRIM101,TAF3,LMX1B,SEC23B,PHF23 |
| ATP-dependent DNA helicase activity | GTF2H4,BRIP1,DHX9,DDX11,RUVBL2,ERCC2,CHST13,RTEL1,BLM,XRCC5 |
| microtubule binding | PSRC1,DCX,NDRG1,MAP1S,MAP205,KIFC3,KIF3B,FMN1,CCDC87,PEX14 |
| DNA binding | PRIM2,CSDC2A,TAF4B,SIX6B,RORCB,RYBPB,HMGB3A,MXTX1,POLR2H,THAP6 |
Interacting Protein
CHD4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CHD4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CHD4.
HDAC1;E7;HDAC2;MYC;MTA2;MBD3;RNF8;NR4A1;TAF9;USP36
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References



