What is C5 Protein?
The Complement Component 5 (C5) protein is a component of the complement system, a small yet critical part of the immune system. It plays a major role in inflammation and forms a vital part of our body's defensive mechanism against infections. This protein was first discovered in the early 1960s during a period of intensive study into the functions and components of the human immune system. Its identification marked a significant breakthrough, allowing for a deeper understanding of the human body's response to foreign and harmful pathogens.
Further progress in molecular genetics led to mapping the gene locus for the C5 protein. Located on the long arm of chromosome 9 at position 9 q33.2, this locus has been essential for geneticists in understanding and investigating several immune response disorders.
C5 Protein Structure
The structure of the C5 protein is multifaceted and complex. It consists of two polypeptide chains, C5a and C5b, linked by a disulphide bond. While the C5a fragment is an anaphylatoxin and a potent chemoattractant, the larger fragment, C5b, initiates the formation of the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) that can damage the membrane of pathogenic cells.
Function of C5 Protein
The primary role of the C5 protein is in the immune response, particularly in inflammation and cell lysis. It stimulates histamine release from mast cells and basophils to increase vascular permeability during inflammation. A major function is to form the C5-convertase, which splits the C5 into C5a and C5b. C5b then helps to form MAC that lyses the cell membrane of the pathogen.
It also has crucial roles in cell signaling, chemotaxis, immune response, and acts as a potent chemo-attractant for neutrophils.
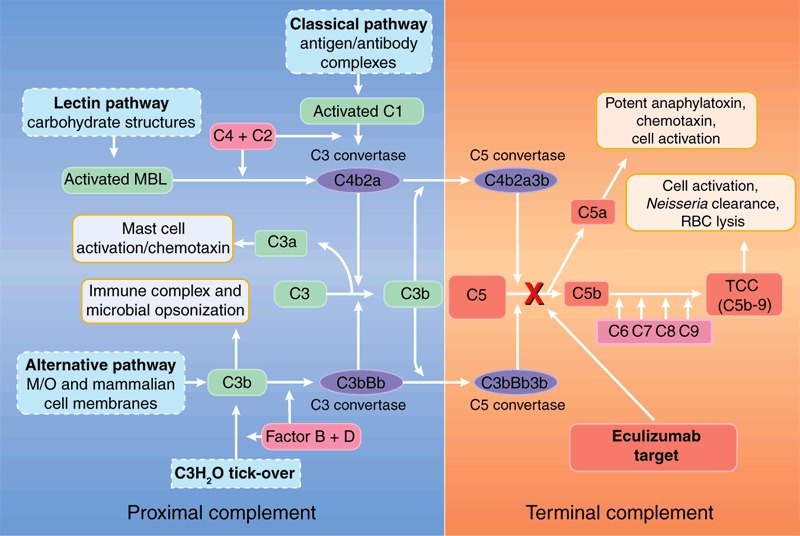
Fig1. Targeted blockade of complement protein C5
C5 Protein Related Signal Pathway
The C5 protein plays a significant role in the complement activation pathway, which includes classical, lectin, and alternative pathways. All three pathways generate C3-convertase, which cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b. The C3b component associates with C3-convertase to form C5-convertase, which in turn cleaves C5 to form C5a and C5b. The C5a fragment acts to attract white blood cells to the site of infection. Meanwhile, C5b contributes to the assembly of the membrane attack complex (MAC) that destroys foreign invaders.
C5 Protein Related Diseases
Dysregulation of the C5 protein has been associated with various diseases. In the rare condition of C5 deficiency, where the body does not produce the C5 protein, individuals are at significant risk of recurrent infections, particularly by Neisseria bacteria.
Further, diseases such as age-related macular degeneration, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria have been linked to uncontrolled complement activation involving the C5 protein. C5a overactivation is also related to harmful inflammatory responses in conditions such as sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and COVID-19.
Applications in Biomedical Science
The C5 protein has held significant interest in biomedical research due to its vital role in the immune response and association with various diseases. It has been a target in the development of therapeutic strategies for conditions such as age-related macular degeneration and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
Eculizumab, the first FDA-approved drug for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, is a C5 inhibitor. This novel treatment significantly reduces clinical symptoms and improves patient survival. Current research focus includes developing therapies to inhibit C5a in diseases where an inflammatory response causes tissue damage.
Overall, the study of the C5 protein offers potential in the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of a wide array of diseases, emphasizing the importance of continued research into this critical complement component. The C5 protein serves as a vivid reminder of how intricate and interconnected the systems in our bodies are and how much there is to learn about the inner workings of our immune system.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C5-4756H | Active Recombinant Human C5 protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| C5-0077H | Recombinant Human C5 Protein, GST-Tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| C5-10539H | Recombinant Human C5, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| C5-2711M | Recombinant Mouse C5 Protein, His-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | N-His |
| C5-0293M | Recombinant Mouse C5 protein | Mouse | E.coli | N/A |
| C5-452C | Recombinant Cynomolgus C5 protein | Cynomolgus | E.coli | |
| C5-1872C | Active Recombinant Cynomolgus C5 protein, His-tagged | Cynomolgus | E.coli | His |
Reference
- Rother, Russell & Rollins, Scott & Mojcik, Christopher & Brodsky, Robert & Bell, Leonard. (2007). Erratum: Discovery and development of the complement inhibitor eculizumab for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Nature biotechnology. 25. 1256-64. 10.1038/nbt1344.

