What is CCL5 Protein
CCL5, officially known as Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligand 5, is a crucial protein in the chemokine family. Also referred to as RANTES (Regulated upon Activation, Normal T Cell Expressed and Secreted), this protein plays a pivotal role in immune responses and inflammation. Structurally, CCL5 is classified as a small cytokine, with a signature four-cysteine motif that characterizes the chemokine family. Recent research advances in the field of molecular biology have shed light on the multifaceted nature of CCL5 and its diverse functions within the human body.
CCL5 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of CCL5 are diverse and impactful. Primarily, this protein acts as a chemoattractant for immune cells, orchestrating their migration to sites of inflammation or injury. CCL5 achieves this by binding to its cognate receptors, such as CCR1, CCR3, and CCR5, which are expressed on the surfaces of various immune cells. Moreover, CCL5 is involved in the activation and recruitment of T cells, monocytes, and eosinophils, contributing to the complex interplay of the immune system.
Molecular mechanisms underlying CCL5 function involve the activation of signaling pathways upon receptor binding. These pathways regulate cellular activities such as migration, adhesion, and cytokine production. The intricate network of interactions involving CCL5 highlights its significance in maintaining immune homeostasis and responding to external challenges.
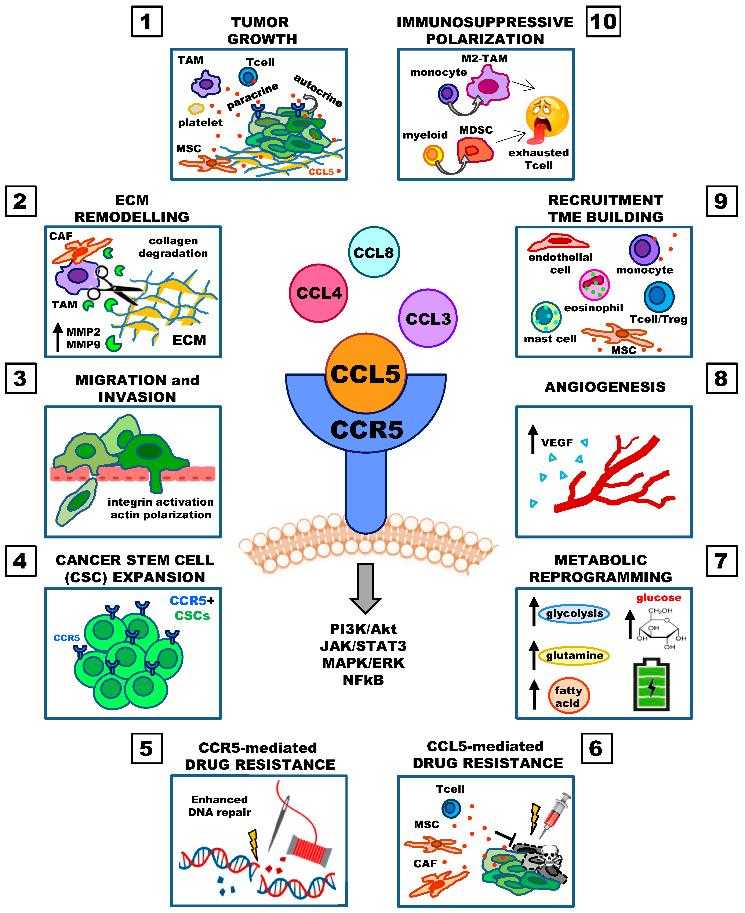
Figure 1. Involvement of the CCL5/CCR5 axis in cancer progression. (Aldinucci D, et al., 2020)
CCL5 Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathways activated by CCL5 are intricate and context-dependent. Upon binding to its receptors, CCL5 can activate various intracellular signaling cascades, such as the MAPK and PI3K pathways. These pathways modulate cellular responses, including chemotaxis, survival, and gene expression. The CCL5-CCR5 axis, in particular, has been extensively studied in the context of HIV infection, where the virus exploits this pathway for cellular entry.
CCL5 Related Diseases
Disruptions in CCL5 expression or function have been implicated in several diseases. In inflammatory conditions, elevated levels of CCL5 are often observed, contributing to excessive immune cell recruitment and tissue damage. CCL5 dysregulation has been linked to chronic inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis. Additionally, CCL5 plays a role in the pathogenesis of infectious diseases, as it facilitates the entry of immune cells into infected tissues.
CCL5's Applications in Biomedicine
Harnessing the properties of CCL5 has significant implications for biomedical applications. In diagnostic development, CCL5 levels can serve as biomarkers for certain diseases, aiding in the early detection and monitoring of inflammatory conditions. Moreover, understanding the molecular mechanisms of CCL5 has paved the way for the development of targeted therapeutics. Researchers are exploring the potential of modulating CCL5 activity to alleviate inflammation and mitigate the progression of related diseases.
In vaccine development, CCL5's role in immune cell activation and recruitment makes it a potential candidate for enhancing vaccine efficacy. Strategies that leverage CCL5 to bolster immune responses are being investigated to improve the effectiveness of vaccines against infectious agents.
As for therapeutics, pharmaceutical interventions targeting the CCL5-CCR5 axis are under scrutiny for diseases where inflammation plays a prominent role. Small molecules and biologics aimed at modulating CCL5 activity or its receptors are being explored as potential treatments for conditions such as autoimmune diseases and certain viral infections.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCL5-4397C | Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey CCL5 Protein | Cynomolgus Monkey | Yeast | N/A |
| CCL5-3993HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human CCL5 protein, Flag-tagged | Human | Mamanlian cells | Flag |
| CCL5-85H | Recombinant Human CCL5, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| CCL5-301H | Recombinant Human CCL5 protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| CCL5-27H | Active Recombinant Human CCL5 Protein | Human | E.coli | |
| CCL5-61H | Recombinant Human chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| CCL5-125H | Recombinant Human Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand 5 | Human | Mammalian cells | N/A |
| CCL5-81H | Active Recombinant Human CCL5 protein | Human | HEK293 | N/A |
| CCL5-4353R | Recombinant Rabbit CCL5 Protein | Rabbit | Yeast | N/A |
| CCL5-4354S | Recombinant Swine CCL5 Protein | Swine | Yeast | N/A |
Reference
- Aldinucci D, Borghese C, Casagrande N. The CCL5/CCR5 axis in cancer progression. Cancers. 2020, 12(7): 1765.

